* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Red Eye
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
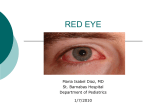
The Red Eye Dr Mahmood Fauzi ASSIST PROF OPHTHALMOLOGY AL MAAREFA COLLEGE Objectives • Define red eye • Record history taking in red eye case • State common symptoms and signs in red eye • Describe physical exam in red eye • Enlist differential diagnoses of red eye • Outline red eye management by primary care physicians • Summarize some important drug induced side effects in red eye What is “RED EYE” • Red Eye is a non-specific term. • Usually refers to injection and prominence of the superficial blood vessels of the conjunctiva, or sclera, which may be caused by disorders of these or adjacent structures. • Slit lamp Examination is Invaluable in diagnosis but initial assessment can be performed using a careful history, testing vision (visual acuity), and carrying out a penlight examination. Differential diagnosis of red eye • Conjunctival • Blepharoconjunctivitis • Bacterial conjunctivitis • Viral conjunctivitis • Chlamydial conjunctivitis • Allergic conjunctivitis • Toxic/chemical reaction • Dry eye • Pinguecula/pteyrgium • Subconjunctival hemorrhage • Lid diseases • Clalazion • Sty • Secondary to Abnormal lid function • Corneal disease • Abrasion • Ulcer • keratitis • Foreign body • Trauma Adnexal Disease • • • • • • • Dacryoadenitis Dacryocystitis Carotid and dural fistula Acute angle glaucoma Anterior uveitis Episcleritis/scleritis Factitious History Onset? Sudden? Progressive? Constant? Family/friends with red eye? Using meds in eye? Trauma? Recent eye surgery? Contact lens wearer? Recent URTI? Decreased VA? Pain? Discharge? Itching? Photophobia? Eye rubbing? Other symptoms? Red Eye: Symptoms Decreased VA (Inflamed cornea, Iridocyclitis, Acute glaucoma) Pain (keratitis, Ulcer, Iridocyclitis, Acute Glaucoma) Photophobia (Iritis Conjunctivitis) Colored halos (Acute Glaucoma) Discharge (Conj. or lid inflammation, corneal ulcer) Purulent/mucopurulent: Bacterial Watery: Viral Scant, white, stringy: allergy, dry eyes Itching (allergy) Physical Exam Vision Pupil asymmetry or irregularity Inspect: pattern of redness (heme, injection, ciliary flush) Amount & type of discharge Corneal opacities or irregularities AC shallow? Hypopyon? Hyphema? Fluorescein staining IOP Proptosis? Lid abnormality? Limitation EOM? Red Eye: Signs Ciliary flush (corneal inflammation, iridocyclitis, acute glaucoma) Conjuctival hyperemia (nonspecific sign) Corneal opacification (iritis, corneal edema, acute glaucoma, keratitis,ulcer) Corneal epithelial disruption (corneal inflammation, abrasion) Pupil abnormality (iridocyclitis, acute glaucoma) Shallow AC (acute angle closure glaucoma) Elevated IOP (iritis, acute glaucoma) Proptosis (thyroid disease, orbital or cavernous sinus mass, infection) Preauricular LN (viral conjunctivitis, Parinaud’s oculoglandular syndrome) Blepharitis • • • • • Adults > children Inflammation of the lid margin Frequently associated with styes Meibomian gland dysfunction Lid hygiene, topical antibiotics, and lubricants are the mainstays of treatment Bacterial Conjunctivitis • • • • • Both adults and children Tearing, foreign body sensation, burning, stinging and photophobia Mucopurulent or purulent discharge Lid and conjunctiva maybe edematous Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and staphylococcus aureus and epidermidis • Conjunctival swab for culture • Topical broad spectrum antibiotics Viral Conjunctivitis • Acute, watery red eye with soreness, foreign body sensation and photophobia • Conjunctiva is often intensely hyperaemic and there maybe follicles, haemorrhages, inflammatory membranes and a preauricular node • The most common cause is an adenoviral infection • No specific therapy but cold compresses are helpful. Allergic Conjunctivitis • Encompasses a spectrum of clinical condition • All associated with the hallmark symptom of itching • There is often a history of rhinitis, asthma and family history of atopy • Signs may include mildly red eyes, watery discharge, chemosis, papillary hypertrophy and giant papillae • Treatment consist of cold compresses, antihistamines, nonsteroidals, mast cells stabilizers, topical corticosteroids and cyclosporine Chlamydial Conjunctivitis • Usually occur in sexually active individuals with or without an associated genital infection • Conjunctivitis usually unilateral with tearing, foreign body sensation, lid crusting, conjunctival discharge and follicles • There is often non-tender preauricular node • Treatments requires oral tetracycline or azithromycin Conjunctivitis Subconjunctival Haemorrhage • Asymptomatic • Diffuse or localised area of blood under conjunctiva. • Idiopathic, trauma, cough, sneezing, aspirin, HT • Resolves within 10-14 days Dry Eye Syndrome • Poor quality • Meibomian gland disease, Acne rosacea • Lid related • Vitamin A deficiency • Poor quantity • KCS • Sjogren Syndrome • Rheumatoid Arthritis • Lacrimal disease ie, Sarcoidosis • Paralytic ie, VII CN palsy Lid Malposition Pterygium Corneal Abrasion • • • • Surface epithelium sloughed off. Stains with fluorescein Usually due to trauma Pain, FB sensation, tearing, red eye Foreign Body Corneal Ulcer • Infection • • • • Bacterial: Adnexal infection, lid malposition, dry eye, CL Viral: HSV, HZO Fungal: Protozoan: Acanthamoeba in CL wearer • Mechanical or trauma • Chemical: Alkali injuries are worse than acid Episcleritis • • • • Superficial Idiopathic, collagen vascular disorder (RA) Asymptomatic, mild pain Self-limiting or topical treatment Scleritis • • • • • • • Deep Idiopathic Collagen vascular disease (RA,AS, SLE, Wegener, PAN) Zoster Sarcoidosis Dull, deep pain wakes patient at night Systemic treatment with NSAI or Prednisolone if severe Uveitis Anterior: Acute Recurrent and Chronic Posterior: Vitritis, Retinal Vasculitis, Retinitis, Choroiditis Panuveitis: Anterior and Posterior Anterior uveitis (iritis) • Photophobia, red eye, decreased vision • Idiopathic. Commonest • Associated to systemic disease • Seronegative arthropathies:AS, IBD, Psoriatic arthritis, Reiter’s • Autoimmune: Sarcoidosis, Behcets • Infection: Shingles, Toxoplasmosis, TB, Syphillis, HIV Posterior synechiae Ciliary flush Fibrin Flare KPs Hypopyon Acute Angle-closure Glaucoma • Symptoms • Pain, headache, nauseavomiting • Redness, photophobia, • Reduced vision • Haloes around lights Ciliary hyperaemia Dilated pupil Corneal oedema Red Eye Treatment Algorithm History Trauma Contact lens wearer Severe pain/photophobia Significant vision changes History of prior ocular diseases Exam - Visual loss Abnormal pupil Ocular tenderness White corneal opacity Increased intraocular pressure YES Refer urgently to ophthalmologist Red eye management Blepharitis: Warm compresses, lid care, Abx ointment or oral (if rosacea or Meibomian gland dysfunction) Stye/Chalazion Warm compresses (refer if still present after 1 month) Subconjuntival hememorrage: Will resolve in 10-14 days Viral conjunctivitis Cool compresses, tears, contact precautions Bacterial conjunctivitis Cool compresses, antibiotic drop/ointment Important drug induced Side Effects Topical anesthetics: Not to be used except for aiding in exam Inhibits growth & healing of corneal epithelium Possible severe allergic reaction Decrease blink reflex: exposure to dehydration, injury, infection Topical corticosteroids: Can potentiate growth of herpes simplex, fungus Can mask symptoms Cataract formation Elevated IOP Test yourself • Red Eye Picture Quiz http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1705668/ Resources • http://www.allaboutvision.com/conditions/red-eyes.htm • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Red_eye_(medicine) • http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/pdf/rr/rr5504.pdf