* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Brain Abscess
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Meningococcal disease wikipedia , lookup
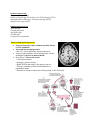
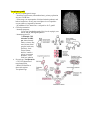
Lecture 18 – Infectious Agents of CNS Disease Types of CNS Infection Meningitis o Inflammation of the meninges surround the brain Encephalitis o Inflammation of the brain parenchyma Meningoencephalitis o Inflammation of brain and meninges Myelitis o Inflammation of the spinal cord Abscess o Necrotic lesion encapsulated by collagen fibers Common Causes of Bacterial Meningitis in CHILDREN Listeria monocytogenes E. coli Ages: 0-6 months Streptococcus agalactiae (main one) Neisseria meningitides Haemophilus influenza type b Ages: 6 months – 6 years Streptococcus pneumoniae (main one) ADULTS Always think Enterovirus 1st then bacteria Ages: 6-50 years Neisseria meningitides military recruits; dorm residents Streptococcus pneumonia (main one) Listeria monocytogene Haemophilus influenza Ages: >50 years CNS infection indicators: 1. WBC numbers (normal = 0-5/microL) will be high >5; w/ PMN predominance (bacterial meningitis) 2. Protein (15-45 mg/dL) will be high (>45) 3. Glucose (40-70 mg/dL) will be low (50 of time), but no change for viruses 4. CSF opening pressure >250 mmH2O = increased intracranial pressure = meningitis, intracerebral hemorrhage, or tumors Bacterial meningitis in children: altered cry (or absence); lethargy; vomiting (after fever); neck stiffness; seizures (w/in 1st few days); HA/irritability Bacterial Meningitis Streptococcus pneumonia (6mos-6yrs)***** Presentation & Labs: 6-month old female; ER; overnight hx of lethargy. In ER 3 days ago w/ fever & URI sx so diagnosed w/ otitis media & given ABs now irritable; less active; vomiting; urine output decreased & no diarrhea - Temp: 104; questionable neck stiffness (grimacing on movement) - high WBC (high in PMN; normal CT Diagnostic work-up: **** - Lumbar puncture: CSF: high WBC (mostly PMN), low glucose, high protein gram + cocci in pairs/chains (strep/staph) alpha-hemolysis on blood agar catalase negative (so not staph) optochin-sensitive (strep. pneumonia) Micro: virulence - Polysaccharide capsule: blocks phagocytosis & complement activation - Pneumolysin: release caused by peroxide build-up; cytotoxic to endothelial cells; inhibits phagocytosis & adaptive response; inhibits ciliary axn; stimulates chemotaxis of PMN (promotes inflamm.) Upper respiratory tract colonization (URT) Streptococcus agalactiae (GBS) – 0-6mos*** Presentation & labs: 1-month old female; in ER w/ 24hr hx of fever, poor feeding & irritability; seizure prompted ER visit - Temp: 100.8; high pulse; slightly low BP; nuchal rigidity - Blood: high WBC (mostly PMNs); normal CT Diagnostic Work-up: - Lumbar puncture: CSF: high WBC; low glucose; high protein gram + cocci in chains (strep/staph) beta-hemolysis on blood agar catalase negative (so not staph) Bacitracin-resistant (so it’s a group B strep) Positive CAMP test (this is only used to confirm group B strep-GBS) o Synergistic rxn enhanced & very visible zone (clear zone) of hemoplysis in region b/t 2 cultures (never in groups A,C, or G strep) - Blood bacteremia (blood culture same as CSF) - Direct detection of capsular Ags - PCR rule out viruses Micro: Leading cause of death among US infants - Early onset neonatal disease (usu. from mom during birth): 1st wk of life; pneumonia & bacteremia - Late-onset disease (usu. from hospitals): 1wk-3mos; meningitis (+/- bacteremia); hearing loss, brain injury may occur (goes straight into brain) - Virulence: Cell surface pore-forming toxins: o Beta-hemolysin/cytoplasm invasion of epithelia/endothelia & BBB; promotes neuro damage o CAMP factor cytolysin; binds Fc of IgG Polysaccharide capsule (capsules provide protection from phagocytes) Neisseria meningitides (meningococcus) Presentation & labs: 19-yr old college student, December to ER w/ 12hr hx of high fever, chills, & severe HA; vomiting upon arrival - Temp: 103.8; high pulse; low BP; can’t answer questions or follow commands; nuchal stiffness; “purple” rash on extremities******(rash means the infection has disseminated; pt probably now septic) - Blood: low WBC (mostly PMN); normal CT Dx Work-up: - Lumbar puncture: CSF: high WBC (mostly PMNs); low glucose; high protein gram – cocci in prs (THERE IS ONLY 1 GRAM – COCCI!!!)