* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Section 17.1
Survey
Document related concepts
Psychedelic therapy wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical marketing wikipedia , lookup
Compounding wikipedia , lookup
Specialty drugs in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Orphan drug wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
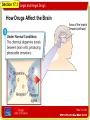
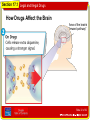
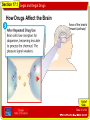
Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs Monday, June 2 “A” Day Throw it off the highest building, and I'll not break. But put me in the ocean, and I will. What am I? TODAY’S AGENDA •Drug Unit Notes • A Tissue or Wave Slide 1 of 32 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs Slide 2 of 32 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs National Drug IQ Challenge 1.) An opioid is a mind-altering chemical that can come from a plant (the opium poppy) or be man-made. Which of these drugs is NOT an opioid? A. Vicodin B. Morphine C. Heroin D. Cocaine Slide 3 of 32 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs National Drug IQ Challenge 2.) What percentage of people who smoke marijuana every day become addicted? A. 5-10% B. 80-90% C. 25-50% D. 60-75% Slide 4 of 32 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs National Drug IQ Challenge 3.) For several years now, there have been more deaths from prescription pain reliever overdoses than from heroin and cocaine combined. The deaths usually result from: A. Damage to the brain, causing a stroke B. Heart valve collapse C. Respiratory failure (breathing stops) D. Choking Slide 5 of 32 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs National Drug IQ Challenge 4.) People who take drugs can develop tolerance over time. This means: A. They become nicer, calmer people. B. They easily get sick to their stomach. C. They need to take more of a drug to get the same effect. D. They get physically stronger Slide 6 of 32 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs National Drug IQ Challenge 5.) Sharing your ADHD medications with a friend is: A. Okay because a doctor prescribes these medications. B. Prescription drug abuse. C. Only abuse if the friend uses them to get high. D. Legal. Slide 7 of 32 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs National Drug IQ Challenge 6.) What is NOT true about “bath salts,” often sold in head shops: A. They can cause intense cravings similar to what methamphetamine users experience. B. They usually contain some type of stimulant drug along with other unknown ingredients. C. They are really only dangerous if snorted or injected. D. They have sent hundreds of people to the emergency room. Slide 8 of 32 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs National Drug IQ Challenge 7.) K2 or Spice is a mixture of chemicals and herbs sometimes called “fake marijuana.” If you smoke it, what will you be inhaling? A. Natural materials from eucalyptus leaves. B. Incense approved by the FDA. C. Powerful chemicals similar to the active ingredient in marijuana, but much stronger and untested in humans. D. Dried wildflowers. Slide 9 of 32 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs National Drug IQ Challenge 7.) K2 or Spice is a mixture of chemicals and herbs sometimes called “fake marijuana.” If you smoke it, what will you be inhaling? A. Natural materials from eucalyptus leaves. B. Incense approved by the FDA. C. Powerful chemicals similar to the active ingredient in marijuana, but much stronger and untested in humans. D. Dried wildflowers. Slide 10 of 32 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs National Drug IQ Challenge 8.) Taking drugs can lead to HIV/AIDS—either through shared needles or risky sexual behaviors. About how many people in the US become infected with HIV each year? A. 7,000 B. 12,000 C. 50,000 D. 110,000 Slide 11 of 32 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs National Drug IQ Challenge 9.) What is the worst thing that can happen to you if you “sniff” an inhalant? A. You can pass out. B. You can die. C. You can start coughing uncontrollably. D. You can get serious muscle spasms. Slide 12 of 32 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs National Drug IQ Challenge 10.) Which best describes a good drug treatment program: A. Never uses medicines to treat addiction. B. Tailors treatment to the needs of each patient. C. Doesn’t drag on past 2 or 3 weeks. D. Expels anyone who relapses while in treatment. Slide 13 of 32 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs National Drug IQ Challenge 11.) What do all drugs of abuse have in common when it comes to the brain? A. They disrupt a region of the brain called the hypothalamus, which influences thirst, appetite, and body temperature. B. They overstimulate the cerebellum, the part of the brain that helps us coordinate movements. C. They cause a spike in