* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology 30 Notes October 8 - Endocrine System Pituitary Gland
Survey
Document related concepts
Hormonal breast enhancement wikipedia , lookup
Vasopressin wikipedia , lookup
Gynecomastia wikipedia , lookup
Sex reassignment therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (female-to-male) wikipedia , lookup
Signs and symptoms of Graves' disease wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Hypothyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Kallmann syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
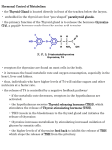
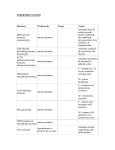
Biology 30 Notes – October 8, 2014 Endocrine System – Pituitary Gland Review Ear – Game http://www.purposegames.com/game/705 Finish notes from yesterday. Review Hormones produced and released by the Anterior Pituitary Gland. Video – The Pituitary Gland https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qJj_-3dZ4ZQ Hormones Produced and Released by the Anterior Pituitary - CONTINUED TSH – Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Is produced and released by the anterior pituitary. It causes the thyroid gland to secrete thyroxine (T4). The role of thyroxine is to increase the rate at which the body metabolizes fats, proteins, and carbohydrates for energy. The thyroid gland lies directly below the larynx (voice box) and has two lobes one on either side of trachea (windpipe). Thyroxine is controlled by a negative feedback loop. 1) The anterior pituitary releases TSH, thyroid stimulating hormone. 2) This causes the thyroid to secrete thyroxine. 3) When thyroxine levels in the blood increase it feeds back to the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary. 4) TSH secretion is suppressed which supresses thyroxine. Hypothryroidism – extremely low amounts of thyroxine, adults feel tires, slow pulse, weight gain, and hair lose. Hyperthyroidism – over production of thyroxine, stimulate metabolism, releases energy as ATP. Symptoms include anxiety, insomnia, weight lost, irregular heartbeat. ACTH – Adrenocorticotropic Hormone Hormone synthesized by the anterior pituitary gland to target the adrenal cortex and regulate the production of glucocorticoids. FSH – Follicle Stimulating Hormone Reproductive hormone produced by the anterior pituitary that stimulates the development of the sex organs and gamete (haploid reproductive cell egg (ovum) and sperm) production in males and females. LH – Luteinizing Hormone Reproductive hormone produced by the anterior pituitary. In the ovaries it triggers ovulation, stimulates the formation of the corpus luteum, and with FSH stimulates estrogen production. FYI – Need to know this for the next unit REPRODUCTION Ovulation – in females the process by which a single follicle in an ovary matures and then ruptures, releasing the ovum (egg) into the oviduct, usually occurs at the midpoint (day 14) of a 28-day menstrual cycle. Corpus Luteum – yellowish gland like structure that develops from a follicle that has matured and released its egg (ovum), it produces progesterone and some estrogen, if pregnancy doesn’t occur it degenerates. In the testes, stimulates the release of testosterone. PRL - Prolactin Stimulates milk production from the mammary glands. Gland Hypothalamus Hormone Hypothalamic releasing and inhibiting hormones Anterior Pituitary hGH – human growth hormone TSH – thyroid stimulating hormone ACTH – adrenocorticotropic hormone FSH – follicle stimulating hormone LH – luteinizing hormone PRL – prolactin Effect on Target Regulates anterior pituitary hormones. - - - - - Posterior Pituitary ADH – antidiuretic hormone OCT – oxytocin - Thyroid Thyroxine (T4) Calcitonin - - Stimulates cell division, bone, muscle growth, and metabolic functions Stimulates the thyroid glands Stimulates the adrenal cortex to secrete glucocorticoids Stimulates the production of ova and sperm Stimulates sex hormone production from the ovaries and testes Stimulates milk production from the mammary glands Promotes the retention of water by the kidneys Stimulates uterine muscle contraction and release of milk by the mammary glands Affect all tissues, increases metabolic rate and regulates growth and development. Targets bones and kidneys to lower blood calcium by inhibiting release of calcium from bone and reabsorption of calcium by the kidneys.