* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pure Substances and Mixtures
Livermorium wikipedia , lookup
Bremsstrahlung wikipedia , lookup
Molecular Hamiltonian wikipedia , lookup
Abundance of the chemical elements wikipedia , lookup
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear binding energy wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Chemical element wikipedia , lookup
Low-energy electron diffraction wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Metastable inner-shell molecular state wikipedia , lookup
Periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Bond valence method wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Auger electron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Electronegativity wikipedia , lookup
Resonance (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital diagram wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Extended periodic table wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Metallic bonding wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
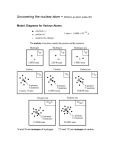
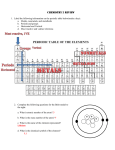
Pure Substances and Mixtures • Pure substances cannot be broken down by physical means. • Pure substances contain only one kind of molecule. – Molecules are small groups of atoms that make up matter. Example: Water is a molecule of two hydrogen atoms, and one oxygen atom • Atoms are the smallest particles of elements • Two types of pure substances: • Elements – pure substance made of only one kind of atom • Compounds – pure substances made of two or more different kinds of elements joined together – Compounds cannot be separated by physical means – Compounds are joined in definite proportions. • Mixtures – combination of 2 or more different kinds of substances ( molecules) • In a mixture, each molecule keeps its own identity. • Mixtures can be separated by physical means. • Two types of mixtures: • Homogeneous mixture – combination of substances in which the appearance is the same throughout; also called a solution. – Examples: salt water, sugar water • Heterogeneous mixture – made of different substances that can be seen – does not appear the same throughout. – Examples – salad, cereal, pizza • Atoms and Elements • Facts about atoms and elements: – Atoms are the basic building blocks of all matter (the smallest particle of matter) – There are different kinds of atoms. – Each kind of atom is an element. – Elements are pure substances that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by ordinary chemical means. • Parts of an Atom: – Nucleus – central dense core of the atom. It is made of: » Protons – positively charged particles » Neutrons – neutrally charged particles – Electron cloud – surrounds the nucleus of the atom » Electrons – negatively charged particles found in the electron cloud • Atomic models – used to represent the atom; the following is needed to make an atomic model – Atomic number – number of protons in the nucleus of an atom – Atomic mass – equal to the number of protons and the number of neutrons in the nucleus of the atom • Making atomic models – the following information is needed for an atomic model – # of protons = the atomic number – # of neutrons = the atomic mass – atomic # – # of electrons = 3 of protons » Energy levels – electrons surround the nucleus in energy levels » Rules for energy levels: • 1st energy level contains no more than 2 electrons • 2nd energy level contains no more than 8 electrons • 3rd energy level contains no more than 18 electrons • Last energy level contains no more than 8 electrons • Valence electrons is the name given to electrons in the last energy level of the atom. There will NEVER be more than 8 valence electrons • Elements in columns 1A through VIIIA: the number of valence electrons can be determined by the column number; 1A has 1 valence electron, IIA has 2 valence electrons, etc. • Electron Dot Configurations • Electron Dot configurations – are used to represent atoms; 2 things are needed: – Symbols of elements – Valence electrons • Draw the electron dot configuration of the following elements: • H Mg B C • N O F He Kr • IV. Compounds – two or more elements held together by a chemical bond. • Chemical bond – the point at which elements are joined in a compound; the bond is made by either sharing or giving and taking valence electrons. • Chemical formula – the recipe for a compound • Bonds for compounds: Sodium Chloride Water