dopamine levels, which makes us feel pleasure and want to repeat the experience. D. They increase the grey matter in the cerebral cortex, making us more aware and alert. Slide 14 of 32 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs National Drug IQ Challenge 12.) Which drugs work by mimicking a chemical naturally found in the brain? A. Heroin B. Marijuana C. Nicotine D. Alcohol E. All of the above F. A, B, and C Slide 15 of 32 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs Myth Medicines from a drugstore can’t harm you. Fact Medicines can be just as dangerous as “street drugs” if they are used inappropriately. •What other myths do teens believe about drugs? Slide 17 of 32 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs Facts About Drug Use • If drugs are not used as directed, serious health problems can result. • Medicines are legal drugs that help the body fight injury, illness, or disease. • Medicines can be classified into two groups: overthe-counter drugs and prescription drugs. Slide 18 of 32 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs Over-the-Counter Drugs • A medicine that is sold legally in pharmacies and other stores without a doctor’s prescription is called an over-the-counter drug. • Any over-the-counter drug can cause harm if the instructions on the label are not followed. Slide 19 of 32 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs Prescription Drugs • A drug that can be obtained only with a written order from a doctor and can be purchased only at a pharmacy is known as a prescription drug. • Prescription drugs require more government control than over-the-counter drugs because of their potential for harm. Slide 20 of 32 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs Illegal Drugs • An illegal drug is a chemical substance that people of any age may not lawfully manufacture, possess, buy, or sell. • Illegal drugs are also called street drugs. Slide 21 of 32 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs Drug Misuse • The improper use of medicines—either prescription or over-the-counter drugs—is called drug misuse. • Examples of drug misuse include • taking more than the prescribed amount of a drug • taking drugs with the wrong foods or at the wrong time of day • not taking a drug for the correct period of time Slide 22 of 32 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs Drug Abuse • When a drug is intentionally used improperly or unsafely, it is known as drug abuse. • Drug abuse occurs when people intentionally use any kind of drugs for nonmedical purposes. Slide 23 of 32 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs Slide 24 of 32 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs Drug Abuse and the Brain • A mood-altering drug, also called a psychoactive drug (sy koh AK tiv), is a chemical that affects brain activity. • Most abused drugs are psychoactive. Slide 25 of 32 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs The “Reward Pathway” • Many psychoactive drugs trigger activity along a pathway of cells in the brain called the “reward pathway.” • Brain cells along the activated reward pathway release a chemical called dopamine (DOH puh meen). • The extra dopamine released during drug use can cause the user to ignore the harmful effects of the drug and want to continue using it. • Flooding the reward pathway with dopamine may lead to intense cravings for the drug. • After a time, drug abuse can dull the brain’s reactions to natural levels of dopamine. Slide 30 of 32 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs How Drugs Affect the Brain Area of the brain’s “reward pathway” Slide 31 of 32 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs How Drugs Affect the Brain Area of the brain’s “reward pathway” Slide 32 of 32 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs How Drugs Affect the Brain Area of the brain’s “reward pathway” Slide 33 of 32 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs Addiction • Abuse of psychoactive drugs may result in addiction. • Addiction is the compulsive use of a drug, despite any cost to health, family, or social standing. • Addiction is a disease that changes the structure and chemistry of the brain. Slide 34 of 32 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs Dangers of Drug Misuse and Abuse • Drugs can produce powerful changes in the body. • But when drugs are misused or abused, many serious health effects can result. Slide 35 of 32 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs Side Effects • A side effect is an unwanted physical or mental effect caused by a drug. • Side effects can include • nausea • dizziness • drowsiness • Side effects of a particular drug vary from person to person. Slide 36 of 32 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs Tolerance and Dependence • When a person uses a drug repeatedly, the body may develop tolerance to the drug. • Tolerance may lead to drug dependence—the body