(neisseria) growth on chocolate or sheep blood agar oxidase-positive (blue color) no lactose fermentation (red); + for glucose & maltose - Blood (bacteremia) culture (same as CSF) - Direct detection of capsular Ags Micro: Leading cause of bacterial meningitis in children & young adults in US (cold, dry months) **** - Virulence: Lipooligosaccharides (LOS): 10x more tosic than LPS; Ag variation; inhibits complement deposition (when sialyated) Polysaccharide capsule Intracellular survival in PMN (allows infection of inflamed tissue as PMN migrate to those sites Fimbriae & porins URT colonization: rapid replication dissemination (bacteremia, shock, purpura, petechia) & enters brain; slow replication into brain, heart, & joints Septic shock (TNF alpha; IL-1) Induces endothelial expression of tissue factor (TF) o TF thrombin fibrin clots in microvasculature Induces expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) o PAI-1 prevents fibrinolysis Inhibits activation of protein C (or activated protein C, APC) o APC blocks PAI-1 production, prevents thrombin production (cleaves factors V, VIII) Listeria monocytogenes Presentation & labs: 61-yr old to ER w/ 5 day hx of fever, HA, confusion; had a 2 day bout of diarrhea that resolved a few days before current sx; hx of dail prednisone for rheumatoid arthritis - fever & high pulse; unable to answer questions; NO nuchal rigidity - Blood: high WBC (lots of PMN); normal head CT Dx work-up: - Lumbar puncture: CSF: high WBC w/ mostly PMNs; normal glucose; high protein gram + bacilli sheep agar growth (weakly beta-hemolytic) growth @ 4 degrees C (or high salt media) – done b/c of diarrhea hx Wet mount “tumbling motility” positive motility test***** Micro: Foodborne illness in adults & meningitis in newborns - high risk: pregnant women; neonates; immune-compromised pts; elderly - Virulence: Listeriolysin O & Phospholipase B induces uptake by epithelia &/or phagocytes; enzymes activated in endosome/phagosome; escape into cytosol & replicate ActA & Actin tails propel bact into host cell memb & into adjacent cells (flagella created as the bact moves; get into adjacent cells to avoid immune response) Ingestion of contaminated meat/diary: successful Tx requires T1/T17 response Haemophilus influenzae type B (Hib) Presentation & labs: 20-month old male ER after seizure; 3 day hx cough & congestion & low-grade fever; fussy & inconsolable; has not received all immunizations - fever & high pulse; nuchal rigidity - Blood: high WBC (lots of PMN); normal head CT Dx work-up: - Lumbar puncture: CSF: high WBC w/ mostly PMNs; low glucose; high protein gram – coccobacilli? chocolate agar growth (@ 5% CO2) growth on heart infusion/trypticase soy agar (+Hemin, +NAD) Oxidase positive (purple in organisms w/ cytochrome C in respiratory chain) Serotype capsule (a-f) Micro: Unencapsulated strains colonize 75% of healthy children & adults - Virulence: Polyribital phosphate (PRP) capsule (adherence, blocks phagocytosis & complement activation, inhibits ciliary axn); Fimbriae; IgA protease URT colonization Subacute/Chronic Meningitis Cryptococcus neoformans Mycobacterium tuberculosis Treponema pallidum Histoplasma capsulatum Coccidioides immitis/posadasii Cryptococcus neoformans Presentation & labs: 42 y.o. white male ER b/c 2 wk hx fever, severe HA, NV, and changes in mental status; previous dx of HIV 2 yrs ago & currently not taking antiretroviral therapy - fever, high pulse, nuchal rigidity, positive Hernig sign (flexing of neck when knee is flexed) - Blood: low WBC (mostly PMNs); normal head CT Dx work-up: - Lumbar puncture: CSF: high WBC (mostly lymphocytes); normal glucose; high protein gram stain not revealing India ink latex agglutination test (polysaccharide capsule) - CSF/Blood culture: growth on Sabouraud-dextrose agar (mucoid, creamy white colonies) Niger Bird Seed agar (dark brown, smooth colonies) Urease-positive Micro: most common pathogen causing fungal meningitis - opportunistic infection - virulence: polysaccharide capsule; melanin production (stable populations of free radicals) Pathogenesis: replication in bird feces & eucalyptus trees fungemia Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Treponema pallidum, Histoplasma capsulatum, Coccidioides immitis/posadasii Presentation: - unrelenting HA - stiff neck - low-grade fever - lethargy for wks - cranial nerve abnormalities & night sweats Mycobacterium tuberculosis Micro: 1/3 of world population infected - virulence: Lipoarabinomannan (LAM) (blocks lysosome-phagosome fusion; inhibits Agpresentation) Transmission: Inhalation of contaminated respiratory droplets (viable for hours on objects) Tuberculosis meningitis in 5% of cases (mostly pulmonary disease) Pathogenesis: - Inflammation at base of brain compromised CSF flow increased intracranial pressure (coma possible) - Granulomas & inflammation around cranial nerves can cause malfunction Dx work-up: Tuberculosis meningitis - Night sweats - Lumbar puncture: CSF: acid fast bacillus (red, mycolic acid wall); lymphocyte pleocytosis (increased cell count) Culture: growth on Lowenstein-Jensen