* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Genetics/Inheritance
Survey
Document related concepts
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of biology wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Mendelian inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Symbiogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to genetics wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
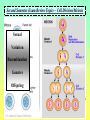
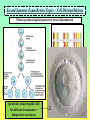
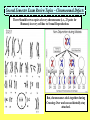
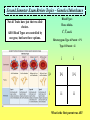
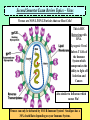
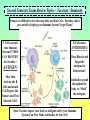
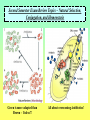
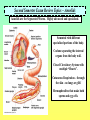
Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Cell Division/Meiosis Sexual Variation Recombination Gametes Offspring Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Cell Division/Meiosis Meiosis produces haploid gametes for Sexual Reproduction 4 genetically unique haploid cells! Chromosomes undergo CrossingOver = Different Gene Combos!! 4 genetically unique haploid cells! Get different chromosomes = Independent Assortment Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Chromosomal Defects There Should be two copies of every chromosome (i.e., 23 pairs for Humans) in every cell due to Sexual Reproduction. But, chromosomes stick together during Crossing-Over and can accidentally stay attached. Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Punnett Squares Parents are Purple because: However, they are Heterozygous - So: Offspring show Variation because: Random because: Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Genetics/Inheritance Their Offspring receive: Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Genetics/Inheritance Complete Dominance! Heterozygous for Red Fruits Red is dominant to yellow Rr R r x Rr R r RR Rr Rr rr What if it was Incomplete Dominance? Examples such as Snapdragon or Fouro’Clock Flowers? What if it was Codominance? Examples such as Sickle-Cell Anemia or Roan Cows? Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Genetics/Inheritance Blood Types Not all Traits have just the two allele choices. Three Alleles. IA, IB, and i. ABO Blood Types are controlled by one gene, but have three options. Heterozygous Type A Parent = IAi Type O Parent = ii i i IA IAi IAi i ii ii What is the first parent was AB? Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Genetics/Inheritance Not all Traits have just the one controlling Gene. Polygenic Traits show great Variation due to the options. Three identical Genes with two possible alleles showing Incomplete Dominance! Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Human Genetics You supposed to know about Human examples of each type of Inheritance and possible Mutational Mistakes. Huntington’s Disease and the Brain – Dominant!! Cystic fibrosis - recessive!! PKU – defective enzyme = diet can be adjusted!! Sickle-Cell Anemia codominant!! Hemophilia – X-linked!! Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Pedigree For this Pedigree If the Trait is recessive – who is affected? Who is a Carrier? ? For this Pedigree If the Trait is Dominant – who is affected? Who is a Carrier? Why is this NOT a Sex-Linked Trait? Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Recombinant DNA Since DNA is “Universal”, it can be cut and transferred from species to species. You need to understand the basic process. Restriction Enzyme to “cut”, Plasmid = Vector to transport Gene, as Recombinant DNA, and Transgenic Organism that Expresses foreign DNA Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Cloning Transgenic Organisms can be difficult to form. Cloning will produce Identical “Offspring” that also express the new Genes. Dolly (right) is a clone, Polly (left) is a clone that carries a human gene for Factor IX that is a treatment for Hemophilia B. Second Semester Exam Review Topics – DNA Fingerprint Why is it clear that D2 and S2 are NOT children of these parents? What is interesting about D2? Who Did It?! Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Pasteur Experiment Remember! The Cell Theory states: 1) The Cell is the Basic Unit of Life. 2) All living things are Cells or made of Cells. 3) Cells come from Preexisting Cells. Pasteur showed BioGenesis!! Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Miller/Urey Exp. Miller/Urey demonstrated that Organic Molecules could form in conditions similar to the early Earth. Organic Molecules are the Building Blocks of Life! Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Endosymbiosis Prokaryotes are the simplest and oldest living things on Earth. Eukaryotes appear later as Team Players = Endosymbiosis! Mitochondria 1st! Chloroplasts 2nd! Aerobic Respiration! Photosynthesis in Algae! Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Evolution Evolution refers to the fact that organisms Change through Time. Horse evolution is well documented in the Fossil Record. They change from smaller, four-toed swamp dwellers into huge grasseating, singletoed grasslands specialists! Individual organisms DO NOT evolve! They already have their DNA that codes for their traits!! Populations evolve as they sort out the possible genes / alleles that support their survival and Fitness! Second Semester Exam Review Topics – The Fossil Record The Fossil Record shows real organisms from the past. Allows comparison to modern groups to evaluate how they have changed. Newest Advanced Cenozoic Age of Mammals! Mesozoic All comparisons of Shape and Structure = MORPHOLOGY!! Age of Dinosaurs, 1st Angiosperms/Insects! Paleozoic w/first vertebrates, trilobites, early plants and animals! Oldest Primitive Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Natural Selection Evolution occurs to make organisms “Adapted” to their Niches. Occurs through Competition that modifies the Survivors. Adaptations: Competition: Any structure, process, or behaviors that allows an organism to survive in its Niche. Direct interactions for the same Resources. There can be Only One per Niche. Peppered Moths of Europe Saw-whet Owl and Kestrel are both small predators. Coexist because? Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Selection, Evolution Evolution leads to differences in Populations that were once all similar. Experiment by Diane Dodd – 1989. 1. Original Population / Species. 2. Separated into two groups using different Food Sources. 3. Generations = Sex/Meiosis/Mutations that form new alleles = Difference!. 4. Stay Separate! New Species of Flies! Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Variation in Evolution If all organisms of a species were THE SAME, they could not be differentiated through Competition. They would be Evenly Matched! A “King” Cheetah importantly represents? Lions in a Pride all look very similar – WHY?! How do Lion Prides make sure there is some Genetic Variation? Cheetahs are in REAL trouble due to Inbreeding. Why is this picture so Rare? Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Variation in Evolution Variation in Populations is essential to Evolution = Choices! Variation in Ladybugs. All different patterns of Garter Snakes. This Variation is in color banding patterns, but could also be in any other trait since they all change randomly and could be important features. Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Variation in Evolution Species always start highly as small inbred populations, but develop Variation over time through what processes? Khoisan “Bushmen” of S. Africa are most ancient recognized “race” of H. sapiens. Hawaiian Happy-Face Spider Mutation forms New Alleles / Options! Meiosis allows for Random Spread of all of those differing traits. Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Speciation Members of the SAME Species should: Look Alike = Same Adaptations = Morphological Species Concept, Interbreed Only with “Their” Species = Biological Species Concept. Bald Eagles and Golden Eagles are obviously related! Once the Same! Interbreeding!! Now! Sexual Selection and Reproductive Isolation Keep them Separate from other species. Do Not Interbreed and they are Different SPECIES!! They were split up as they were separated into small discrete populations = Geographic Isolation! Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Fitness Survival of the Fittest is based on the ability to survive and have Offspring. Offspring then pass on the Genes that provide for the successful Adaptations of Evolution. Pallidus Octopus guarding its eggs. And Newly hatched Octopus. Three Striped Poison Dart Frog carrying its eggs on its back until they hatch. Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Evolution/Adaptation PRO! EU! Life on Earth is all related! But the broad diversity stems from Evolution of new and different Traits for new and different Niches. Endosymbiosis! Multicellular! Prokaryotes 1st Eukaryotes 2nd Multicellular Kingdoms Next And so on! Different Niches = Different Adaptations. All from the same original Organism! Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Evolutionary Traits All have same basic structure indicating that they are related = Tetrapod Vertebrates!! HOMOLOGOUS!! Divergent Evolution. But, These are Wings! ANALOGOUS!! Convergent Evolution. BUT – Both are adapted for Flight via different successful structure. Wings Fly and LOOK similar, but Different! Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Adaptive Radiations Organisms have to come from somewhere! Pre-existing species CHANGE as they adapt to new environments. Divergent Evolution. In some spectacular cases, major groups start with a single species that separates into many species = Divergence. Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Convergent Evolution Organisms that live in similar Niches tend to possess similar adaptations. This is called “Convergent” because different groups become alike. Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Names and Groups Naming Organisms is important to separate and recognize them. Binomial Nomenclature provides very specific names for organisms that cannot be confused with other organisms, Genus species are two words! Linnaeus’s Seven Levels. Panthera pardus K-P-C-O-F-G-s! White-Yellow animal, panther Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Virus Viruses are NON-LIVING Particles that use Host Cells! This is HIV. Retrovirus with RNA. Lysogenic Virus! Infects T Cells of the Immune System which compromises the ability to fight off Infection and Cancer. Also similar to Influenza which causes Flu! Viruses can only be defeated by YOUR Immune System! Smallpox has a 30% death Rate depending on your Immune System. Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Vaccines / Immunity Viruses are difficult to treat because they use Host Cells. But they can be prevented by helping your Immune System Target Them! T Cells activate your Immune System IF THEY CAN IDENTIFY the Invader = ANTIGEN! They then Activate the B Cells and attack Cell Targets like Tumors and Viral Infected Cells! B Cells make ANTIBODIES! These Bind to and Target the Antigens for Destruction!! Antibodies spread throughout the body to “Mark” the Antigens. Since Vaccines expose your body to Antigens safely, your Immune System Can Now Make Antibodies for Survival! Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Bacteria First and simplest Cells. Characterized by lack of a Nucleus and other Membrane-Bound Organelles. DECOMPOSERS!! DISEASE Causing!! Critical Recyclers that finish breaking down/Recycling matter back to the Producers! Can use living tissues to survive! Different species can Metabolize anything if they have the correct Enzymes! Remember NITROGEN-FIXING Bacteria in Legume Root Nodules that produce Nitrates. Consume flesh or release toxic molecules that damage the organism! ANTIBIOTIC TREATMENTS can Kill them! Should Know about Streptococcus as a Disease example. Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Natural Selection, Conjugation, and Homeostasis Green is more adapted than Brown – Unless?! All about overcoming Antibiotics! Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Protista Unicellular Eukaryotic Organisms. You need to know Four (4)! Paramecium with Cilia and Contractile Vacuoles Euglena with Chloroplasts and Flagella Plasmodium showing “spores” erupting from red blood cells and their “Vector” mosquito Amoeba showing Pseudopodia and Food Vacuoles Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Fungi Multicellular Terrestrial Decomposers. Niche involves break-down of tough food sources such as Cellulose. Extracellular Digestion. Drill, Digest, and Drink! Many Fungi compete with bacteria and produce various Antibiotics. Yeast are Fungi and are important in food production of bread and alcohol. Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Plant Adaptations Bryophytes = Mosses First – small, nonvascular, spores, swimming gametes. Ferns = Vascular Plants Second – Vascular and Large, but spores and swimming gametes? Seedless. Gymnosperms = Conifers Third – Large and Vascular, Pollen, Cones with Seeds. Angiosperms = Flowering Plants Fourth – Flowers and Pollination. Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Plant Diversity Multicellular Autotrophs! Know the basic forms of plants to recognize Names and Traits. Seed Plants make Pollen which can Spread through the Air! Fully Terrestrial!! Gymnosperms possess Cones to protect their Seeds. Angiosperms produce Flowers and often Fruits to facilitate Sexual Reproduction with Insects. Monocots and Dicots. Two main groups of Angiosperms. Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Animal Kingdom Multicellular Heterotrophs that ingest and consume their Prey. Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Annelids Annelids are the Segmented Worms. Highly advanced and specialized. Semented with different specialized portions of the body. Coelom separating the internal organs from the body wall. Closed Circulatory System with multiple “Hearts”. Cutaneous Respiration – through the skin - no lungs or gills! Hermaphrodites that make both sperm and egg cells. Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Insecta Insects possess Exoskeletons and have highly specialized body parts. Weaver Ant Can See the Tracheal Tubes that Insects Breath through via Spiracles in each Segment. But no Blood Vessels = Open Circulatory System. Metamorphosis with different stages in Development. Internal Fertilization in Terrestrial Environments. Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Amphibians Amphibians require Water to Reproduce. Amazon Horned Frog Cutaneous Respiration with a three-chambered Heart. External Fertilization in Water. Gelatinous Eggs that hatch as Tadpole Larvae. Metamorphosis into adult stage Frogs and Salamanders. Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Placental Mammals Advanced Mammals that carry Offspring internally until they are well developed at Birth. Then fed with Milk from Mammary Glands. Complex animals that require Parental Care during extensive development. Four-Chambered Heart with Closed Circulation (high pressure = Active!). Large Lungs = Aerobic! Placental embryo showing the placenta with its connecting circulation to the Uterus. Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Immunity Breast Feeding is Important because it provides the baby antibodies from the Mother. Bottle Won’t Help!! Active Immunity. When the Immune System activates and responds to infection by producing Antibodies that target the Pathogen. Long Term – Vaccines provide this Protection!! Passive Immunity. When Antibodies are donated to the person. Either injection or breast feeding in infants. Short-term protection from another source. Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Innate Behavior Innate Behaviors are Genetically Determined and “Inborn”. Instincts and Reflexes! S u c k l i n g Migration So Instinctive that Whooping Crane Chicks will follow an Ultralight Aircraft. Hibernation, Dormancy, Estivation. Imprinting on Mother. Second Semester Exam Review Topics – Learned Behavior Learned Behaviors are acquired during the lifetime of the organism. Allows organisms to adjust to their Environment. Habituation Classical Conditioning with Pavlov’s Dogs! They have been trained to respond to a Bell = Food! They are Instinctively Opposites, but are so used to each other that they can reject their natural tendencies. Trial and Error Learning Not born with these behaviors, but through persistent “Practice” they can increase their abilities.