* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3.1 Trig Functions of Non-Acute Angles
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
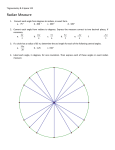
Math 170 Trigonometry Lecture Notes Chapter 3 3.1 Trig Functions of Non-Acute Angles Video: Trig Functions of Non-Acute Angles (7:39) Reference Angles: ∙Acute angle made with the ________ -axis ∙ symbol for reference angle: _____ To find the Reference Angle: a) Find a coterminal angle between __________ and __________ by adding or subtracting 360. b) Draw the coterminal angle and reference angle. Find the reference angles for: 1) 1216⁰ 2) - 986⁰ 3) 575⁰ Theorem: A trigonometric function of an angle and its reference angle are the same, except, perhaps, for a difference in sign. sin 150o = ____ = sin ____ sin 210o = _____ = sin ____ (See HW video for more practice on Reference angles) Definition: The trigonometric functions of an angle and any angle coterminal to it are always equal. (pg 118) for any Integer k: sin (ϴ + 360ok) = sin ___ cos(ϴ + 360ok) = cos ____ Example: 1. cos 495o = cos _____ ? 2. Find ϴ to nearest degree if sin ϴ = -0.5592 and ϴ terminates in QIII with 0o < ϴ < 360o 1 Math 170 Trigonometry Lecture Notes Chapter 3 “Special Angles”: Any angle whose reference angle is 30, 45, or 60 * We can find “Exact Values” for all the Trig functions of these angles * “Exact Values” will have radicals, they are not decimal approximations from the calculator. Find exact value of each of the following: 1) tan 315⁰ 2) cos (-1860⁰) 3) sin (750⁰) Use your knowledge of Trig, not a calculator, to find if the following are True or False: 1) sin 30˚ + sin 60˚ = sin(30˚ + 60˚) 2) sin 120˚ = sin 150˚ – sin 30˚ CA 3.1 #5, 15, 27, 57, 61, 75 3.2 Radian Measure Definition: ϴ (in radians) = s , r for circle with radius r and s = arc length of the arc cut off by ϴ Definition: A central angle that cuts off of an arc equal in length to the radius of the circle has a measure of ___ radian What is the formula for the Circumference of a Circle? C = _____ What happens if the radius = 1? • In Radians, an angle measurement, there are ___________ radians in a circle. • Converting between Degrees and Radians: __π radians__ = ______________ • 1 radian ≈ 57.3o Radian measurements will not have any unit symbol. So if we say: “Find sin 2,” we mean 2 radians. 2 Math 170 Trigonometry Lecture Notes Chapter 3 Draw the following in standard position: Convert from Degrees to Radians and find the reference angle in both degrees and radians: 1) 45⁰ 2) 60⁰ 3) 90⁰ Convert from Radians to Degrees and find the reference angle in both radians and degrees. 1) 2π 3 2) 3π 4 3) 5π 6 CA: 3.2 # 19, 11, 68, 73, 77, 83 3.3 Approximating trig functions of values in radians ** Be sure to change to Radian Mode ** a) cot 3.79 ← note no o sign so this is in radians b) sec 0.12 c) csc θ = 8.5 3.3 The Unit Circle & Circular Functions On the Unit Circle we have r = 1 → Note: cos ϴ = x/r = x/1 = x → Given arc of length t, such that ϴ = t/r = t/1 = t We can actually calculate: cos t , since t = ϴ 3 Math 170 Trigonometry Lecture Notes Chapter 3 Find the patterns: Function P(x,y) radius, r Unit Circle, r=1 Function ϴ=t sin θ csc θ cos θ sec θ tan θ cot θ P(x,y) radius, r Unit Circle, r=1 ϴ=t Use “Unit Circle Handout” from HW video: How to remember the unit circle cc (12:02) (pg 141) Domains of Circular Functions Ranges of Circular functions sin t, cos t tan t, sec t cot t, csc t CA: 3.3 # 26, 29, 78, 72, 32 4 Math 170 Trigonometry Lecture Notes Chapter 3 3.4 Applications of Radian Measure Recall: : ϴ (in radians) = s , r Solve equation for ‘s’ to get equation for Arc Length on a Circle. s= Find the arc length, “s” 1) r = 3 m, θ = 315⁰ 2) r = 5 cm θ = 200⁰ Example 2 (pg 148) – For the ferris wheel, find the distance traveled by the rider for ϴ = 45o & ϴ = 105o Definition: subtends - an angle subtended by an arc, line segment, or other curve is one whose two rays pass through the endpoints of the arc See Example 4 (pg 150): A person standing on earth notices that a 747 Jumbo Jet flying overhead subtends an angle of 0.45o. If the length of the jet is 230 feet, find its altitude to the nearest thousand feet. CA 3.4 #27, 29, 23, 35 5 Math 170 Trigonometry Lecture Notes Chapter 3 Area of a Sector (of a circle). This is really just finding the area of a portion of a circle ( a slice of the pie) Area of circle = πr2 Area of sector is a portion of the area of the circle A= θ 2 π r , ϴ in radians 2π simplify… Area sector = *** Note you MUST be able to use these formulas ANY way. You MUST be ready to solve for whatever the missing value is, not just the one that is currently solved for.*** 1) If a 12” pizza is divided into 8 equal pieces, find the area of one piece. If the pizza is half an inch thick, find the volume. 2) If a 10” pizza is divided into 6 equal pieces, find the area and volume of one piece (again assuming the pizza is half an inch thick). CA: 3.4 # 43, 49, 55 3.5 Linear & Angular Speed Rotation of a Wheel: Look at how fast any point on the wheel is moving. Linear velocity (speed), v = _____ Angular velocity (speed), ω = ____ How are linear speed & angular speed related? If a point is moving with uniform circular motino on a cirlce of radius r, then v = rω 6 Math 170 Trigonometry Lecture Notes Chapter 3 1) Let P be a point on a wheel with r = 10 cm, ω = π/8 rad/sec, t = 5 sec a) Find v b) find the distance traveled c) angle “traveled” In Class Activity Book Find the missing variables using Circular Motion: a) θ = 4π/3, t = 2 sec, ω = __________ b) v = 3 ft/sec, r = 2 ft, ω = __________ c) s = 8π, r = 3 cm, t = 20 sec, v = _________, θ = __________, ω = __________ d) ω = 3π/2 rad/sec; r = 7 in, t = 10 sec. v = _________, s = __________, θ = __________ Applications: (Do #3 on this page) 3) Clock Speeds: The second hand of a clock makes one rotation _________, in ___________ sec. The minute hand of a clock makes one rotation _________, in ___________ min or ________ sec. The hour hand of a clock makes one rotation _________, in ___________ hour or _________ min. a) Find the linear and angular speed of the second hand of a clock, if the second hand is 5 in long. b) Find the linear and angular speed of the minute hand of a clock, if the minute hand is 4 cm long. Express both in units/minute and units/second. CA 4) A wheel makes 36 rev/min. If the radius is 12 cm, find: v and ω 7