* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1 - IIE
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Night vision device wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Music technology (electronic and digital) wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electronic paper wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
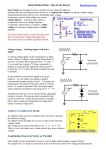
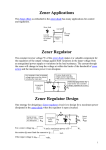
EELE 2321 – Electronics Spring, 2013 Zener Diode Eng. Wazen M. Shbair Content Zener diode principles Zener diode application Electronic Devices, 9th edition Thomas L. Floyd © 2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458. All rights reserved. Zener diodes A major application for zener diodes is as a type of voltage regulator for providing stable reference voltages for use in power supplies, voltmeters, and other instruments. A zener diode is a silicon pn junction device that is designed for operation in the reverse-breakdown region. Electronic Devices, 9th edition Thomas L. Floyd © 2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458. All rights reserved. Zener diode V-I characteristics Electronic Devices, 9th edition Thomas L. Floyd © 2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458. All rights reserved. Breakdown Characteristics As the reverse voltage (VR) is increased – the reverse current (IR) remains extremely small up to the “knee” of the curve. – The reverse current is also called the zener current, IZ. – At this point, the breakdown effect begins; – the internal zener resistance, also called zener impedance (ZZ), begins to decrease as the reverse current increases rapidly Electronic Devices, 9th edition Thomas L. Floyd © 2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458. All rights reserved. Breakdown Characteristics Electronic Devices, 9th edition Thomas L. Floyd © 2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458. All rights reserved. Zener Regulation The ability to keep the reverse voltage across its terminals essentially constant is the key feature of the zener diode. A minimum value of reverse current, IZK, must be maintained in order to keep the diode in breakdown for voltage regulation. When the reverse current is reduced below the knee of the curve, the voltage decreases drastically and regulation is lost. a maximum current, IZM, above which the diode may be damaged due to excessive power dissipation Electronic Devices, 9th edition Thomas L. Floyd © 2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458. All rights reserved. Zener Equivalent Circuits Electronic Devices, 9th edition Thomas L. Floyd © 2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458. All rights reserved. Zener Equivalent Circuits Electronic Devices, 9th edition Thomas L. Floyd © 2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458. All rights reserved. Example Calculate Zener impedance Electronic Devices, 9th edition Thomas L. Floyd © 2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458. All rights reserved. Temperature Coefficient The temperature coefficient specifies the percent change in zener voltage for each degree Celsius change in temperature. For example, a 12 V zener diode with a positive temperature coefficient of will exhibit a 1.2 mV increase in VZ when the junction temperature increases one degree Celsius Electronic Devices, 9th edition Thomas L. Floyd © 2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458. All rights reserved. Example Electronic Devices, 9th edition Thomas L. Floyd © 2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458. All rights reserved. Zener Power Dissipation Zener diodes are specified to operate at a maximum power called the maximum dc power dissipation, PD(max). Electronic Devices, 9th edition Thomas L. Floyd © 2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458. All rights reserved. ZENERDIODE APPLICATIONS The zener diode can be used as a type of voltage regulator for providing stable reference voltages Electronic Devices, 9th edition Thomas L. Floyd © 2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458. All rights reserved. From No Load to Full Load Example 3.5 Zener Regulation with a Variable Load Electronic Devices, 9th edition Thomas L. Floyd © 2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458. All rights reserved. From No Load to Full Load When the output terminals of the zener regulator are open – the load current is zero and all of the current is through the zener; When a load resistor is connected, – part of the total current is through the zener and part through The total current through R remains essentially constant as long as the zener is regulating. The zener diode continues to regulate the voltage until reaches its minimum value, At this point the load current is maximum, and a full-load condition exists. Example 3.6, 3.7(very important) Electronic Devices, 9th edition Thomas L. Floyd © 2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458. All rights reserved.