* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Essential Question: What is active and passive transport?
Survey
Document related concepts
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
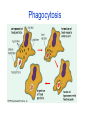
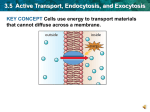
Essential Question: What is active and passive transport? Cells transport materials across the cell membrane by active transport and passive transport. Passive Transport: movement of materials without the use of energy from a high to low concentration. There are two types of Passive Transport: Diffusion Osmosis Diffusion• No energy is involved. • Movement from a high concentration to a low concentration. • End result is an equal concentration in and out of the cell (equilibrium). • Exs. Perfume, Pizza, Locker Room Osmosis • Osmosis: • No energy is involved. Movement of WATER from a high to low concentration. Three Situations Involving Osmosis: Isotonic Solution: • Amount of dissolved substances in the cell = the amount of dissolved substances out of the cell. • EX.: 1.Thus no movement of water. Hypotonic Solution • Hypotonic Solution- the amount of dissolved substances in the environment is lower than the amount of dissolved substances in the cell. • Thus water will flow into the cell. The cell begins to swell. If too much water goes into the cell, it will burst like a balloon. Hypertonic Solution Hypertonic Solution- the amount of dissolve substances is larger in the environment than in the cell. • Thus cell will loose water. The cell will shrink. Ex. Wilted celery, cooking meat. Types of Solutions Essential questions : What is active transport? What are the types of active transport? Active Transport Active Transport-movement of materials from a low to high concentration with the use of energy. There are Two Types of Active Transport: Endocytosis Exocytosis Endocytosis: Uses energy. Process of surrounding an organism and taking it in. Phagocytosis is a type of endocytosis Process by which a cell surrounds and takes in material (food) from its environment Ex. WBC- bacteria Phagocytosis Die E. Coli Exocytosis: Uses energy •Reverse of endocytosis •Process by which a cell expels or secretes material from a cell. Ex. Waste products, hormones