* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download geometry lesson
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
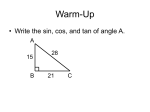
Geometry Lesson Teacher’s name: ___Cara Pruiett_________________ Subject: Geometry Date: __November 18, 2008 ___ Grade Level: __9-12 _Topic: _Trigonometric Functions_ Essential Questions/Big Ideas: How can trigonometric functions be used to determine lengths of sides and angle measures of a right triangle? Learning Objectives: VA SOL: Standard G.7 The student will solve practical problems involving right triangles by using the Pythagorean Theorem, properties of special right triangles, and right triangle trigonometry. Solutions will be expressed in radical form or as decimal approximations. NCTM: In grades 9-12 all students should Use trigonometric relationships to determine lengths and angle measures. Students will understand: The relationship between the sides and angles of a right triangle can be represented using trigonometric functions. The relationship between the sides and angles of a right triangle can be useful in many real-world situations. Students will know: Trigonometric functions: Sine, Cosine, Tangent How to use these functions on a graphing calculator Acronym to remember trigonometric functions: SOH CAH TOA Students will be able to: Given a side and an angle of a right triangle, use trigonometric functions to find the remaining sides and angle Given two sides of a right triangle, use trigonometric functions to find the remaining side and angles Student and Teacher Activities with Estimated Time Blocks: 1. Hook: Draw a right triangle on the board with only one given side and one given angle. Ask the students to determine if and how they can find the two unknown sides and the unknown angle. Write their answers on the board, and discuss each answer as a class to determine why they will or will not work. (At this point the students have only used the 1. The students will discuss with the students around them how they think they could find the unknown sides and unknown angles of a right triangle drawn on the board. They will give their answers to the teacher to be written on the board and then discussed as a class. Answer the questions asked by the teacher when called upon. Pythagorean Theorem to find missing sides of triangles. They should realize that they will have difficulty finding a missing side when they are only given one side of the triangle. They will also realize that they can only find missing angles when given two of the angles in a triangle.) Ask the students if they will need to find another method to find unknown sides and angles in these special cases. (15 minutes) What are the different methods we have so far that can help us find unknown sides and angles of a right triangle? (Knowledge) Do we need another way to find unknown sides and angles of right triangles? (Evaluate) 2. Introduce students to sine, cosine, and tangent using a right triangle. Explain the abbreviations for these trigonometric functions (sin, cos, and tan), how they are pronounced (not pronounced literally, still use the actual terms sine, cosine, and tangent when reading them), how they can be used (only on right triangles!!), and how to find their functions on a graphing calculator. Ask the students to recall what the parts of a right triangle are called according to a given angle (opposite side, adjacent side, and hypotenuse). (10 minutes) What are the different parts of a right triangle called? (Knowledge) 3. Show students the acronym SOH CAH TOA, what each letter stands for (sine, opposite, hypotenuse, cosine, adjacent, hypotenuse, tangent, opposite, adjacent), and what it means (sin(x)=opp/hyp, cos(x)=adj/hyp, tan(x)=opp/adj, where x is an angle measure.) (Can also suggest the acronym: Some Officers Have Curly Auburn Hair Till Old Age and let them decide which one is easier for them to remember.) Do an example problem on the board of how to use each of the three trigonometric functions on a right triangle. Show the students how to perform the appropriate calculations on a graphing calculator to complete the problem. In review, ask the students to explain what 2. The students will take notes on their own paper and ask questions if they need clarification. They will practice finding the trigonometric functions on their own graphing calculators. Answer the questions the teacher asks when called upon. 3. The students will take notes on their own paper and ask questions if they need clarification. They will follow along on the example problems as the teacher shows them the solutions. They will also practice using their graphing calculators to find the solutions. The students will answer the questions asked of them by the teacher. unknown values can be found using these trigonometric functions (angles, hypotenuse, adjacent, and opposite sides.) Ask the students how they could use these functions to solve real-world problems in professions other than mathematics (architecture, landscaping, engineering, etc.) (10 minutes) What unknown values can be found using these trigonometric functions? (Analysis) How might these functions be used to solve real-world problems in other professions? (Evaluate) 4. Ask students to discuss how the trigonometric functions explain the relationship between sides and angles of a right triangle (the functions express the sides of a triangle as ratios as compared to the angles.) Write their answers on the board. Check for student understanding before moving on; go over the main ideas again if necessary or show them another example problem. Give students a worksheet of multiple problems involving various trigonometric functions and have them work in pairs to complete the worksheet. Post an answer key at the front of the room for students to use to check their answers when they are done. Walk around the room and answer any questions that students may have. (45 minutes) How do the trigonometric functions explain the relationship between sides and angles in right triangles? (Synthesis) 5. Closure: When the students finish their worksheets, collect them and grade them. Give students the following exit slip before the end of class. (10 minutes) Exit Slip (Formative assessment): What are the three trigonometric functions? What is the acronym we use to remember how to use them? Given a triangle with one angle measure of 30 degrees, one of 90 degrees, and a hypotenuse of length 7, find the lengths of the two missing sides and the missing angle. 4. The students will discuss trigonometric functions and how they explain the relationship between sides and angles in right triangles. They will tell the teacher their answers to be written on the board. The students will let the teacher know if they are unclear on anything they have learned so far in the lesson. The students will then complete a worksheet with a partner and check their answers with the answer sheet posted at the front of the room when they are done. 5. The students will turn in their worksheets and then complete an exit slip before the end of class. Materials Needed for the Lesson: Worksheet Graphing Calculators Resources: http://www.sosmath.com/trig/Trig2/trig2/trig2.html http://www.intmath.com/Trigonometric-functions/Trig-functions-intro.php