egg media Treponema pallidum Micro 3-stage disease 1. Primary syphilis: painless papule (chancre); 4-6 wk duration 2. Secondary Syphilis: rash (macular, popular, pustule); also on palms of hands and feet; 2 wk duration 3. Latent Syphilis: lesion (gumma) development in multiple organs; 1-20 yrs after secondary syphilis - asymptomatic neurosyphilis (CSF abnormal): increased protein; pleocytosis - symptomatic neurosyphilis: meningitis <1 yr after infection; meningitis + cerebral vasculitis; widespread brain parenchymal damage (delusions, hallucinations, memory & speech & balance loss, altered personality) Dx work-up: Neurosyphilis CSF exam - Venereal disease research lab test - FTA-ABS (fluorescent treponemal Ab absorption) - Serodia TP-PA test (indirect agglutination for Ig against microbe) Histoplasma capsulatum Micro: most prevalent endemic mycosis in N. America (Ohio & Mississippi river valleys) - soil enriched w/ bird/bat droppings fungal growth cases from spelunking, excavation, cleaning chicken coops, demolition/remodeling buildings, or cutting down dead trees - Virulence: prevent acidification of phagolysosome in macrophages; iron-acquisition enzymes Pathogenesis: inhalation of microconidia Dx work-up: Histoplasmosis - Lumbar puncture: CSF: hitoplasma polysaccharide antigen detection w/ enz. Immunoassay (EIA) - Blood exam: positive for Ag/Ab; complement fixation for Ab to H or M Ags; EIA - Bone marrow: Aspirate gets here via migratory infected macrophages; infects cells of reticuloendothelial system (culture on SDA) Coccidioides immitis/posadasii Micro: - immitis: endemic in Southwest US - posadasii: remaining central and western US - soil enriched w/ bat/rodent droppings Fungal growth - Virulence: induction of arginase I in phagocytes (block NO production); urease promotes ammonia production @ infection site (tissue damage) Dx work-up: Coccidioidomycosis - Lumbar puncture: CSF exam complement fixation/EIA for Abs to coccidioides Ags culture only successful 50% of time - Blood exam: complement fixation for Abs to cocc. Ags Brain Abscess Presentation (usu. 11-12 days after sx onset) HA (constant, dull, aching; hemicranial or generalized) Fever (50% pts at dx) Seizure (reason for visit) Focal neuro deficits (dependent on lesion location) - Frontal lobe hemiparesis - Temporal dysphasia - Cerebellum ataxia - Occipital visual field defects Predisposing conditions: Otitis media; sinusitis; feverish infections of chest, penetrating head wound, trauma, neurosurgery, dental infections Pathogenesis: Must be pre-existing areas of ischemia, necrosis, or hypoxia in brain tissue - Early stage (1-3d): inflamm. cell infiltration (surround central core of necrosis - Late stage (4-9d): pus forms enlarging necrotic center; surrounded by macrophages & fibroblasts - Capsule formation (10-13d): collagenous capsule initiates - Late capsule formation (>14d): well-formed necrotic center & surrounding capsule Dx work-up: - MRI & CT; needle aspiration (stain and culture); peripheral leukocytosis, elevated Creactive protein & ESR Immunocompetent pts: Streptococcus spp. (40%) Enterics [Proteus spp., Escherichia coli, Klebsiella spp.] (25%) Anaerobes [Bacteroides spp., Fusobacterium spp.] (25%) Staphylococcus spp. (10%) Immunosuppressed pts Nocardia spp. Toxoplasma gondii Aspergillus spp. Candida spp. Cryptococcus neoformans Taenia solium (pork tapeworm) Neurocysticercosis is most common parasitic disease of CNS worldwide Increased intracranial pressure: - HA; NV; vision difficulites; dizziness & atazia Seizures, hydrocephalus, altered mental status, chronic meningitis (cysticerci in subarachnoid) Dx work-up: Neurocysticercosis - Clinical presentation - Imaging: cysticerci lesions - Blood: ELISA detection of Abs against cystcerci - Therapy: resolution of disease albendazole or praziquantel alonw - Detection of lesions in other sites of body (along w/ the CNS ones) Toxoplasma gondii Micro: see pathogenesis image - Nonfeline stage (human, intermediate host): primary replication sites are CNS & mm - Feline stage: cat consumption of infected animals (rodents) and harbor bradyzoites carry out sexual phase in cat produce oocytes (these are ingested by humans) - By adulthood: 50% Americans = seropositive for T. gondii Clinical presentation: - Immunocompetent: Cervical lymphadenopathy; HA; fever & myalgia; sore throat; abd pn; meningoencephalitis - Immunosuppressed: Principle CNS infection of AIDS pts; altered mental status; seizures; Has; mass lesions (basal ganglia, brain stem, pituitary); focal lesions (motor deficits, cranial n palsies, movement disorders, visual field loss, aphasia) Dx work-up: Toxoplasmosis - CSF: PCR detection of toxoplasma DNA - Blood: ELISA/EIA to detect Abs against Toxoplasma Ags