* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Major Conflicts of World War II
Operation Bodyguard wikipedia , lookup
Military history of Greece during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Swedish iron-ore mining during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Operation Torch wikipedia , lookup
Military history of the United Kingdom during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
German military administration in occupied France during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Mediterranean and Middle East theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Invasion of Normandy wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
United States Navy in World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
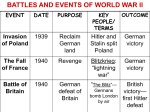
World War II • Standard: Demonstrate an understanding of the global political, economic, and social impact of World War II. • Essential Question: What was the global political, economic, and social impact of World War II? Major Conflicts • Element: Describe the major conflicts and outcomes to include Pearl Harbor, El-Alamein, Stalingrad, D-Day, Guadalcanal, the Philippines (Leyte Gulf) and the end of the war in Europe and Asia. • Vocabulary: Pearl Harbor, El-Alamein, Stalingrad, D-Day, Guadalcanal, Leyte Gulf World War II • 1939-1945 • Axis Powers – Nazi-Germany – Italy – Japan • Allied Powers – – – – United Kingdom France Russia United States Blitzkrieg • “Lightning War” • using fast-moving airplanes and tanks • followed by massive infantry forces • designed to take enemy defenders by surprise and overwhelm them quickly Blitzkrieg • Poland: on September 1, 1939 Germany attacked and took over leading Great Britain and France to declare war on Germany by September 3 • Bulgaria, Romania and Hungary joined the Axis powers with force of will by Hitler • The Phony War: France and Britain stationed troops at the Maginot Line while German troops were stationed on the Siegfried Line. No one tried to cross Early Victories • Denmark & Norway: German forces launched surprise attack on April 9, 1940 • allowed Germany to build bases along the NorwegianDanish cost to launch attacks on Britain. • Netherlands, Belgium & Luxembourg: Germans took control over the Northern border of France in May of 1940 in preparations of an invasion into France • France: crossed at the Ardennes woodland crossing the gap of the Maginot Line to push the British and French army’s out of France at Dunkirk Rescue at Dunkirk • French and British forces were pinned in at Dunkirk • crossed English Channel with 850 ships from May 26 to June 4, 1940 • used Royal Navy ships, civilian crafts-yachts, lifeboats, paddle steamers and fishing boats • amateur armada carried some 338,000 battleweary soldiers to safety Stop and Think! • What was “Blitzkrieg”? • Why do you think it was so effective in the early part of World War II? Fall of France • Hitler took Paris by June 14, 1940 • Northern France under control of Germany • Vichy, France and headed by Marshal Petain a World War I hero for France – assisted Nazi-German forces Results of France • General Charles de Gaulle set up a government in exile at London for France – Organized Free French military forces that battled the Nazis until Frances liberation in 1944 • after Germany took France, Japan seized the French colony of Indo-china in September 1940 Why do you think the German occupation of France was so signficant? The Battle of Britain • Operation Sea Lion: plan to invade Great Britain, the last strong hold in the west • British Royal Air Force outnumbered and withheld German invasion • operation abandoned • many major cities in Great Britain, including London were bombarded constantly for several months until October 1940 Churchill after Bombing • Throughout the German bombing raids of London, Churchill kept his country together by visiting the bombing sites giving hope to his people through several speeches: “I would say to the House as I said to those who have joined this government: I have nothing to offer but blood, toil, tears and sweat. We have before us an ordeal of the most grievous kind. We have before us many, many long months of struggle and of suffering. You ask, what is our aim? I can answer in one word: Victory. Victory at all costs — Victory in spite of all terror — Victory, however long and hard the road may be, for without victory there is no survival.” Stop and Think! • Read the quote to the left by Winston Churchill. Compare his sentiments to the British sentiments during the years of appeasement before 1939. Why do you think this change occurred? • “You ask, what is our aim? I can answer in one word: Victory. Victory at all costs — Victory in spite of all terror — Victory, however long and hard the road may be, for without victory there is no survival.” Axis Balkan Dominance • Greece and Yugoslavia: resisted and fell to Germany in days during April, 1941 • Crete: German forcing Allied powers off of Europe • Operation Barbarossa: June 22, 1941 Germans invaded Soviet Union who were not prepared, Soviets retreated destroying everything as they retreated Winston Churchill “Even though large tracts of Europe and many old and famous States have fallen or may fall into the grip of the Gestapo and all the odious apparatus of Nazi rule, we shall not flag or fail. We shall go on to the end, we shall fight in France, we shall fight on the seas and oceans, we shall fight with growing confidence and growing strength in the air, we shall defend our Island, whatever the cost may be, we shall fight on the beaches, we shall fight on the landing grounds, we shall fight in the fields and in the streets, we shall fight in the hills; we shall never surrender, and even if, which I do not for a moment believe, this Island or a large part of it were subjugated and starving, then our Empire beyond the seas, armed