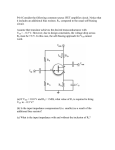
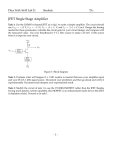
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download d-mosfet
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
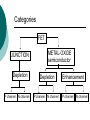
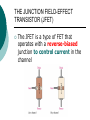
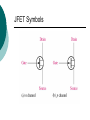
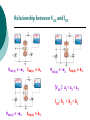
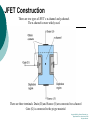
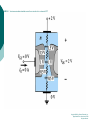
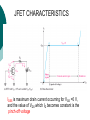
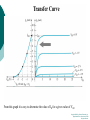
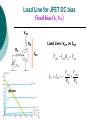
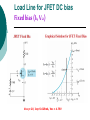
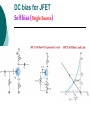
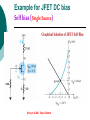
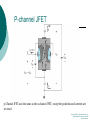
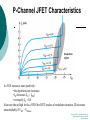
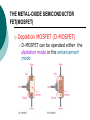
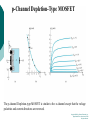
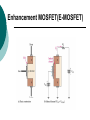
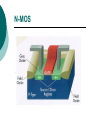
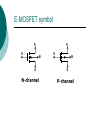
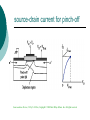
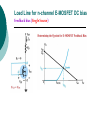
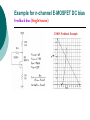
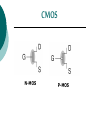
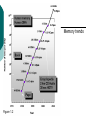
FET FET’s (Field – Effect Transistors) are much like BJT’s (Bipolar Junction Transistors). Similarities: • Amplifiers • Switching devices • Impedance matching circuits Differences: • FET’s are voltage controlled devices whereas BJT’s are current controlled devices. • FET’s also have a higher input impedance, but BJT’s have higher gains. • FET’s are less sensitive to temperature variations and because of there construction they are more easily integrated on IC’s. Copyright ©2002 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. FET Types • JFET ~ Junction Field-Effect Transistor • MOSFET ~ Metal-Oxide Field-Effect Transistor - D-MOSFET ~ Depletion MOSFET - E-MOSFET ~ Enhancement MOSFET Categories FET JUNCTION Depletion P channel N channel METAL-OXIDE semiconductor Depletion P channel N channel Enhancement P channel N channel Junction Field Effect Transistor (JFET) THE JUNCTION FIELD-EFFECT TRANSISTOR (JFET) The JFET is a type of FET that operates with a reverse-biased junction to control current in the channel JFET Symbols ++ JFET Basic Operation VGS <= 0 - The JFET is always operated with + Drain-to-Source channel of current (เส้ นทางการเดินของกระแส) n-channel or p-channel Gate-to-Source pn junction reverse-biased door to control amount of current flow between DrainSource VGS (CUT_OFF) <= VGS <= 0 a IDS How VGS control IDS? การควบคุมกระแส IDS ทาได้ โดย การปรับการขยายตัวของ depletion region ระหว่ าง Gate กับ channel |VGS |= 0 ให้ ค่ากระแส IDS สูงที่สุด ประตูปิดช้ า กระแสไหลผ่ านได้ มาก |VGS |<0 ให้ ค่ากระแส IDS น้ อยลง เร่ งให้ ประตูปิดเร็วขึน ้ กระแสไหลได้ น้อยลง Relationship between VGS and IDS VGS(1) = -a1 IDS(1) = k1 VGS(2) = -a2 IDS(2) = k2 |VGS |: a1 < a2 < a3 IDS: k1 > k2 > k3 VGS(3) = -a3 IDS(3) = k3 VGS controls ID. •JFET must be operated between VGS =0 and VGS(off) VGS (off) = VGS (MAX) -> IDS = 0 JFET Construction There are two types of JFET’s: n-channel and p-channel. The n-channel is more widely used. There are three terminals: Drain (D) and Source (S) are connected to n-channel Gate (G) is connected to the p-type material Copyright ©2002 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. FIGURE 5-5 Varying reverse-bias potentials across the p-n junction of an n-channel JFET. Copyright ©2002 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. A. VGS = 0, VDS increasing to some positive value Three things happen when VGS = 0 and VDS is increased from 0 to a more positive voltage: • the depletion region between p-gate and n-channel increases as electrons from n-channel combine with holes from p-gate. • increasing the depletion region, decreases the size of the n-channel which increases the resistance of the n-channel. • But even though the n-channel resistance