develops a chemical need for the drug and can’t function normally without it. Slide 37 of 32 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs Withdrawal • If a person who is dependent on a psychoactive drug stops taking the drug, that person will experience withdrawal symptoms. • Withdrawal symptoms include • nausea or vomiting • headaches or dizziness • fever • digestion problems • paranoia or panic • tremors, seizures, or death Slide 38 of 32 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs Drug Interactions • When a person takes more than one drug at a time, the drugs may interact in different ways than when taken alone. • Antagonism A drug antagonism (an TAG uh niz um) occurs when each drug’s effect is canceled out or reduced by the other. • Synergism A drug synergism (SIN ur jiz um) occurs when drugs interact to produce effects greater than those that each drug would produce alone. Slide 39 of 32 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs Impurities • Many illegal drugs are contaminated with chemicals that may themselves be harmful or cause dangerous drug interactions. • Illegal drugs may vary widely from batch to batch in the concentration of psychoactive chemicals they contain. Slide 40 of 32 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs Other Health Risks • Hepatitis and HIV If drug users share needles to inject drugs, contaminated blood left in the needle can carry disease-causing viruses from user to user. • Risks to Fetus and Newborn Drug abuse by a pregnant woman places her baby at risk for a broad range of developmental problems. Slide 41 of 32 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs Depressants • A psychoactive drug that slows brain and body reactions is called a depressant. • Depressants slow body functions by decreasing heart and breathing rates and lowering blood pressure. Slide 42 of 31 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs Barbiturates • One class of depressants is the barbiturates (bahr BICH ur its) —also called sedative-hypnotics. • In small doses, barbiturates are sedatives—they relax a person. • In high doses, barbiturates are hypnotics—they induce sleep. Slide 43 of 31 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs CNS Depressants • A CNS depressant is a sedative that slows the activity of the central nervous system (CNS). • CNS depressants • slow nerve activity • relax muscle tension • lower alertness • cause drowsiness Slide 44 of 31 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs Opiates • An opiate (OH pee it) is any drug made from psychoactive compounds contained in the seed pods of poppy plants. • In small doses, opiates act to dull the senses, relieve pain, and induce sleep. • Heroin is an illegal opiate made from morphine in a laboratory. • Heroin is highly addictive. Slide 45 of 31 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs Slide 46 of 31 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs Stimulants • A stimulant is a drug that speeds up activities of the central nervous system. • Stimulants increase • heart rate • blood pressure • breathing rate • alertness • Physicians sometimes prescribe certain stimulants to treat sleep disorders and behavioral disorders. Slide 47 of 31 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs Amphetamines • Amphetamines (am FET uh meenz) are prescription drugs that are sometimes sold illegally as “speed” or “uppers.” • Amphetamine abuse produces feelings of well-being and high energy. • The effects wear off quickly and the abuser is often left feeling depressed. Slide 48 of 31 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs Methamphetamine • A stimulant that is related to amphetamines, but is even more powerful, is methamphetamine. • Methamphetamine initially produces a rush, or “high.” • But, after the rush wears off, the user may become • confused • shaky • anxious • irritable • violent Slide 49 of 31 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs Cocaine • Cocaine is a powerful but short-acting stimulant. • Cocaine is highly addictive. • When cocaine’s effects wear off, abusers often experience depression, which can be severe. • Crack is the strongest form of cocaine. Slide 50 of 31 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs Slide 51 of 31 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs Hallucinogens • A hallucinogen (huh LOO sih nuh jun) is a drug that distorts perception, thought, and mood. • Hallucinogens overload the brain with sensory information, causing a distorted sense of reality. • Abusers • cannot tell what is real • may experience memory loss and personality changes • may be unable to perform normal activities • may lose track of time and their surroundings Slide 52 of 31 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs LSD • The strongest known hallucinogen is lysergic acid diethylamide, or LSD. Psilocybin • Another hallucinogen is psilocybin (sil uh sy bin)—sometimes called “shrooms.” PCP • One of the most dangerous of all drugs is PCP, short for phencyclidine. • Because the drug eliminates the sensation of pain, abusers may unintentionally injure or even kill themselves. Slide 53 of 31 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs Marijuana Marijuana (mar uh WAH nuh) is the leaves, stems, and flowering tops of the hemp plant Cannabis sativa. • Marijuana is one of the most frequently abused psychoactive drugs. Slide 54 of 31 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs Club Drugs, Inhalants, and Steroids • Three classes of drugs that are of growing concern in recent years are club drugs, inhalants, and anabolic steroids. • The effects of club drugs and inhalants are extremely unpredictable and dangerous. • Abuse of steroids causes lifelong damage to the body and brain. Slide 55 of 31 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs Club Drugs • Club drugs got their name from the fact that they first gained popularity at dance clubs and raves. Ecstasy – E, X, XTC, MDMA, Adam Ketamine - K, Special K, Ket, Vitamin K, Kit Kat Date Rate Drugs GHB – Liquid Ecstasy, Liquid X, Grievous Bodily Harm, Georgia Home Boy Rohypnol – Roofies, R-2 Slide 56 of 31 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs Inhalants A breathable chemical vapor that produces mind-altering effects is called an inhalant (in HAYL unt). Slide 57 of 31 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs Anabolic Steroids • Anabolic steroids are synthetic drugs that are similar to the hormone testosterone. • Steroids are abused primarily by people who want bigger muscles. • Steroids can make a user’s personality very aggressive. Slide 58 of 31 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs Drug Scheduling Information 1. The drug's actual or relative potential for abuse. 2. Scientific evidence of the drug's pharmacological effects. 3. The state of current scientific knowledge regarding the substance. 4. Its history and current pattern of abuse. 5. The scope, duration, and significance of abuse. 6. What, if any, risk there is to the public health. I 7. The drug's psychic or physiological dependence liability. 8. Whether the substance is an immediate precursor of a substance already controlled. Slide 59 of 32 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs Schedule 1 • The drug or other substance has a high potential for abuse. • The drug or other substance has no currently accepted medical use in treatment in the United States. • There is a lack of accepted safety for use of the drug or other substance under medical supervision. • Examples of Schedule I substances include heroin, lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), marijuana, and methaqualone. Slide 60 of 32 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs Schedule II • The drug or other substance has a high potential for abuse. • The drug or other substance has a currently accepted medical use in treatment in the United States or a currently accepted medical use with severe restrictions. • Abuse of the drug or other substance may lead to severe psychological or physical dependence. • Examples of Schedule II substances include morphine, phencyclidine (PCP), cocaine, methadone, and methamphetamine. Slide 61 of 32 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs Schedule III • The drug or other substance has less potential for abuse than the drugs or other substances in schedules I and II. • The drug or other substance has a currently accepted medical use in treatment in the United States. • Abuse of the drug or other substance may lead to moderate or low physical dependence or high psychological dependence. • Anabolic steroids, codeine and hydrocodone with aspirin or Tylenol®, and some barbiturates are examples of Schedule III substances. Slide 62 of 32 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs Schedule IV • The drug or other substance has a currently accepted medical use in treatment in the United States. • Abuse of the drug or other substance may lead to limited physical dependence or psychological dependence relative to • The drug or other substance has a low potential for abuse relative to the drugs or other substances in Schedule III. the drugs or other substances in Schedule III. • Examples of drugs included in schedule IV are Darvon®, Talwin®, Equanil®, Valium®, and Xanax®. Slide 63 of 32 Section 17.1 Legal and Illegal Drugs Schedule V • The drug or other substance has a low potential for abuse relative to the drugs or other substances in Schedule IV. • The drug or other substance has a currently accepted medical use in treatment in the United States. • Abuse of the drug or other substances may lead to limited physical dependence or psychological dependence relative to the drugs or other substances in Schedule IV. • Cough medicines with codeine are examples of Schedule V drugs. http://www.justice.gov/dea/pubs/abuse/1-csa.htm#Formal Slide 64 of 32