* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download TheEar
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Auditory processing disorder wikipedia , lookup
Sound localization wikipedia , lookup
Audiology and hearing health professionals in developed and developing countries wikipedia , lookup
Noise-induced hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Otitis media wikipedia , lookup
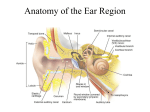
SENSORY ORGANS (VISION, HEARING, AND EQUILIBRIUM) Ears HEARING How old are your ears? ASAP Science Hearing Test Discovery: How Hearing Works Process of Hearing: Animation ** Organ of Corti 2.) Ears a. External ear (1) Auricle (a.k.a. pinna) collects sound waves (2) External auditory meatus – S shaped tube in temporal bone, approx 2.5 cm b. Middle ear (1) Tympanic cavity – air filled space in temporal bone (2) Tympanic membrane (eardrum) (a) Outer surface: thin layer of skin; inner: mucous membrane (b) Vibrates from sound waves THE EAR (3) Auditory ossicles (3) (a) Hammer (malleus), anvil (incus), stirrup (stapes) (b) Bridge from the eardrum to inner ear – transmit vibrations from eardrum to fluid of inner ear (c) Stapes – transmits vibrations to fluid in oval window of inner ear, causing fluid to vibrate (d) Also amplify vibrations (large SA of eardrum to smaller SA of oval window leads to increased vibration force & pressure) THE EAR (4) Eustachian tubes-connect middle ear to nasopharynx aka pharyngotympanic (auditory) tubes (a) Equalize air pressure on inside of eardrum (b) Allow bacteria & infections to travel to ear from nose are c. Inner ear-complex system of intercommunicating chambers & tubes-a.k.a. labyrinths (2) (1) Osseous labyrinth-bony canal in temporal bone (2) Membranous labyrinth-tube inside osseous labyrinth (has same shape) LABYRINTHS (a) Endolymph-fluid inside membranous labyrinth (b) Perilymph-fluid between the two labyrinths (3) Parts of labyrinths (a) Cochlea-bony core & thin bony self (threads on a screw) i. Shelf divides bony labyrinth into 2 compartments: • Upper: scala vestibuli (oval window leads to scala vestibuli) • Lower: scala tympani (leads to round window) ii. Cochlear duct: membranous labyrinth between the scala vestibuli & scala tympani; houses the organ of Corti iii. Vestibular membrane-separates the cochlear duct from the scala vestibuli iv. Basilar membrane-separates the cochlear duct from the scala tympani v. Organ of Corti • [a] contains hearing receptors called hair cells • [b] on upper surface of basilar membrane • [c] covered by tectorial membrane • [d] best frequency perception: 2-3 thousand cycles per second (cps) (b) semicircular canals-equilibrium (c) vestibule-bony chamber between cochlea & semicircular canals; for hearing & equilibrium d. Auditory nerve pathway (1) auditory nerve to temporal lobes (cochlear nerve to medulla to midbrain to thalamus to auditory cortex in temporal lobes) (2) some fibers cross over to other side (not all); so impulses are interpreted by both sides of brain e. sense of equilibrium-two parts (sense of static & dynamic equilibrium) (1) static equilibrium-maintains stability of head & body when they’re motionless (a) organs of static equilibrium located in vestibule (between cochlea & semicircular canals) (b) membranous labyrinth inside vestibule expands into 2 chambers: the utricle & the saccule (c) macula-small patch of hair cells in saccule and anterior wall of utricle i. hair cells and supporting cells ii. Hair cells project into a gelatinous mass studded with otoliths (CaCO3 crystals) iii. Otoliths in mass of material increase inertia (resistance to change in motion) iv. Bending hair cells leads to sending of impulses informing brain of head’s position (2) dynamic equilibrium-balance during movement (a) three semicircular canals (at right angles & in different planes) detect motion (b) Ampullae-swelling on ends of semicircular canals where they join the vestibule (c) crista ampularris-sensory organs in ampullae i. sensory cells & supportive cells ii. Hairs extend upward into gelatinous mass called the cupula iii. Respond to changes in acceleration & deceleration iv. Impulses sent to cerebellum for analysisactivate muscles to maintain balance LABYRINTHS