* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download FAMILY LIFE
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
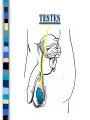
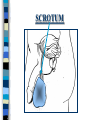
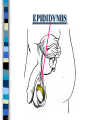
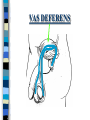
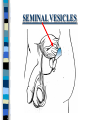
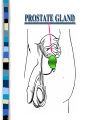
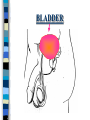
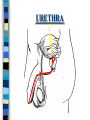
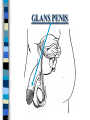
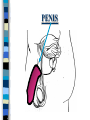
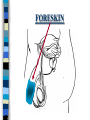
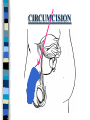
FAMILY LIFE The Male Reproductive Anatomy SPERM The male sex cell. Produced by the testes. The minute cells are released 100-400 million at a time and are mobile. Each sperm has 23 chromosomes. Sperm are produced by a man from puberty until he dies. SEMEN Semen is made up of sperm and seminal fluid. Sperm is made by the testes and is combined with fluid made by the seminal vesicles, cowper’s gland, and the prostate gland. This fluid gives the sperm energy in the form of sugar and also acts as a base to protect the sperm from acids primarily found in the urethra. TESTES The diameter of a teste is about 1 to 1 1/2 inches. Testes produce sperm and testosterone. Each man has two testes. Testes begin to produce sperm and testosterone as soon as puberty begins and continues until death. Testosterone is the male sex hormone Testes are held outside the body cavity by the scrotum. Testicular cancer is generally found in young adults and all men should perform a self-exam monthly. TESTES SCROTUM Holds the testes. External skin sack that holds the testes outside of the body cavity. The scrotum’s job is to regulate the temperature of the testes…too hot and the sperm die…too cold and the sperm cannot be produced fast enough. SCROTUM EPIDIDYMIS Their job is to store the matured sperm (up to 400 million). There are two of them, one on each teste. They are the shape of a “comma”. If the epididymis stores the sperm for too long a time and the sperm die, if the sperm are no longer viable,the body will absorb them as protein. EPIDIDYMIS VAS DEFERENS Tubes leading from each teste to the urethra. There are two of them, one from each teste. Tubes can be cut in an operation called a VASECTOMY. The only thing that travels in them is sperm. VAS DEFERENS VASECTOMY Male sterilization. This operation cuts and plugs the vas deferens, preventing the sperm from ever leaving the male’s body. This operation is NOT 100% effective in preventing pregnancy and provides NO protection against STD’s. Once blocked, the sperm are absorbed by the male’s body as it would absorb any protein. VASECTOMY SEMINAL VESICLES The primary job of the seminal vesicles is to produce the seminal fluid. There are two of them. They are glands and the fluid they produce acts as a BASE. The seminal fluid gives the sperm the necessary sugar for energy to make the sperm mobile. SEMINAL VESICLES COWPER’S GLAND Produces seminal fluid. They are glands that are the size of peas. Releases its’ fluid PRIOR to ejaculation. The fluid act as a BASE to neutralize the acidic environment of the male’s urethra (from urine). There is a small amount of sperm also released at this time. COWPER’S GLAND PROSTATE GLAND Produces prostatic fluid and helps in the control of the release of semen or urine down the urethra. The fluid produced by the prostate gland acts as a BASE. There is one prostate gland and it is the size of a walnut. As men age they may experience a condition that causes the prostate gland to enlarge. This condition gives the man a frequent urge to urinate even when it is not physiologically necessary. Prostate cancer is a common problem for men as they age and it is a very treatable form of cancer. PROSTATE GLAND BLADDER The bladder’s job is to store urine. Both males and females have bladders and their jobs are the same for both men and women. BLADDER URETHRA Tube or passageway for semen and urine to leave the male’s body. The only two things that travel through the urethra are semen and urine. Urine and semen cannot exit the body at the time. The urethra connects the vas deferens and prostate/vas deferens area to the end of the penis. The urethra is the only duct in the human body that functions for two systems, the urinary and reproductive systems. URETHRA GLANS PENIS The “HEAD” or end of the penis. It is external. It has the most nerve endings and is the most sensitive part of the male reproductive anatomy. Its’ only purpose is for sexual pleasure. It is covered by the foreskin, unless the foreskin in removed in an operation called a “CIRCUMCISION”. GLANS PENIS PENIS The penis is the male sex organ. The penis is filled with lots of tiny blood vessels that fill up with blood when the man is sexually excited. When these blood vessels are filled, the man to get an erection. An erection makes it possible for a man to have sexual intercourse. The urethra runs through the penis. PENIS FORESKIN Fold of skin that partially covers the glans penis. The job of the foreskin is to protect the glans penis and to protect the opening of the urethra (from infection). The foreskin may be removed in an operation called a circumcision. FORESKIN CIRCUMCISION An operation that removes the foreskin. This operation may be performed for hygienic, cultural, or religious reasons. CIRCUMCISION DIRECTIONS FOR THE QUIZ: Now go back to the disc and open THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE ANATOMY QUIZ and check to see what you have learned. Do not use your notes for the quiz and try to do your own work. (Do not work together.) At the end of the quiz the answers will be provided for you, please grade your own quiz.