* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download sol 11 a, b mesoamerica
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
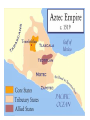
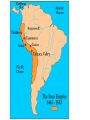
WHI: SOL 11a, b Mesoamerica Early inhabitants • Migrated from Asia during the last Ice Age, crossing the Bering Strait by foot • Hunter-gatherers: • During global warming, they migrated east and south to follow the herds. • Different cultures formed as they spread out. • Cut off from Asia as Ice Age ended, they developed independently from cultures in the Eastern Hemisphere. • Technology: • Metal was rarely used; many cultures were still in the Stone Age. • Wheel was used, but not for transportation. Olmec Civilization • • • • • • • • • • • • Name means “rubber people.” Parent or base culture of Mesoamerica: Settled along the Gulf Coast Influenced area through trade; evidence of trade confirmed by Olmec jade carvings found throughout Central America Polytheistic religion: Performed ritual sacrifices Played pok-a-tok game Built temple and pyramids Went on pilgrimages Constructed “Colossal Heads” Achievements: Calendar Mayan Civilization • Located in the Mexican and Central American rain forests on the Yucatan Peninsula (present-day Mexico, Guatemala, Honduras, and Belize) • Economy based on agriculture (including irrigation) and trade • Groups of city-states ruled by kings: • Represented by Chichén Itzá, the premier city-state • Priests, nobles, and warriors—upper class • Everyone else— peasants who paid taxes to the king (using corn) • No rights for women Mayan Civilization • • • • • • • • • • Polytheistic religion: Pyramids Priest preoccupied with concept of time Human sacrifices Achievements: Hieroglyphics Complex 365-day calendar system Astronomy Number system Between 850 and 1000 A.D. (C.E.), city-states abandoned Aztec Civilization • Located in arid valley in central Mexico • Represented by the capital Tenochtitlan, an island city in Lake Texcoco • Government: • Ruled by an emperor with absolute power • Indirect rule; trade and tribute from conquered peoples held empire together. • Empire built by the conquest of fierce warriors; conquest provided prisoners and slaves for religious sacrifices • Right of slaves to buy freedom Aztec Civilization • Economy: • Based on agriculture (beans, squash, tomatoes, and peppers) • Chinampa farming (practice of draining swamps and building up fields in shallow lake beds) • Polytheistic religion: • Chief god—the sun god • Priests, a special social class • – Recorded knowledge and ran schools • – Served as astronomers and mathematicians • Ritualistic ceremonies performed daily • Based on warfare • Pyramids • Frequent sacrifices Aztec Civilization • • • • • Achievements: Causeways Aqueducts Canals Dams Incan Civilization • Location: • Developed in the Andes Mountains • Area includes primarily present-day Peru and northern Chile, as well as smaller area in southern Colombia, Ecuador, Bolivia, and northwestern Argentina • Important cities: • Cuzco, capital • Machu Picchu Incan Civilization • • • • • Government: Ruled by an emperor with absolute power Direct rule – Government arranged marriage. – Citizens were required to have passes for travel. • – Government controlled harvest. • – Conquered people were forced to adopt Incan ways Incan Civilization • Economy: • Based on high-altitude agriculture (potatoes, beans, squash, peanut, cotton, llamas, guinea pigs, and alpacas) • Used terrace-farms • Polytheistic religion: • Chief god—the sun god Incan Civilization • Achievements: • Kept records on quipus, a system of knotted strings • Demonstrated themselves to be superb engineers • Created vast network of roads linking entire empire