* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Final Exam Review - Milton
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
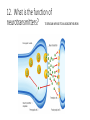
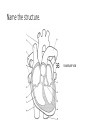
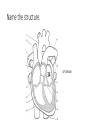
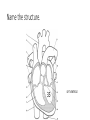
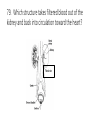
Final Exam Review Human Biology 1. Name this cell. NEURON 2. What does this cell do? SENDS AND RECEIVES MESSAGES 3. From where do these cells gather information? OUTSIDE THE BODY THROUGH THE FIVE SENSES 4. What are these information-gathering neurons called? SENSORY NEURONS 5. To where do these cells send information? THE BRAIN OR SPINAL CORD FOR PROCESSING 6. What kind of neuron sends a response back? MOTOR NEURON Label the parts of the neuron. 7 DENDRITE 8 NUCLEUS 10 9 AXON MYELIN SHEATH 11. What does the arrow represent? THE DIRECTION OF AN IMPULSE BEING SENT 12. What is the function of neurotransmitters? TO SEND AN IMPULSE TO AN ADJACENT NEURON Name the phase of a nerve impulse. (Resting, Action, or Refractory) 13. An impulse travels down the axon away from the cell body. ACTION POTENTIAL 14. Na+ and K+ channels are closed. RESTING POTENTIAL 15. Neuron is slightly negative on the inside of the cell compared to the outside of the cell. RESTING POTENTIAL 16. Na+ and K+ channels open allowing Na+ to move into cell and K+ to move out of the cell. ACTION POTENTIAL 17. The neuron receives a signal from a stimulus. RESTING POTENTIAL 18. Na+ channels close and K+ flow back into cell. REFRACTORY PERIOD 19. Which part of the brain regulates body temperature and primitive instincts like hunger? HYPOTHALAMUS 20. Which side of the brain controls the muscles of a right-handed person? LEFT 21. The “animal brain” that controls the instincts and primitive drives and is stimulated by drugs is LIMBIC SYSTEM also known as the ________________? 22. Which neurotransmitter plays a role in drug addiction? DOPAMINE Name the type of sensory receptor. 23. Responds to light. PHOTORECEPTOR 24. Responds to an injury. PAIN RECEPTOR 25. Responds to taste and smell. CHEMORECEPTOR 26. Responds to changes in temperature. THERMORECEPTOR 27. Responds to touch or pressure. MECHANORECEPTOR 28. Name a function of the cardiovascular system? TAKE OUT CARBON DIOXIDE FROM TISSUES BRING OXYGEN TO TISSUES CIRCULATE NUTRIENTS THROUGHOUT THE BODY 29. What are the three main structures of the cardiovascular system? HEART BLOOD VESSELS BLOOD Name the structure. RIGHT ATRIUM 30 Name the structure. RIGHT VENTRICLE 31 Name the structure. 32 PULMONARY ARTERY Name the structure. 33 PULMONARY VEIN Name the structure. 34 LEFT ATRIUM Name the structure. 35 LEFT VENTRICLE Name the structure. AORTA 36 37. Which type of vessels have the thickest walls? ARTERIES 38. In relationship to the heart, where do arteries carry blood? AWAY FROM THE HEART TO BODY TISSUES AND ORGANS 39. In relationship to the heart, where do veins carry blood? TOWARD THE HEART FROM BODY TISSUES AND ORGANS 40. Name the smallest blood vessels, in which oxygen is delivered to tissues and organs. CAPILLARIES Name the blood cell. 41. Fights infection. WHITE BLOOD CELL 42. Most numerous in the body. RED BLOOD CELL RED BLOOD CELL 43. Carries oxygen. 44. Is involved in clotting blood at an injury site. PLATELETS 45. Name the protein converted from fibrinogen that helps to clot blood. FIBRIN Name the structure. 47 PLAQUE 48. What is plaque made of? CHOLESTEROL/FATS/ LIPIDS 49. How is high blood pressure (hypertension) harmful to the cardiovascular system? IT CAN LEAD TO BLOOD VESSEL DAMAGE CAUSING HEART ATTACK AND STROKE 50. Which vessels supply the heart tissue with oxygen and if they are blocked, a heart attack can occur? CORONARY ARTERIES 51. Which digestive organ manufactures cholesterol? LIVER 52. If a substance has a pH lower than 7, then it is a/an ____________. ACID 53. What kind of protein works best at a specified pH and has a specific shape for its substrate? ENZYME 54. Name a food high in fiber. ANY FOOD FROM PLANT PRODUCTS: FRUITS, VEGETABLES, WHOLE GRAINS, ETC. 55. How many Calories does the average teen need per day? 2200-2800 56. Which structure extracts water from digested food? H 57. Which structure uses a smooth muscular contraction called churning? D 58. Which structure(s) has chemical digestion taking place? D and G 59. Which structure carries food from the pharynx to the stomach? A Match the phase of digestion with its description. 60. The physical and chemical breakdown of food into small molecules. DIGESTION 61. The process of getting food into the opening of the digestive tract. INGESTION 62. The movement of small molecules from the digestive tract into the blood. ABSORPTION 63. The movement of undigested materials, like fiber, out of the body. ELIMINATION Match the enzyme with its description. 64. Digests proteins in the stomach. Work bests with HCl. PEPSIN 65. Breaks maltose into glucose. A “brush border enzyme” in the intestinal villi. MALTASE 66. Secreted by the pancreas as part of the “juices.” Breaks down fat droplets. LIPASE 67. Found in the saliva and pancreas. Breaks down starch into sugars. AMYLASE 68. Made by the liver and stored in the gall bladder. Packages fats into droplets. BILE 69. Breaks proteins into their smallest components, amino acids. PEPTIDASE 70. Name the structure that closes over the trachea when food is swallowed. EPIGLOTTIS 71. What structure is a common passageway for air and food? PHARYNX 72. Put these in order according to how oxygen flows through them: • Bronchioles • Blood • Bronchi • Alveoli BRONCHI, BRONCHIOLES, ALVEOLI, BLOOD 73. What is the muscle that when contracts to force air into the lungs? DIAPHRAGM 74. What body system ultimately controls breathing? NERVOUS SYSTEM 75. Bronchi that are inflamed and clogged with mucus is a symptom of what respiratory disease? BRONCHITIS 76. Which system of the body controls homeostasis and removes waste? EXCRETORY SYSTEM 77. Which excretory organ secretes excess water as sweat? SKIN 78. Which structure removes excess water, urea, and metabolic waste from the blood? 79. Which structure takes filtered blood out of the kidney and back into circulation toward the heart? 80. What is the functional unit of the kidney that consists of the Loop of Henle, Glomerulus, and Bowman’s Capsule? NEPHRON 81. Which part of the nephron is the first to filter blood? GLOMERULUS Name the kidney disorder. 82. Kidneys are no longer filtering blood properly and are placing protein in the urine, so artificial filtration must be accomplished through kidney dialysis. KIDNEY FAILURE 83. A urine sample contains high levels of glucose in the blood. DIABETES 84. A urine sample contains a high number of white blood cells and has a strong odor. URINARY TRACT INFECTION References • http://classconnection.s3.amazonaws.com/811/flashcards/141811/jp g/neuron21320853416098.jpg • http://scienceofstudy.wikispaces.com/file/view/neurotransmitters.gif /313540244/455x327/neurotransmitters.gif