* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Supply - Attica Central School
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
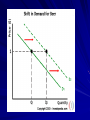
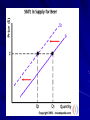
Chapter 5: Supply Chapter 5: Supply KEY CONCEPT – Supply is the willingness and ability of producers to offer goods and services for sale. WHY THE CONCEPT MATTERS – Most people are producers. Doing household chores, working at a job, providing rides to others are ways of producing goods and services. Participating on a team is a way of supplying skills, knowledge, and support to one’s school. Producers incur costs and receive rewards for the work they do. What Is Supply? The Law of Supply KEY CONCEPTS – Supply—willingness and ability of producers to offer goods, services – Anyone who provides goods or services is a producer – Law of supply: producers willing to sell more of product at higher than at lower price Supply Schedules KEY CONCEPTS – Supply schedule shows amount of product individual willing, able to offer at each price – Market supply schedule shows amount of product all producers willing, able to offer at each price The Law of Supply EXAMPLE: Price and Supply – Smiths sell tomatoes at farmers’ market willing to offer 24 pounds at standard price of $1 per pound willing to offer 50 pounds at $2 per pound willing to offer 10 pounds at 50 cents per pounds not willing to supply any tomatoes below 50 cents Supply Curves KEY CONCEPTS – Supply curve shows data from supply schedule in graph form – Market supply curve shows data from market supply schedule Supply Curves EXAMPLE: Market Supply Curve – Market supply curve differs in scope from individual supply curve both constructed same way – Supply curves for all types of producers follow law of supply will provide more at higher prices although costs more to produce more reason: higher prices signal potential for higher profits Reviewing Key Concepts Explain the differences between the terms in each of these pairs: – supply and law of supply – supply schedule and supply curve – market supply schedule and market supply curve What Are the Costs of Production? Labor Affects Production KEY CONCEPTS – Marginal product—change in total output caused by adding one worker – Specialization—having a worker focus on one aspect of production Labor Affects Production EXAMPLE: Marginal Product Schedule – Marginal product schedule—relation between labor, marginal product – Increasing returns—new workers cause marginal product increase – Diminishing returns—total output grows at decreasing rate – Negative returns—output decreases through crowding, disorganization Production Costs KEY CONCEPTS – Fixed costs—expenses owners incur no matter how much they produce – Variable costs—expenses that vary as level of output changes – Total cost—the sum of fixed and variable costs – Marginal cost—additional cost of making one more unit of the product Production Costs EXAMPLE: Fixed and Variable Costs – Fixed costs: mortgage, insurance, manager salaries, machinery – Variable costs: workers’ wages, electricity, materials, shipping Production Costs EXAMPLE: Production Costs Schedule – Fixed costs remain the same no matter what total product amounts to – Calculating marginal cost: divide change in total cost by change in total product – Diminishing returns result in increase in marginal cost Earning the Highest Profit KEY CONCEPTS – Marginal revenue—money made from sale of each additional unit sold same as price – Total revenue—income from selling a product Total revenue = P (price) x Q (quantity purchased at that price) Earning the Highest Profit EXAMPLE: Production Costs and Revenues Schedule – To make most profit, owner decides number workers hired, units made – To decide, owner performs marginal analysis comparison of costs, benefits of adding a worker, making another unit – Profit-maximizing output—level of production yielding highest profit Reviewing Key Concepts Explain the differences between the terms in each of these pairs: – marginal product and profit-maximizing output – increasing returns and diminishing returns – fixed cost and variable cost What Factors Affect Supply? Changes in Quantity Supplied KEY CONCEPTS – Change in quantity supplied: rise or fall in amount offered for sale because of change in price – Different points on supply curve show change in quantity supplied Changes in Supply KEY CONCEPTS – Change in supply —producers offer different amounts at every price – As production costs rise, supply drops; as costs drop, supply rises – Change in supply shifts the supply curve – Six factors cause change in supply What Is Elasticity of Supply? Elasticity of Supply KEY CONCEPTS – Elasticity of supply—measures producer response to price changes – Elastic— price change leads to larger change in quantity supplied – Inelastic— price change leads to smaller change in quantity supplied – Unit elastic— price and quantity supplied change by same percentage What Affects Elasticity of Supply? KEY CONCEPTS – Main factor determining elasticity is ease of changing production given enough time, elasticity rises for most goods and services – Industries that respond quickly to rising or falling prices: do not need much capital, skilled labor, hard-toobtain resources