* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Fiscal policy and Stablization
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
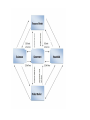
Tip: Simplify your calculations, the tax multiplier is always 1 less than the spending multiplier and the opposite sign. When taxes and government spending both increase or decrease by the same amount, the net change in real GDP is simply the change in government spending. ( the balance budget multiplier is 1.) Fiscal policy Action taken by the Federal Government to stabilize the US economy “In the long run we are all dead” John Maynard Keynes • This quote is why governments do not generally wait for the economy to fix itself. • It may take over a decade and during that period the economy and citizens have suffered a great deal. • This is the rationale for active stabilization policy. C o n t r a c t i o n a r y • To contract the economy would cause the AD to shift to the left • Taxes: increase • Spending: decrease AD shifts to the left: PL decreases, Unemployment increases Employment decreases • Transfer payments (part of spending): decrease E x p a n s i o n a r y • To expand the economy (expansionary action) AD shifts to the right • Taxes: decrease so that Disposable income increases AD shifts to the right: PL increases, Unemployment decreases • Spending: increase Employment increases • Transfer payments(part of spending): increase Stabilization policy: • The use of government policy to reduce the severity of recessions and rein in excessively strong expansions. • Does it work- there are not good records prior to WWII to compare, but for periods after that the use of stabilization policy has reduced the recessionary gap to fewer years, (4 or 5 compared to what economist believe would normally take upwards of a decade) Either the Federal Government with fiscal policy or the Federal Reserve with monetary policy can take action to stabilize the economy. If they act quickly enough to fill in the demand needed and if they are able to correctly determine how much is actually needed they can short-circuit the whole process shown in figure 19.5 and instead of going through a period of low output and falling prices the government could maintain E. Why is it desirable to short-circuit • 1. the temporary fall in aggregate output is associated with high unemployment. • 2. price stability is generally regarded as a desirable goal. Preventing deflation is a good thing. Should they always? No! When shouldn’t they? • If the action will increase the budget deficits • May have long-term costs in terms of lower long – run growth • They are not always informed correctly • The actions are not always predictable There are no easy remedies for a supply shock Any action that they take will only fix one problem at the cost of the other- they must chose between higher prices or higher unemployment. Review the circular flow model • Remember the money flows into the government from taxes and government borrowing; • Funds flow out in the form of government purchases of goods and services and government transfers to households. • What type of taxes do individuals pay: • Personal income taxes, taxes on corporate profits, social insurance taxes are the major contributors. • Other tax revenues are: property taxes, sales taxes and other miscellaneous taxes and fees The government spending is really in 2 categories • Purchases of goods and services with the biggest areas: • national defense 12% • Education 14% • Government transfers • Social security 23% • Medicare and Medicaid 21% Taxes are collected at 3 levels • City/county • State • Federal Tip for the test: if the question asks you to identify a policy that would be appropriate to close a recessionary or an inflationary gap • Don’t just say expansionary or contractionary- be more specific like a change in spending, taxes, transfer payments and be specific if they should increase or decrease in that change. Lags are an issue • Government does not always realize the issue or extent for some time, creating a lag (collecting data, analyzing it and then getting legislation through) the lag might be long enough that the situation has started correcting itself and action could hurt the recovery