* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 6.4 The Path to War - Grants Pass School District 7
Survey
Document related concepts
Luxembourgish collaboration with Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Anglo-German Naval Agreement wikipedia , lookup
Role of music in World War II wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Pursuit of Nazi collaborators wikipedia , lookup
Nazi views on Catholicism wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Propaganda of Fascist Italy wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Fascism in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
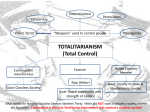
Warm-up #15: What is the Cartoon Saying? Is it painting the U.S. in a Positive light? Essential Question • What events lead to the start of World War II? Rise of Fascism • WWI forced governments to assume large amounts of control. • Powerful leaders who promise better futures arise. • Beginnings of totalitarian states • Nation in which the government controls every aspect of citizen’s lives • Dictators Fascist Italy • Lower class resisting wealthy elite • Workers in cities on strike • Italy did not gain much in Treaty of Versailles • Benito Mussolini and fascist party come to power • Fascism: glorifies nation over • • • • self and dedication to a strong leader Elections and political parties weaken Private property okay War and violence okay as long as it is to promote national goals Silenced critics, controlled schools, secret police • Italy takes over Ethiopia • League of Nations tries to intervene, but has no real power • Place economic sanctions • Restricts weapons and raw materials sale • Does not cut off sale of oil, coal, or iron What were the conditions like in Germany after WWI? Germany • Democratic government (Weimar Republic) set up after WWI faces frequent turmoil: • Threat of revolution • Economic ruin/Huge debts • Hyper Inflation • Reparations • 1930’s – Great Depression world wide, hit GER hard. • Unemployment German Inflation • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IiSFXt-Ogm4 Nazi Party • Core beliefs • Nationalism: Germans part of superior Aryan race. • Anti-Semitism: blamed Jews for Germany’s defeat in WWI and current econ. problems. • Fascism: Violence and strong government control needed to advance Germany • Anti-communist • Eliminated other political parties • Controlled every aspect of GER life Warm Up # 16 • What conditions lead to more Fascist and Totalitarian leaders in Europe? Warm Up # 17 • What are 2 things that you learned from the video last time? • -Hint: look at your video question on pg. 9 Reminders • Appeasement Thesis Statement already due • Friday April 21st • Project Fixes Due • Wednesday April 26th • Unit 6 Test • Unit 6 Workbook Due • Unit 6 Overview Due Nazi Rule • Secret Police • Controlled press, schools, and churches • Strengthened German Men • Preached hard work, sacrifice, and service to state • Employed men in building program and military • Anti-Jewish campaign • Concentration camps Nazi Aggression • 1936: GER sends troops into the Rhineland. • 1938: GER annexes Austria • World responds with policy of appeasement • Making concessions to an aggressor in order to keep peace. • Other nations have no money or desire to enter conflict • Gave GER part of Czechoslovakia where many Germans lived. • Hitler takes the rest 6 months later. Munich Conference • 1938 – Hitler promised to settle future disputes with negotiations and not take any more land by force. Germany Builds Allies • 1939 – GER and Soviet Union sign non- aggression treaty. • Would not attack each other • GER wants to gain Poland, now eliminates threat from other side The Path to War • 1920’s and 30’s: European nations struggle to recover from WW1. • Economic hardships • Political unrest • Fear of revolution (like in Russia) The Politics of Hunter • 1. In early March 1919, General Herbert Plumer, commander of the British Army of Occupation, informed Prime Minister Lloyd George that his men were begging to be sent home; they could no longer stand the sight of "hordes of skinny and bloated children pawing over the offal" from the British camps. • 2. A German child who was ten years old in 1918, and who survived, was twenty-two in 1930. Vincent raises the question of whether the miseries and suffering from hunger in the early, formative years help account to some degree for the enthusiasm of German youth for Nazism later on. League of Nations • League of Nations exists to keep peace among countries. • Has no real power • No money • No military • No U.S. The Century: Civilians at War pg. 9 • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BMWYblZ8gwQ&t=40 0s • 3rd Period: 28:58 • 6th Period: 32:50 • 7th Period: 34:00 • Skip from 32:45 – 49:55 Essential Question • What events lead to the start of World War II?