* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 14.1 History of the Solar System
De revolutionibus orbium coelestium wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Circumstellar habitable zone wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Planetary system wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
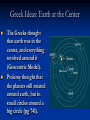
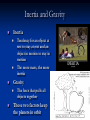
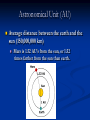
14-1 History of Solar System Study Wandering Stars Greeks called the stars that “wandered” planets, Greek for wandering star. Greek Ideas: Earth at the Center The Greeks thought that earth was in the center, and everything revolved around it (Geocentric Model). Ptolemy thought that the planets still rotated around earth, but in small circles around a big circle (pg 741). Copernicus’s Idea: Sun in the Center Heliocentric – The sun in the center, planets revolve around it. This is correct Galileo’s Observations Noticed moons around Jupiter Venus goes through similar phases as the moon Brahe and Kepler Discovered that the orbit of planets are ellipses (ovals) Inertia and Gravity Inertia Gravity Tendency for an object at rest to stay at rest and an object in motion to stay in motion The more mass, the more inertia The force that pulls all objects together These two factors keep the planets in orbit Astronomical Unit (AU) Average distance between the earth and the sun (150,000,000 km) Mars is 1.52 AU’s from the sun, or 1.52 times farther from the sun than earth.