* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 10. Interventions for clients with renal and urinary problems
Intersex medical interventions wikipedia , lookup
Interstitial cystitis wikipedia , lookup
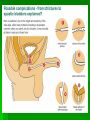
Kidney stone disease wikipedia , lookup
Kidney transplantation wikipedia , lookup
Urinary tract infection wikipedia , lookup
Urethroplasty wikipedia , lookup
Renal angina wikipedia , lookup
Chronic kidney disease wikipedia , lookup
IgA nephropathy wikipedia , lookup
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease wikipedia , lookup
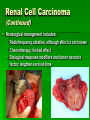
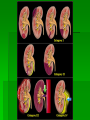
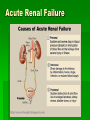
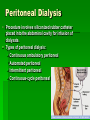
Interventions for Clients with Renal Disorders Pyelonephritis Bacterial infection in the kidney (upper urinary tract) Key features include: Fever, chills, tachycardia, and tachypnea Flank, back, or loin pain Abdominal discomfort Turning, nausea and vomiting, urgency, frequency, nocturia General malaise or fatigue Key Features of Chronic Pyelonephritis Hypertension Inability to conserve sodium Decreased concentrating ability Tendency to develop hyperkalemia and acidosis Acute Pain Interventions Pain management interventions Lithotripsy Percutaneous ultrasonic pyelolithotomy Diet therapy Drug therapy Antibiotics Urinary antiseptics Surgical Management Preoperative care Antibiotics Client education Operative procedure: pyelolithotomy, nephrectomy, ureteral diversion, ureter reimplantaton Postoperative care for urologic surgery Renal Abscess A collection of fluid and cells caused by an inflammatory response to bacteria Manifestations: fever, flank pain, general malaise Drainage by surgical incision or needle aspiration Broad-spectrum antibiotics Renal Tuberculosis Diagnosis Antitubercular therapy with rifampin, isoniazid, and pyrazinamide Complications renal failure, kidney stones, obstruction, and bacterial superinfection of the urinary tract Surgical excision possible Acute Glomerulonephritis Assessment Management of infection Prevention of complications Diuretics Sodium, water, potassium, and protein restrictions Dialysis, plasmapheresis Client education Chronic Glomerulonephritis Develops over a period of 20 to 30 years or longer Assessment Interventions include: Slowing the progression of the disease and preventing complications Diet changes Chronic Glomerulonephritis (Continued) Fluid intake Drug therapy Dialysis, transplantation Nephrotic Syndrome Nephrosclerosis Renovascular Disease Diabetic Nephropathy Cysts and Benign Tumors Renal Cell Carcinoma Paraneoplastic syndromes include anemia, erythrocytosis, hypercalcemia, liver dysfunction, hormonal effects, increased sedimentation rate, and hypertension. (Continued) Renal Cell Carcinoma (Continued) Nonsurgical management includes: Radiofrequency ablation, although effect is not known Chemotherapy: limited effect Biological response modifiers and tumor necrosis factor: lengthen survival time Renal Trauma Minor injuries such as contusions, small lacerations Major injuries such as lacerations to the cortex, medulla, or branches of the renal artery Collaborative management Nonsurgical management: drug therapy and fluid therapy Surgical management: nephrectomy or partial nephrectomy Polycystic Kidney Disease Inherited disorder in which fluid-filled cysts develop in the nephrons Key features include: Abdominal or flank pain Hypertension Nocturia Increased abdominal girth Polycystic Kidney Disease (Continued) Constipation Bloody or cloudy urine Kidney stones Hydronephrosis, Hydroureter, and Urethral Stricture Provide privacy for elimination. Conduct Credé maneuver as necessary. Apply double-voiding technique. Apply urinary catheter as appropriate. Monitor degree of bladder distention. (Continued Hydronephrosis, Hydroureter, and Urethral Stricture (Continued) Catheterize for residual. Intermittently catheterize as appropriate. Follow infection protection measures. Nephrostomy Client preparation Procedure Follow-up care including: Assess for amount of drainage. type of urinary damage expected. manifestations of infection. Monitor nephrostomy site for leaking urine. Interventions for Clients with Acute and Chronic Renal Failure Acute Renal Failure Phases of Acute Renal Failure Phases of rapid decrease in renal function lead to the collection of metabolic wastes in the body. Phases include: Onset Diuretic Oliguric Recovery Acute syndrome may be reversible with prompt intervention. Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy Standard treatment Dialysate solution Vascular access Continuous arteriovenous hemofiltration Continuous venovenous hemofiltration Chronic Renal Failure Stages of Chronic Renal Failure Diminished renal reserve Renal insufficiency End-stage renal disease Clinical Manifestations Neurologic Cardiovascular Respiratory Hematologic Gastrointestinal Urinary Skin Hemodialysis Client selection Dialysis settings Works using passive transfer of toxins by diffusion Anticoagulation needed, usually heparin treatment Peritoneal Dialysis Procedure involves siliconized rubber catheter placed into the abdominal cavity for infusion of dialysate. Types of peritoneal dialysis: Continuous ambulatory peritoneal Automated peritoneal Intermittent peritoneal Continuous-cycle peritoneal Complications Peritonitis Pain Exit site and tunnel infections Poor dialysate flow Dialysate leakage Other complications Nursing Care During Peritoneal Dialysis Before treating, evaluate baseline vital signs, weight, and laboratory tests. Continually monitor the client for respiratory distress, pain, and discomfort. Monitor prescribed dwell time and initiate outflow. Observe the outflow amount and pattern of fluid. Renal Transplantation Candidate selection criteria Donors Preoperative care Immunologic studies Surgical team Operative procedure