* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Animal Evolution
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
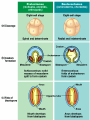
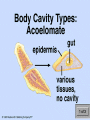
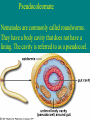
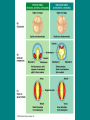
DO NOW • Juniors – tell Mrs. Strickhart what you are taking for science next year •• What is an Animal? Questions! • 1. What are the characteristics of animals? • 2. How do protostomes differ from deuterstomes? • What is the ancestral protistan of animals? • What are the two major groups based on “tissues”? • What are the two types of symmetry? More things to write! • • • • • Describe the three types of body cavities. Describe a blastula. Describe a Blasopore What are Lophotrochozoans? What are Ecdysozans? Animal Characteristics • ingestion – eating other organisms or decomposed material • cell structure – lack of cell wall, form collagen in the ECM, tight junctions, desmosomes, gap junctions • unique tissues – muscle and nervous tissues for movement Parazoa - Eumetazoa • Parazoa – no tissues • Eumetazoa – true tissues Radiata - Bilateria • Radially symmetrical • Bilateral • Bilateral Symmetry • If split in two, two mirror images result • Cephalization - nerves and sensory organs concentrated toward the head end – evolved to help organisms locate food Acoelomate, Pseudocoelomate, and Coelomate • A = without a body cavity • Pseudo = false body cavity, not completely lined • Coelomate = body cavity lined, fluid filled Pseudocoleomate Nematodes are commonly called roundworms. They have a body cavity that does not have a lining. The cavity is referred to as a pseudocoel. The blastula is a hollow ball of cells that forms in early embryonic development. Some cells migrate upward into the blastula to form a blastopore. This opening eventually forms the mouth of animals called protostomes. If the opening does not form the mouth, but instead forms the anus, the animals are deuterostomes. Deuterstome vs Protostome Do It NOW!!!! Quiz Today you will be dissecting two invertebrates and earthworm and a grasshopper. Using your animal clad, answer the following. 1. Are these two animals Parazoans or Eumetazoans? What does that mean? 2. Are these two animals part of Radiata or Bilateria? What does that mean? 3. Are these animals Protostomes or Deuterostomes? What does that mean? 4. Which animal is a Lophotrochozoan? What does that mean? 5. Which animal is a Ectyzoan? What does that mean? Do It NOW!!!! Quiz Today you will be dissecting two invertebrates and earthworm and a grasshopper. Using your animal clad, answer the following. 1. Are these two animals Parazoans or Eumetazoans? What does that mean? 2. Are these two animals part of Radiata or Bilateria? What does that mean? 3. Are these animals Protostomes or Deuterostomes? What does that mean? 4. Which animal is a Lophotrochozoan? What does that mean? 5. Which animal is a Ectyzoan? What does that mean? The Lophotrochozoa comprise one of the major groups within the animal kingdom, In turn, the Lophotrochozoa belongs to a larger group within the Animalia called the Bilateria, because they are bilaterally symmetrical with a left and a right side to their bodies. Lophotrochozoans • Grouped together because of the molecular evidence • Trocho = development of trochophore larvae • Lophophore = horseshoe shaped crown of ciliated tentacles •• Ecdysozoa • Separated into the clad via molecular data • Morphologically – produce exoskeletons therefore growth must occur via molting