* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 3 STRUCTURE AND STEREOCHEMISTRY OF ALKANES
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
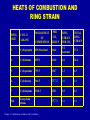
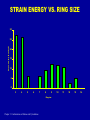
Chapter 3 CONFORMATIONS OF ALKANES AND CYCLOALKANES Chapter 3: Conformations of Alkanes and Cycloalkanes HEATS OF COMBUSTION AND RING STRAIN RING SIZE CYCLO ALKANE MOLAR HEAT OF COMBUSTION PER CH2 GROUP RING STRAIN PER CH2 TOTAL RING STRAIN 3 Cyclopropane 499.8 kcal/mol 166.6 9.2 kcal/mol 27.6 4 Cyclobutane 655.9 164.0 6.6 26.4 5 Cyclopentane 793.5 158.7 1.3 6.5 6 Cyclohexane 944.5 157.4 0.0 0.0 7 Cycloheptane 1108.3 158.3 0.9 6.3 Ref. Long-chain alkane 157.4 0.0 0.0 Chapter 3: Conformations of Alkanes and Cycloalkanes STRAIN ENERGY VS. RING SIZE 30 Strain energy [kcal/mol] 25 20 15 10 5 0 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Ring size Chapter 3: Conformations of Alkanes and Cycloalkanes 10 11 12 13 14 TYPES OF STRAIN IN ORGANIC MOLECULES (SUMMARY) 1. Torsional Strain: The strain due to eclipsing of bonds at neighboring carbon atoms. Energy cost – about 1 kcal/mol for C-H --- C-H eclipse, or 1.3 kcal/mol for C-H --- C-CH3 eclipse. 2. Steric Hindrance: The strain due to repulsive interactions, when atoms or groups approach each other too closely. Energy cost – about 0.8 kcal/mol for C-CH3 --- C-CH3 gauche interaction. NOTE: The C-CH3 --- C-CH3 eclipsed interaction is a cumulative torsional strain + steric hindrance!!! 3. Angle Strain: The strain due to expansion or compression of bond angles. Energy cost – varies, depending on the actual bond angle. Chapter 3: Conformations of Alkanes and Cycloalkanes