is increasing, the current (ID) from Source to Drain through the n-channel is increasing. This is because VDS is increasing. Copyright ©2002 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Pinch-off If VGS = 0 and VDS is further increased to a more positive voltage, then the depletion zone gets so large that it pinches off the n-channel. This suggests that the current in the nchannel (ID) would drop to 0A, but it does just the opposite: as VDS increases, so does ID. Copyright ©2002 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. JFET CHARACTERISTICS IDSS is maximum drain current occurring for VGS =0 V, and the value of VDS which ID becomes constant is the pinch-off voltage Comparison of Pinch-Off and Cutoff Vp is the value of VDS which the drain current becomes constant and is always measured at VGS =0 V VGS(off) and Vp are always equal in magnitude but opposite in sign Transfer Curve From this graph it is easy to determine the value of ID for a given value of VGS. Copyright ©2002 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. The transfer characteristic of input-to-output is not as straight forward in a JFET as it was in a BJT. In a BJT, indicated the relationship between IB (input) and IC (output). In a JFET, the relationship of VGS (input) and ID (output) is a little more complicated: VGS 2 ID IDSS(1 ) VP Copyright ©2002 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. DC Bias for JFET 2 types of DC bias for JFET Fixed bias - 2 sources Self bias - Single source ( 1 source) DC bias for JFET Fixed bias (2 DC sources) Load Line for JFET DC bias Fixed bias (ID, VDS) VDD Load Line: VDS vs IDS RD RG IDS VDD I DS RD VDS I D I DS VDS VDD RD RD Load Line for JFET DC bias Fixed bias (ID, VGS) VGSQ=-2V, IDQ=5.625mA, VDS = 4.75V DC bias for JFET Self bias (Single Source) VDD VG = 0 RD RG IDS Load Line: VDS vs IDS RS VDD I DS RD VDS I DS RS I DS 1 RD RS 1 VDS RD RS VDD DC bias for JFET Self bias (Single Source) Example for JFET DC bias Self bias (Single Source) VGSQ=-2.6V, IDQ=2.6mA DC bias for JFET Voltage Divider Bias (Single Source) Load Line for JFET DC bias Voltage Divider bias (ID, VDS) Example for JFET DC bias Voltage Divider bias (Single Source) P-channel JFET p-Channel JFET acts the same as the n-channel JFET, except the polarities and currents are reversed. Copyright ©2002 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. P-Channel JFET Characteristics As VGS increases more positively: • the depletion zone increases • ID decreases (ID < IDSS) • eventually ID = 0A Also note that at high levels of VDS the JFET reaches a breakdown situation. ID increases uncontrollably if VDS > VDSmax. Copyright ©2002 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Specification Sheet (JFETs) Copyright ©2002 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. MOSFETs MOSFETs have characteristics similar to JFETs and additional characteristics that make then very useful. - Low power consumption - No gate current: SiO2 at Gate There are 2 types: • Depletion-Type MOSFET • Enhancement-Type MOSFET Copyright ©2002 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Depletion MOSFET (D-MOSFET) THE METAL-OXIDE SEMICONDUCTOR FET(MOSFET) Depletion MOSFET (D-MOSFET) D-MOSFET can be operated either the depletion mode or the enhancement mode D-MOSFET Symbols Main Function of Depletion MOSFET Control Current flow from Drain-to-Source Two main control mode Depletion mode Enhancement mode Depletion Mode N-channel Vgs -> negative Electrons from D-to-S channel Push to P-type substrate The more the negative value of Vgs The less amount of current flow from D-to-S Enhancement mode N-channel Vgs -> positive Electron from p-substrate Pulled into D-to-S channel Increase amount of electrions in the channel Basic Operation (n-channel D-MOSFET) A Depletion MOSFET can operate in two modes: Depletion or Enhancement mode. I D k (VGS VP ) 2 k ID(on) (VGS(ON) VP) 