* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Immunity Ch. 11.1-6
Survey
Document related concepts
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
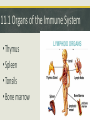
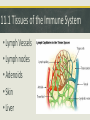
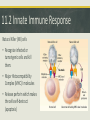
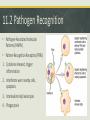
Immunity Ch. 11.1-6 Microbiology Immunology Study of how the body protects against and responds to pathogens or disease to keep you healthy. Overview of Immune System • Protects against disease (pathogens) • Three Levels of Defense 1. Physical & Chemical barriersskin, mucous, flora 2. Innate-immediate non-specific, inflammation, phagocytes 3. Adaptive (acquired)-slower, develops over time, specific, antibodies 11.1 Organs of the Immune System • Thymus • Spleen • Tonsils • Bone marrow 11.1 Tissues of the Immune System • Lymph Vessels • Lymph nodes • Adenoids • Skin • Liver 11.1 Cells of the Immune System Hematopoietic stem cells • Innate Leukocytes (white blood cells) • Phagocytes • Macrophages • Neutrophils • Dendritic cells • Mast cells • Eosinophils • Basophils • Natural killer (NK) cells 11.1 Cells of the Immune System • Adaptive Leukocytes (Lymphocytes) • B cells-bone marrow • T cells-thymus 1.1 Human-Microbial Interactions Human Microbiome Project • Flora-Mutualistic both benefit or Commensal-one benefits, other is not harmed • Skin-protection from pathogens • Gut-vitamins, hormones, protection, remove toxins & immune system development • Relatively few microbes are pathogenic 11.2 Innate Immune Response Natural Killer (NK) cells • Recognize infected or tumorigenic cells and kill them. • Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) I molecules • Release perforin which makes the cells self-destruct (apoptosis) 11.2 Physical & Chemical Barriers • Skin • Cilia-lungs • Tears • Mucus • Sweat • pH-stomach, vagina 11.2 The Complement System • Around 20 soluble proteins help destroy extracellular microorganisms • Produced by the liver & macrophages • Proteins bind to invaders (non-self) (opsonization) to identify them for destruction. 11.2 Pathogen Recognition • Pathogen-Associated molecular Patterns (PAMPs) • Pattern-Recognition Receptors (PRRs) 1. Cytokines released, trigger inflammation 2. Interferons warn nearby cells, apoptosis 3. Interleukins help leukocytes 4. Phagocytosis 11.3 Phagocytosis Engulfment of foreign material in the body by a specialized cell • Macrophages • Dendritic cells • Neutrophils 11.3 Antigen-presenting B & T cells • Recognizes antigens derived from pathogens. • If you have a secondary infection from the same or a similar pathogen, memory B and T cells will give you immunity. • This natural process of creating immunity is enhanced artificially by the use of vaccines. 11.4 The Complement System Three Biochemical Pathways: 1. Classical 2. Alternative 3. Lectin Four Functions: 1. Opsonization 2. Chemotaxis 3. Lysis 4. Clumping 11.4 Innate Defenders • Toll-Like Receptors (TLRs) recognize molecules associated with pathogens • Iron-Binding Proteins remove iron from blood to limit pathogenic growth. • Antimicrobial peptides kill bacteria, found on skin and in blood 11.5 Adaptive Immune Response Humoral Response • Defends against pathogens using antibodies against pathogenspecific antigens. • B & T cells Differentiation • Hematopoiesis (stem cells) 11.6 Antigens & Antibodies Immunodeficiency • Failure to respond, HIV/AIDS Antibody Functions 1. Neutralization 2. Opsonization 3. Complement activation