* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Art of Ancient Egypt
Egyptian temple wikipedia , lookup
Plagues of Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Memphis, Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Joseph's Granaries wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian race controversy wikipedia , lookup
Mastaba of Kaninisut wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian medicine wikipedia , lookup
Egyptian pyramids wikipedia , lookup
Mastaba of Hesy-Re wikipedia , lookup
Thebes, Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Index of Egypt-related articles wikipedia , lookup
Egyptian pyramid construction techniques wikipedia , lookup
Khnumhotep and Niankhkhnum wikipedia , lookup
Prehistoric Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian religion wikipedia , lookup
Middle Kingdom of Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Egyptian funerary practices wikipedia , lookup
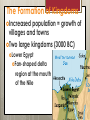
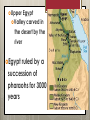
The Art of Ancient Egypt The Growth of Egyptian Civilization Early Inhabitants Along the Nile Yearly summertime flooding of the Nile River Deposits of fertile soil in the valley People change from gatherers to producers Rely more on animals they raised for food The Formation of Kingdoms Increased population = growth of villages and towns Two large kingdoms (3000 BC) Lower Egypt Fan-shaped delta region at the mouth of the Nile Upper Egypt Valley carved in the desert by the river Egypt ruled by a succession of pharaohs for 3000 years Three Major Periods of Egyptian History Each kingdom divided into dynasties. Dynasty: a period during which a single family provided a succession of rulers Blood HAD to be pure = marry from in immediate family Earliest Dynasty 3100 BC when Egypt united under Menes founded the first of the 31 Egyptian dynasties The OLD KINGDOM 2686 start BC – 2150 BC of the third dynasty Capital at Memphis Ended when centralized government was weakened by rise of independent nobles. country split into small states and civil wars broke out The MIDDLE KINGDOM 2050 – 1800 BC Nobles regained control of the country Capital at Thebes Time of law and order and prosperity Pharaoh supreme head but not as powerful as those in the Old Kingdom Ended when Egypt easily overrun by the Hyksos from western Asia Inhabited Lower Egypt and forced Egyptian people to pay tribute The NEW KINGDOM 1570 BC – 332 BC Warrior pharaohs used expertise to extend control over neighboring nations Amenhotep III – pharaoh during the peak of Egypt’s power and influence Amenhotep Akhenaton) IV (later called Changed Tradition (not a popular move) Moved capital to Tel el-Amarna Established Aton (sun god) as the supreme god Decline of Ancient Egypt After Akhenaton’s death, traditions returned Alexander the Great of Macedonia conquered Egypt in 332 centuries of Hellenistic rule Egypt made a province of Rome 30 BC The Pyramids Covered with polished layer of white limestone The Pyramid of Khufu 13 acres big and 48 stories high 2.3 million stone blocks Design of the Pyramids Almost perfectly square floor plan Base larger than height = Solidity and permanence Solid limestone with exception of passage-ways and small galleries Influence of Religion Importance placed on resurrection of the soul and eternal life after death (reincarnation) -- The soul = ka Purpose to protect and preserve the body after death Embalmed and wrapped in strips of cloth; placed in the tomb, awaiting the soul’s return The Pyramids as Tombs Most impressive tombs were built for pharaohs. Dead-end passageways and false burial chambers to confuse grave robbers Evolution of the Pyramid Shape Dead buried in hidden pits and piled sand and stone over top Use of sundried bricks to build mastabas Mastaba: low, flat tomb Rectangular in shape with sloping sides and a chapel, as well as false and true burial chambers Mastaba at Meydum in the Old Kingdom Several mastabas of diminishing size placed on top of each other = step pyramid Mastaba Sakkara at Mastabas built without steps and a point added to top = true pyramid form Construction of the Pyramids Each pyramid took many thousands of workers and decades to build Middle Kingdom: construction impractical permanent tombs for pharaoh cut into rock cliffs The Temples Temples erected along eastern banks of the Nile near Thebes Each built by command of pharaoh and dedicated to pharaoh’s favorite god/gods At pharaoh’s death, temple became his funeral chapel Temple of Amon-Re at Karnak Temples to honor particular gods were enlarged to tremendous proportions by several pharaohs Structure of the Temple Great doorway flanked by obelisks (tall, four-sided, pointed stone shafts) Statues of pharaoh and banners opened onto uncovered courtyard Entry into great hall at end of courtyard Massive stone columns of 70 feet Sanctuary: small dark and mysterious chamber where only the pharaoh and certain priests were permitted