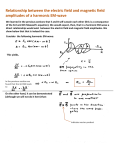
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ME 3214 – Dynamics of Particles and Rigid Bodies Credits and
Four-vector wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Derivations of the Lorentz transformations wikipedia , lookup
Eigenstate thermalization hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Inertial frame of reference wikipedia , lookup
Tensor operator wikipedia , lookup
Fluid dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Old quantum theory wikipedia , lookup
Brownian motion wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Hamiltonian mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Angular momentum wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
N-body problem wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Angular momentum operator wikipedia , lookup
Laplace–Runge–Lenz vector wikipedia , lookup
Computational electromagnetics wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Photon polarization wikipedia , lookup
Lagrangian mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Routhian mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Analytical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic angular momentum wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
ME 3214 – Dynamics of Particles and Rigid Bodies Credits and Contact Hours: 3 Credits. Three 50 minute or two 75 minute lectures per week. Instructors: George Lykotrafitis Textbook: Specific Course Information: a. Catalog Description: Kinematics and dynamics of particles. Motion relative to a translating and rotating observers; inertial reference systems; central forces and orbits. Kinematics and dynamics of groups of particles and rigid bodies. Lagrangian description of motion. b. Prerequisites: CE 2120 c. Required, Elective or Selected Elective: Elective Specific Goals: a. Course Outcomes: After completing ME 3214 students should be able to: 1. Utilize Cartesian, polar or cylindrical coordinates to describe velocity, acceleration, and relative motion. 2. Apply Newton’s second law and equations of motion in various coordinates systems for a system of particles and for a system of variable mass. 3. Compute work from forces, power and efficiency, angular momentum, rate of change of angular momentum, potential and kinetic energy. 4. Apply conservation of energy and principle of impulse and momentum. 5. Compute centroids, first moments, and moments of Inertia. 6. Compute rigid-body velocity and acceleration with respect to a rotating reference frame. 7. Apply equations of rigid-body motion in curvilinear translation and in rotation about a fixed point. 8. Compute linear momentum, angular momentum, potential energy, and kinetic of twodimensional rigid-bodies. 9. Apply equations of motion of a three-dimensional rigid-body. b. Relationship of Course Outcomes to Criterion 3 Student Outcomes: a) an ability to apply knowledge of mathematics, science, and engineering: This course specifically develops fundamentals and advanced problem solving skills using vector mathematics and scientific principles of dynamics, and emphasizes recognition of the principles used. b) an ability to design and conduct experiments, as well as analyze and interpret data: not applicable c) an ability to design a system, component, or process to meet desired needs: not applicable d) e) f) g) h) i) j) k) an ability to function on multi-disciplinary teams: not applicable an ability to identify, formulate, and solve engineering problems: Solving problems in dynamics is the main thrust of this course. In addition, selected problems are assigned in which formulation and solution approach are not predetermined. an understanding of professional and ethical responsibility: not applicable an ability to communicate effectively: not applicable the broad education necessary to understand the impact of engineering solutions in a global and societal context: not applicable a recognition of the need for, and an ability to engage in life-long learning: Class discussion will often consider the need for continued learning, and students will learn one section of the material independently with a follow up lecture following the submission of their solutions. a knowledge of contemporary issues: not applicable an ability to use the techniques, skills, and modern engineering tools necessary for engineering practice: Students will be required to use commercial software (preferably MatLab) to solve eigen value problems. Topics Covered: Vector mathematics Particle kinematics Rigid body kinematics Multiple rotating reference frames Derivative of a vector Relative motion 3D kinematics Moments and products of inertia Principal moments of inertia as an eigen value problem Impulse momentum in 3D Conservation of Energy in 3D Kinetic equations in 3D Euler’s Equations Gyroscopic motion