* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download an artificial key to the common aquatic invertebrates of university bay
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
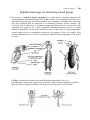
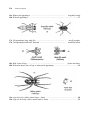
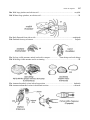
208 Pickle Jar Aquaria APPENDIX B An Artificial Key to the Common Aquatic Invertebrates of University Bay (Note that Welsch, 1992 is an excellent booklet for identifying aquatic plants) AN ARTIFICIAL KEY TO THE COMMON AQUATIC INVERTEBRATES OF UNIVERSITY BAY Prepared for the Biology Core Curriculum by Kandis Elliot and James W. A. Jaeger, 1991 Pickle Jar Aquaria 209 Helpful terminology for identifying animal groups 1. The presence of branched, jointed appendages is a major feature separating arthropods, the largest phylum in the animal kingdom, from all other groups. These appendages refer not only to legs and leg-like structures, but also to antennae, tails, mouthparts, and many other organs that have been modified from an embryonic or evolutionarily primitive leg-like structure. The "branches" may be easily seen, as in daphnia antennae and the uropods of a crayfish tail, or the appendage may appear to be a single, apparently unbranched structure such as a crayfish antenna. Unfortunately for the novice taxonomist, some juvenile forms of "jointed-appendage" animals appear to have no appendages whatsoever- the maggots of flies, for example. Most immature arthropods, however, have very distinctive branched, jointed appendages of all shapes and sizes. 2. Wings of invertebrate animals are not modified jointed appendages. They are a developmentally separate and unique feature, and help to further separate subgroups of animals. Many juveniles of winged invertebrates will possess small wing pads of various shapes. 210 Pickle Jar Aquaria 3. Tentacles are taxomically distinct from whiplike forms of jointed appendages like crayfish antennae. Tentacles are fleshy structures without hardened internal or external supports and are highly mobile and contractile. They are almost always placed around an animal's mouth and used for food gathering. Tentacles are found in many unrelated groups of animals, from tiny bryozoans to giant squids. 4. As used in this key, a shell refers to a hard, permanent, protective case excreted by an animal's body. True shells are distinct from exoskeletons and carapaces, which are shed periodically, and from cases which are constructed by the animal from sand grains, bits of leaf, or other materials. Shells may be either hinged (thus appearing to be two separate halves) or a single unit. We are familiar with the shells of clams, snails, and other mollusks, but ostracods and conchostracans, which are relatives of shrimp and lobsters, also grow very shell-like, modified exoskeletons called carapaces. Pickle Jar Aquaria 211 5. Nymphs, larvae and naiads are terms referring to juvenile forms of various invertebrates. Nymphs resemble the adult form and are easily identifiable. Aquatic insects with nymphs are mayflies, and bugs such as water-boatmen, backswimmers and water-striders. Larvae, on the other hand, look very different from the adult animals and are notoriously difficult to identify. For example, the larvae of crane flies and mosquitoes are legless maggots; larvae of aquatic beetles and alderflies are often fleshy and wormlike, with small legs, huge mandibles, or rows of elaborate abdominal gills. The various stages of development of larvae are called instars. Naiad refers specifically to the juvenile stages of dragonflies and damselflies. Nauplii refer to juvenile forms of some crustaceans. 212 Pickle Jar Aquaria 1a. Body without visible segments, no jointed appendages .............................................................. 2 1b. Body with visible segments, appendages may be present ........................................................... 7 2a. Animal with a shell ...................................................................................................................... 3 2b. Animal without a shell................................................................................................................. 4 3a. Shell single....................................................................................................................... 3b. Shell double ..................................................................................................................... snails clams 4a. Body asymmetrical .......................................................................... sponges and moss animals 4b. Body symmetrical........................................................................................................................ 5 5a. Radial symmetry .............................................................................................................. hydras 5b. Bilateral symmetry ...................................................................................................................... 6 Pickle Jar Aquaria 213 6a. Flattened; swim with gliding motion......................................................................... flatworms 6b. Cylindrical; swim with wiggling motion................................................................... roundworms 7a. Without obvious jointed legs (fleshy prolegs may be present) ................................................... 8 7b. With obvious jointed legs ...........................................................................................................11 8a. With front and rear suckers ............................................................................................. leeches 8b. Without suckers .......................................................................................................................... 9 9a. Without obvious appendages (may be shell) ........................ mosquito larvae and midge larvae 9b. Without obvious appendages or fleshy prolegs...........................................................................10 214 Pickle Jar Aquaria 10a. Transparent with front and rear air sacs ........................................ phantom midge larvae 10b. Not transparent, no air sacs ............................... freshwater earthworms and cranefly larvae 11a. With 3 pairs of jointed legs........................................................................................................12 11b. With more than 3 pairs of jointed legs ......................................................................................18 10b. No trace of wings.......................................................................................................................13 10b. With external wings or wing pads .............................................................................................14 13a. Living in external case ............................................................................... 13b. Free living, no case .................................................................................... caddisfly larvae beetle larvae 14a. With fully developed wings.......................................................................................................15 14b. With wing pads or shortened wings ..........................................................................................16 Pickle Jar Aquaria 15a. Front pair of wings fully hardened; chewing mouthparts ............................................. 15b. Front pair of wings partially hardened; piercing mouthparts ....................................... 215 beetles bugs 216 Pickle Jar Aquaria 16a. Without tail appendages ............................................................................ dragonfly naiads 16b. With tail appendages ...............................................................................................................17 17a. Tail appendages long, whip-like ................................................................ 17b. Tail appendages blade-like, flattened ......................................................... mayfly nymphs damselfly naiads 18a. With 4 pairs of legs .................................................................................... spiders and mites 18b. With more than 4 pairs of legs or other paired appendages ....................................................19 19a. Legs obviously visible; animal large (> 5mm) ........................................................................20 19b. Legs not obviously visible; animal small (< 5mm) .................................................................22 Pickle Jar Aquaria 217 20a. With large pinchers and obvious tail ............................................................................ crayfish 29b. Without large pinchers; no obvious tail..................................................................................... 21 21a. Body flattened from side to side ...................................................................................amphipods 21b. flattened from top to bottom ......................................................................................... isopods 22a. No long visible antenna, animal enclosed in carapace ............... clam shrimp and seed shrimp 22b. With long visible antenna used in swimming............................................................................ 23 23a. Antenna branched, swims in head up position ............................................................. daphnids 23b. Antenna unbranched, swims in horizontal position ..................................................... copepods