* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
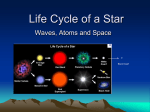
Download How the Universe Works Extreme Stars Name 1. When a star dies
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
History of supernova observation wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Astrophysical X-ray source wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
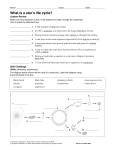
How the Universe Works Extreme Stars Name _______________ 1. When a star dies (gravity) (fusion) wins out. 2. The sun will run out of fuel in about (3) (7) (10) billion years. 3. When the sun runs out of hydrogen fuel, it will become a (red giant) (neutron star) (black hole). 4. Eventually, the helium in the core begins to fuse into (oxygen) (iron) (carbon). 5. After the sun blasts away its outer layers, all that remains is an intensely hot, core called a (planetary nebula) (white dwarf) (pulsar). 6. At the core of a white dwarf astronomers believe lies a core of (iron) (nickel) (carbon). 7. Betelgeuse is (older) (younger) (the same age as) our sun. 8. Betelgeuse is a (white dwarf) (blue giant) (red supergiant). 9. From the moment a massive star creates (iron) (silicon) (gold) it has only seconds to live. 10. The single most violent event in the universe is a (pulsar) (supernova) (quasar). 11. Gold, silver and platinum are all created when (a star explodes) (a black hole forms) (a white dwarf forms). 12. The remnants of a supernova explosion is a super dense core called a (neutron star) (white dwarf) (quasar). 13. A neutron star is about (the size of the sun) (the size of the earth) (twenty miles across). 14. Every atom in your body was formed in a (stellar explosion) (black hole) (main sequence star).