* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Design principle of biological networks—network motif
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
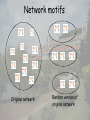
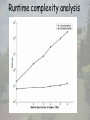
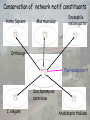
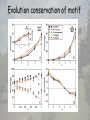
Design principle of biological networks—network motif Definition of motifs • Motifs are those subgraphs that occur significantly more often in the real network than in randomized networks. Network motifs Original network Random version of original network Criteria for network motif Z N real N rand rand 2.0 N real : number of subgraph in real network N rand : average number of subgraph in random network rand : standard deviation of number of subgraph among random networks Motifs in genetic network of yeast Motifs in genetic network of E. coli Enumeration methods to identify motifs • Generating an ensemble of random networks • Counting subgraphs in real network and random network Subgraph concentration Ni Ci Ni i N i : The number of appearance sof subgraphs of type i with n nodes Ci : Concentrat ion of n node subgraph of type i Random sampling of n node subgraphs • Pick a random edge from the network and expand the subgraph iteratively by picking random neighboring edges until the subgraph reaches n nodes. Sampling algorithm • P: probability of sampling a specific subgraph • Define a score Si for each subgraph of type i, and set to Si zero initially. • Si= Si+1/P until ST samplings are finished. • Assume L types of subgraphs were sampled. Ci Si L S k 1 k Compare between sampling and enumeration Runtime complexity analysis Conservation of network motif constituents Homo Sapiens Mus musculus Drosophila melanogaster Orthologs Four nodes motif Saccharomyces cerevisiae C. elegans Arabidopsis thaliana Inparanoid: Eukaryotic Ortholog Groups Evolution conservation of motif Evolution conservation of motif Network motif software Homework • Download the mfinder motif detection software from Uri Alon’s web page, http://www.weizmann.ac.il/mcb/UriAlon Read the manual and make yourself being familiar with this software. Use this software to find the motifs for the E. coli gene regulatory network. The interaction file can be downloaded from Uri Alon’s homepage. References • Uri Alon, An Introduction to Systems Biology: Design Principles of Biological Circuits