2 Copyright ©2002 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. p-Channel Depletion-Type MOSFET The p-channel Depletion-type MOSFET is similar to the n-channel except that the voltage polarities and current directions are reversed. Copyright ©2002 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Specification Sheet Copyright ©2002 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. คุณลักษณะของ D-MOSFET Channel การไหลของกระแสแคบกว่า JFET มาก Switching speed ่ การเปิ ดปิ ดประตู (Gate) เพือควบคุ มปริมาณกระแสให้ไหล ตามต้องการได้เร็วกว่า JFET On (กระแสไหล) -> Off (กระแสไม่ไหล) หรือ ในทางกลับกัน เร็วกว่า JFET เหมาะกับวงจร Digital ได้ดก ี ว่า JFET Example for n-channel D-MOSFET DC bias Voltage Divider bias (Single Source) I D k (VGS VP ) 2 Enhancement MOSFET (E-MOSFET) Enhancement MOSFET(E-MOSFET) N-MOS E-MOSFET symbol D D G G B S N-channel B S P-channel คุณลักษณะของ E-MOSFET ไม่ มี channel ที่แท้ จริง (no physical channel) ใช้ virtual channel ที่สร้ างขึน ้ จาก ใช้ VGS ควบคุม การมีหรื อไม่ มี virtual channel การดึงดูด carrier ชนิดเดียวกับ channel มาเชื่อมช่ องทางเดิน กระแส เพื่อให้ กระแส IDS เป็ นตามต้ องการ Switching speed ความเร็วในการให้ กระแสไหล หรื อ หยุดไหล เร็วมากกว่ า JFET และ D-MOSFET หยุดป้ อน VGS virtual channel หายไปเกือบจะทันที นิยมใช้ ใน Combinational Logic, CPU, Memory โดยเฉพาะ CMOS ซึ่งเป็ น E-MOSFET ชนิดหนึ่ง How to induce the Channel D-to-S source-drain current below saturation Semiconductor Devices, 2/E by S. M. Sze, Copyright © 2002 John Wiley & Sons. Inc. All rights reserved. source-drain current for pinch-off Semiconductor Devices, 2/E by S. M. Sze, Copyright © 2002 John Wiley & Sons. Inc. All rights reserved. source-drain current in saturation Semiconductor Devices, 2/E by S. M. Sze, Copyright © 2002 John Wiley & Sons. Inc. All rights reserved. Transfer Curve I D k (VGS VT ) 2 To determine ID given VGS: [Formula 5.13] where VT = threshold voltage or voltage at which the MOSFET turns on. k = constant found in the specification sheet k can also be determined by using values at a specific point and the formula: ID(on) [Formula 5.14] k (VGS(ON) VT) 2 VDSsat can also be calculated: VDsat VGS VT [Formula 5.12] Copyright ©2002 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Load Line for n-channel E-MOSFET DC bias Voltage Divider bias (Single Source) I D k (VGS VT ) 2 k ID(on) 0.12 x103 A / V 2 2 (VGS(ON) VT) VDD = 40V, R1=22MOhm, R2=18MOhm, RD=3kOhm, Rs=0.82kOhm E-MOSFET (2N4351): VGS(Th)=VT=5V, ID(on)=3mA, VGS(on)=10V VGSQ=12.5V, IDQ=6.7mA Load Line for n-channel E-MOSFET DC bias Feedback bias (Single Source) Example for n-channel E-MOSFET DC bias Feedback bias (Single Source) Specification Sheet Copyright ©2002 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. VMOS VMOS – Vertical MOSFET increases the surface area of the device. Advantage: • This allows the device to handle higher currents by providing it more surface area to dissipate the heat. • VMOSs also have faster switching times. Copyright ©2002 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. CMOS CMOS – Complementary MOSFET p-channel and n-channel MOSFET on the same substrate. Advantage: • Useful in logic circuit designs • Higher input impedance • Faster switching speeds • Lower operating power levels Copyright ©2002 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. CMOS N-MOS P-MOS From device to system SYSTEM MODULE + GATE CIRCUIT DEVICE G S n+ Figure 1.5 D n+ Application of CMOS Microprocessor Transistor Counts 1 Billion Transistors K 1,000,000 100,000 10,000 1,000 i486 i386 80286 100 10 Pentium® III Pentium® II Pentium® Pro Pentium® 8086 Source: Intel 1 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 Projected Figure 1.1 Courtesy, Intel Application of CMOS 1970: Fairchild introduces 256-bit Static RAMs 1970: Intel starts selling1K-bit Dynamic RAMs Fairchild 4100 256-bit SRAM Intel 1103 1K-bit DRAM Memory trends Figure 1.2