* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PROBLEMS
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
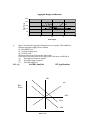
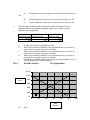
PROBLEMS 1. LO: 3 Illustrate these events with AS or AD shifts: a. Government increases defense spending. b. The Headline story on p. 246. c. Imported raw materials get cheaper. d. Congress cuts corporate income tax. AACSB: Analytic BT: Application ASA ASB Price Level ADA ADB Real Output a. b. c. d. 2. LO: 4 An increase in government spending would shift AD from ADA to ADB. The Headline story on p. 263 would result in a shift from ADB to ADA. A decline in wealth results in shifting AD from ADB to ADA. Imported raw materials are a factor of production and thus affect AS. A decrease in the price of imported raw materials will result in shifting AS from ASA to ASB. A cut in corporate income taxes is a supply side cut and would result in shifting AS from ASA to ASB. Based on the Headline on p. 247: a. Illustrate the AS shift that occurs. b. Identify the old (Eo) and the new (E1) macro equilibrium. c. What macro ailments result? d. How can the economy stay healthy in this case? AACSB: Analytic a. and b. BT: Application Price Level AS2 AS AD E1 c. d. E0 Real Output The macro ailment that results is recession. Government intervention to promote investment will help the economy stay healthy. 3. Graph the following aggregate supply and demand curves (be sure to draw to scale). a. What explains the shape of the AS curve? b. What is the equilibrium price level? c. What is the equilibrium output? d. If the quantity of output demanded at every price level increases by $1 trillion, what happens to equilibrium output and prices? Graph your answer. LO: 3 AACSB: Analytic a. b. c. d. BT: Application An upward sloping AS curve indicates that as the average price level increases output supplied in the economy increases. The equilibrium price level is slightly above P= 110 where aggregate quantity supplied equals aggregate quantity demanded. The equilibrium output level is between 10 and 11 where AS=AD at a common price. If the quantity of output demanded at every price level increase by $1 trillion, the equilibrium output and prices will increase. Aggregate Supply and Demand 250 Real Prices 200 150 AS AD2 AD1 100 50 0 0 5 10 15 20 Real Output 4. Draw a conventional aggregate demand curve on a graph. Then add three different aggregate supply curves, labeled S1: Horizontal curve S2: Upward-sloping curve S3: Vertical curve all intersecting the AD curve at the same point. If AD were to increase (shift to the right), which AS curve would lead to (a) The biggest increase in output? (b.) The largest jump in prices? (c) The least inflation? LO: 1,3 AACSB: Analytic BT: Application ASv ASu Real Prices ASh AD2 AD1 Real GDP ASh 5. (a) The biggest increase in output occurs on the horizontal AS curve, (b) The largest jump in prices occurs on the vertical AS curve, ASv (c) The least inflation would occur on the horizontal AS curve, ASh The following schedule provides information with which to draw both an aggregate demand curve and an aggregate supply curve. Both curves are assumed to be straight lines. Average Price Quantity Demanded Quantity Supplied (dollars per unit) (units per year) (units per year) $1,000 0 1,000 100 900 100 a. b. c. d. e. LO: 4 At what price level does equilibrium occur? What curve would have shifted if a new equilibrium were to occur at an output level of 700 and a price level of $700? What curve would have shifted if a new equilibrium were to occur at an output level of 700 and a price level of $500? What curve would have shifted if a new equilibrium were to occur at an output level of 700 and a price level of $300? Compared to the initial equilibrium (a), how have the outcomes in (b), (c), and (d) changed price levels or output? AACSB: Analytic BT: Application $1,200 AS $1,000 Price Level $800 $600 $400 $200 AD $0 0 (a) $500 200 400 600 Real Output 800 1000 1200 6. LO: 4 (b) AD shifts to the right, raising both prices and output (c) Both AD and AS must shift to the right for this to occur. Prices stay the same and output increases. (d) AS shifts to the right, raising output and lowering prices (e) The answers to part (e) are contained in answers (b) - (d) above. Graph the situation described in the Headline on p. 244. AACSB: Analytic BT: Application Output of Capital Goods A Output of Consumption Goods The Headline describes a macro equilibrium that has left the economy inside its production possibilities curve, as shown here at point A.