* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PowerPoint – Elec L9 – V I Graphs
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
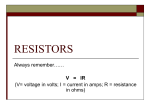
ELECTRICITY VOLTAGE CURRENT GRAPHS B Attention Grade A Lesson time (mins) D E Stress How much energy I have Revision time (hours) Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Your love of Science What conclusions can make from the information given below? C No. of Science lessons F Axes not labelled so no relationship shown Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun B Attention Grade A Revision time (hours) Lesson time (mins) Your love of Science Why do we use graphs? What’s the point? C No. of Science lessons To visualise information to help identify trends and relationships. Graph A – As revision time goes up, grade goes up. Graph B – As lesson time increases, pupil attention decreases. Graph C – The more science lessons you have, there is no change in your love of Science. THESE GRAPHS ARE JUST FOR EXAMPLES, I KNOW YOU LOVE SCIENCE MORE AND MORE AS I TEACH IT! RELATIONSHIPS DISPLAYED ON GRAPHS What general trends do these graphs show? Positive correlation Negative correlation No correlation As A increase, B increase As A increases, B decreases No relationship, data spread GRAPH VOCABULARLY UP RISE, INCREASE, GROW DOWN FALL, DEACREASE,DROP, DECLINE NO CHANGE CONSTANT.STABLE, STAY THE SAME FREQUENT CHANGE FLUCTUATE, VARY AT THE TOP PEAK, HIGHEST POINT/VALUE AT THE BOTTOM LOW/LOWEST POINT DATA ANALYSIS You should have data for each different component (filament bulb, diode and fixed resistor). Using this data you now need to draw a graph for each component. Plot current against voltage to produce and I-V characteristic graph Our axes look like this I Use a ruler! V I–V GRAPH FOR A FILAMENT BULB I V The resistance of a bulb increases as the temperature of the metal Discuss the trend of the graph and try to describe it in filament increases. The ions in the metal vibrate more as temperature your book and explain become constant increases. Thiswhy resistscurrent the flowmay electrons. RESISTANCE OF AN RESISTOR I V Ohm’s law The current resistorand at a constant temperature Discuss theflowing trendthrough of theagraph try to describe it inis directly proportional to the potential your book. difference across it. I-V GRAPH FOR A DIODE Explain the trend of the graph for a diode. (What does a diode do?) A diode only lets current flow in one direction I V In the forward direction the line curves towards the current axis, the current is able to flow but isn’t directly proportional to potential difference. In backwards direction the resistance is very high so current cannot flow so the line is flat. CURRENT-VOLTAGE GRAPHS SUMMARY I I Bulb V Resistor V I V Diode You need to be able to recognise each of these THERMISTOR A thermistor is a component which changes resistance due to temperature. As the temperature increases a thermistors resistance decreases. Resistance (Ω) What might a thermistor be useful for? Temperature (oC) Draw a general graph trend to show how resistance of a thermistor will change as the temperature increases. LDR – LIGHT DEPENDENT RESISTOR An LDR is a component which changes its resistance due to intensity of light. As the light intensity increases an LDRs resistance decreases. Resistance (Ω) What might an LDR be useful for? Light intensity (Lux) Draw a general graph trend to show how resistance of an LDR will change as the light intensity increases.