* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Neurons, nerves and glia
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
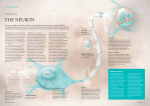
Neurons, nerves and glia Lucija Milošević 2nd year University of Zagreb, School of Medicine 2013/14 Mentor: A. Žmegač Horvat Introduction Neuron – individual nerve cell – microscopic structure Nerve – bundle of neurons which travel together – macroscopic structure Glial cell – individual stromal cell What is the main function of a neuron? Conducting impulses (in one direction) Neuron Dendrites – branching fibers Cell body – contains the cell nucleus Neuron Axon – the biggest branch extending from the cell body Myelin sheath – fatty tissue which covers axons White and gray matter Synapse Space where the nervous impulse jumps from one neuron to another Neurotransmitters Contained in tiny sacs E.g. acetylcholine, epinephrine, dopamine, serotonin Nerves Sensory nerves – carry impulses to the brain and the spinal cord Motor nerves – carry impulses from the CNS to organs Mixed nerves – contain both sensory and motor fibers Do glial cells and neurons have the same origin? Neurons - ectodermal origin - parenchymal tissue Glial cells - mesodermal origin - stromal tissue Glial cells Do not transmit impulses Far more numerous than neurons Can reproduce Three types of glial cells Oligodendrocytes – form the myelin sheath which protects neurons in the CNS Microglia – as phagocytes protect neurons in response to inflammation Astrocytes Transport water and salts between capillaries and neurons Blood-brain barrier – regulates passage of potentially harmful substances from the blood References The language of medicine, Davi-Ellen Chabner http://www.merriam-webster.com/ Thank you for your attention!