* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Population pp
Source–sink dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Two-child policy wikipedia , lookup
The Population Bomb wikipedia , lookup
Human overpopulation wikipedia , lookup
World population wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
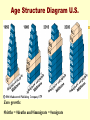
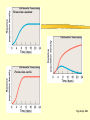
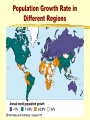
Population Growth and Regulation Characteristics of Populations Demographics are characteristics of populations Populations can be characterized by their: Population Size Population Density Population Distribution Age structure Reproductive base # Reproductive and younger Age Structure Diagram Green - Pre-reproductive years Dark Blue- Reproductive years Light blue - Post- reproductive years Age Structure Diagram U.S. Zero growth: #births = #deaths and #immigrate = #emigrate Regarding Population Density: The same area may be home to many species but they may vary by density Density refers to the number of individuals in an area but not how they are dispersed Population density variations are largely due to ecological relationships and organism interactions in an area Population Size and Exponential Growth: How population size changes Size depends on births, immigration, deaths, emigration and migrations Zero population growth is a near balance between all the positive and negative factors Ground Zero to Exponential Growth Increase in population of field mice J Shaped Growth Curve Effects of Deaths on Populations The effects of deaths on the rate of increases in 2 bacterial populations Regarding the Biotic Potential: The biotic potential of a population is its maximum rate of increase under ideal conditions Biotic potentials vary from species to species based on: What age reproduction begins How frequent reproduction is How many offspring are born at a time Limits on the Growth of Populations: The actual rate of growth depends on the environmental conditions Limiting factors are collectively called environmental resistance and include: Nutrient supply Predation Competition for space Pollution Metabolic wastes Limiting Factors on Growth The sustainable supply of resources defines the carrying capacity for a population in an environment The capacity can vary over time Note the S shaped logistic growth Carrying Capacity Density - Dependent Controls: The main controls are: Competition for resources Predation Parasitism Disease They exert their effects in proportion to the number of individuals present Density - dependent factors Events resulting in more deaths Fewer births Paramecium caudatum Paramecium aurelia Fig. 48.4, p. 856 PREY POPULATION PREDATOR POPULATION Fig. 48.7, p. 858 Fig. 48.8, p. 859 Density Independent Factors: Some events such as weather tend to increase the death rate without respect to the number of individuals present Lightning, floods, snowstorms affect both large and small populations! Life History Patterns: Life Tables Demography is the study of the age-specific patterns of particular populations Life tables follow the fate of a group (cohort) and calculate survivorship schedules A note on… Human Population Growth Increase in growth rate Expansion of habitat Increased capacity in existing habitats Population has sidestepped limiting factors Technology Medicine Population Growth Rate in Different Regions Population Growth Rate in Different Regions 1996 - Orange 2025 - Blue