and guarded by the British Fleet, would carry on the struggle, until, in God's good time, the New World, with all its power and might, steps forth to the rescue and the liberation of the Old.” Japanese Aggression • Japan threatened British Malaysia, the Dutch East Indies, and the American Philippines • Admiral Yamamoto: leader of the Japanese navy, saw the U. S. military base in Pearl Harbor, Hawaii as a threat Pearl Harbor Description: • Pacific Theater • December 7, 1941 • Japanese surprise attack on U.S. Naval Base at Hawaii Pearl Harbor Outcome: • U.S. responded by declaring war on Japan • because of Axis alliance U.S. at war with Germany and Italy • U.S. joined Great Britain and Soviet Union to form the Allied Powers Allied Leaders Winston Churchill Charles de Gaulle Franklin D. Roosevelt Joseph Stalin Island Hopping • General Douglas MacArthur plan to attack the weaker Islands closer to Japan rather than taking every Island one by one Guadalcanal Description: • Pacific Theater • May 1942 to February 1943 • land forces Campaign • Allied forces spotted construction of an airfield on Guadalcanal in the Solomon Islands Guadalcanal Outcome: • first amphibious landing of the war for Allied forces • took island over and Japanese forces evacuated in February 1943 • stopped Japanese expansion Battle of Midway • • • • June 4 to June 7, 1942 Pacific Theater Naval Campaign regarded as the most important naval engagement of the Pacific Campaign • United States navy defeated an attack by Japan • Permanently weakened the Imperial Japanese Navy Stop and Think! • How did the war in the Pacific theater begin? • How was the war in the Pacific different from the war in Europe? Stalingrad Description: • European Theater • August 23, 1942 to February 2, 1943 • Germany invaded Soviet Union with 300,000 soldiers • almost took capital at Moscow and Stalingrad • by February 2, 1943 remaining 90,000 frostbitten, hungry German soldiers surrendered Stalingrad Outcome: • USSR’s Red army and Russian winter turned Germans back • high death rate and increased destruction of the Soviet Union • Stalin pleaded with Great Britain and U.S. to invade western Europe Stop and Think! • Why was the Battle of Stalingrad significant? • Can you think of any other instance in world history when invading Russia didn’t work? Why do you think this is the case? El Alemein Description: • European Theater • October 23 to November 4, 1942 • invasion of Africa • Allied forces led by General Bernard “Monty” Montgomery of Britain • German Army led by General Rommel El Alemein Outcome: • attack in Africa relieved pressure on the eastern front in the Soviet Union • Allied forces took Africa and invaded into Italy • toppled Mussolini from power by September 3 Stop and Think! • Why was the El-Alamein significant? D-Day Description: • European Theater • June 6, 1944 • Operation Overlord was a false operation at Calias to draw attention from Normandy • largest amphibious (land and sea) invasion D-Day Outcome: • a month later additional troops landed under General Patton • punched through German defenses by July 25 • by August the Allies were back in France Stop and Think! • Why was D-Day so important for the Allies? Leyte Gulf Description: • Pacific Theater • October 23, 1944 • Naval Campaign of the Philippines • Allied forces led by General Douglas MacArthur of the U.S. • took four days Leyte Gulf Outcome: • Japanese navy had lost, eliminating it as a fighting force • last Japanese naval battle of the war Stop and Think! • Why was the war in the Philippines significant? Battle of the Bulge • December 16, 1944 • European Campaign • Germans attacked at the Ardennes • the allies were caught off guard • pulled back together and pushed back the Germans V-E Day Description: • European Theater • Fall of Berlin • by March, 1945 Allied forces crossed the Rhine river into Germany • on April 25 Soviet forces surround Germany capital of Berlin and bomb it with artillery fire V-E Day Outcome: • Hitler marries his long-time girlfriend Eva Braun then they both commit suicide on April 30, 1945 • Hitler’s body was carried outside and burned • May 7, 1945 V-E day, Victory in Europe Day • the Third Reich Germany offer General Eisenhower their unconditional surrender V-E Day It is believed that Hitler shot himself in the head while simultaneously biting down on a cyanide pill. He had his dog, Blondi, put to death as well. How did the war end in Europe? • Write a one sentence summary describing the end of the war in the European theater. Be prepared to share Fighting still in the Pacific Iwo Jima: • February to March 1945 • Pacific Land Forces Campaign • American Marines took island 760 miles from Tokyo Fighting still in the Pacific Okinawa: • April 1 to June 21 1945 • Pacific Land Forces Campaign • American troops moved to this island about 350 miles from southern Japan • the bloodiest land battles • Japanese lost 100,000 troops • America lost 12,000 Einstein’s letter to the President Einstein was one of several foreign scientists that recognized the danger of German scientists working on an Atom bomb. In this letter Einstein urged President Roosevelt to begin the Manhattan Project, which would lead to the first Atom Bomb. Victory in Asia Description: • Pacific Theater • Land Forces Campaign • President Truman of the U.S. approves to drop an atomic bomb on Japan • on August 6 the first is dropped on Hiroshima • on August 9 the second and final is dropped on Nagasaki Hiroshima and Nagasaki Between 140,000 and 150,000 people died, almost all instantly, because of these 2 bombs. The bomb dropped on Hiroshima was dropped by the Enola Gay. Victory in Asia • V-J Day • Japanese unconditional surrender to General MacArthur September 2, 1945 V-J Day, Sep. 2, 1945 How did the war end in the Pacific theater? • Write a one sentence summary describing the end of the war with Japan. Be prepared to share