* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Network Technology and the 5000 Series
Remote Desktop Services wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
TCP congestion control wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
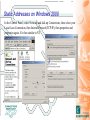
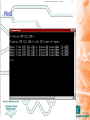
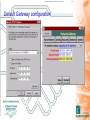
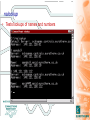
TCP-IP Primer Internet David Cozens Targets • Have a basic understanding of Ethernet network technology • Be aware of how this technology is applied on the 5000 series. • Be aware of simple debug tools and techniques to perform basic fault finding Network Training - Underlying Technology • Ethernet • IP • TCP Ethernet • Physical Ethernet • MAC Addresses • Ethernet and the 5000 series Physical Ethernet • 10baseT/100baseT - twisted pair • 10baseT is a subset of the 100baseT specification – 100baseT equipment is backwards compatible – You can cable 10baseT and 100baseT equipment together and it will operate at 10Mbps • 10 base 2 - coaxial • Fibre standards • 802.11 - wireless standards MAC Addresses • MAC addresses are fixed with particular pieces of hardware - they cannot be changed - if you change the hardware you change the number. • The number is normally written 08:00:48:80:00:10 Ethernet on the 5000 Series • We use 10baseT Ethernet. – Green light on the connector TX – Orange light on the connector RX Hubs and Switches Used to connect 10 base T devices together. • Aides and Pitfalls – Power – Connection LED – Uplink setting – Utilization/collision LEDs Ethernet (Revision) • Physical Ethernet • MAC Addresses • Ethernet and the 5000 series IP Address Classes • Classes are defined by the most significant 4 bits of the address – Class A - 0xxx - 128 networks with 2M hosts » 0.0.0.0 to 127.255.255.255 – Class B - 10xx - 16K networks with 64k hosts » 128.0.0.0 to 191.255.255.255 – Class C - 110x - 2M networks with 256 hosts » 192.0.0.0 to 223.255.255.255 – Class D - 1110 - Reserved for multicast » 224.0.0.0 to 247.255.255.255 – Class E - 1111 - Reserved » 248.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255 Private Networks • Some network addresses are reserved for private networks not connected to the internet. If you are setting up a standalone network use these numbers. – 10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.255 (10/8 prefix) – 172.16.0.0 - 172.31.255.255 (172.16/12 prefix) – 192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255 (192.168/16 prefix) Subnet Mask and Network Numbers • IP Addresses have two components. A network number and a node number. The subnet mask logically ANDed with the IP address gives the network number. • The IP Address with the network number removed gives the node number. • Network numbers are usually written as the IP address of the network with trailing 0 followed by a the number of bits set in the subnet seperated by a / eg 192.168.1.0/24 has 24 bits of network number and 8 bits for the node number. • If you need to use the AND function on the windows calculator! Subnet Exercise IP 192.168.100.18 Subnet 255.255.255.0 What is Network Number and node number? Network Number 192.168.100/24 IP Node number is 18 192.168.100.18 Subnet 255.255.255.240 What is Network Number and node number? Network Number 192.168.100.16/28 Node number is 2 Static Addresses on NT In the Control Panel, select Network, then protocols, then TCP/IP and then properties Static Addresses on Windows 2000 In the Control Panel, select Network and dial-up Connections, then select your Local Area Connection, then Internet Protocol(TCP/IP), then properties and properties again. It’s then similar to NT. Static Addresses on the 5000 Series Use the Network/Address menu PING Subnets and Gateways • Why do we need Subnets? – Logically segregate the network – Minimize bandwidth used • Gateways connect networks/subnets together Routing • When a node wants to talk to another if it is on the same network it talks directly. • If it is on a different network it talks to the gateway which forwards (routes) the message on. Default Gateway configuration Tracing the route to another host (tracert) Address Assignment • Static Configuration • BootP • DHCP BootP At startup the following conversation happens between a BootP Client and server. Client Server Hello everyone, I have MAC address 00-d0-b7-3e-b0-b3 what are my network parameters? Hello 00-d0-b7-3e-b0-b3 here is you IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, DNS Server etc. BootP Configuration on 5000 Series The BootP timeout is how long to wait for the server to respond. It may need to be increased on a busy network, or if the server is slow. DHCP - Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol The following dialog goes on between client and server Client • Hello everyone, I have MAC address 00-d0-b7-3e-b0-b3 what are my network parameters? Server Hello 00-d0-b7-3e-b0-b3 here is you IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, DNS Server etc. You may lease it for X hours. Hello server, Can I renew my lease. Yes, have another X hours. Hello server, Can I renew my lease. Yes, have another X hours. …. …. DHCP configuration on NT In the Control Panel, select Network, then protocols, then TCP/IP and then properties IP - Internet Protocol (Revision) • IP Address Classes • Subnets • Gateways • BootP/DHCP • Basic Routing TCP - Transmission Control Protocol • Connection Based • Ports and Sockets • Firewall Basics TCP is Connection Based • TCP - Transmission Control Protocol Ports and Sockets • Ports – Think of our phone analogy - Ports are like phone extensions. – Port Numbers are between 0 and 65535 • Sockets – A socket is a two way communication channel established on a particular port. Firewalls and the 5000 Series Firewalls at their simplest block connections one way or both ways through the firewall for specific protocols or ports. To use the 5000 series across a firewall the following ports must be open. For FTP ports 20 and 21 (the 5000 series does not support passive mode) For Bridge 1264 (and 50010 for trend review) For Modbus TCP 502 If the product is configured to use DNS it must also be able to communicate with the DNS server and PING the DNS server. TCP - Transmission Control Protocol (Revision) • Connection Based • Ports and Sockets • Firewall Basics Whats in a Name? hydra.eurotherm.co.uk • Hostname Domain Name These are NOTHING to do with NT domains. Domain Name Service (DNS) • DNS servers provide a means of finding the name for an address, or the address for a name. • A server knows about its domain and servers in parent and child domains. • There are often more than one DNS servers for a domain - both have the same information - it is so the network will still operate if one fails. DNS Setup on the 5000 Series nslookup • Tests lookups of names and numbers Ipconfig and winipcfg • Microsoft tools for showing network settings • Also used to release and renew dhcp leases manually. Other protocols in the TCP/IP suite MODBUS TCP ARP ICMP DNS UDP http TCP IP PPP SLIP Ethernet FTP Application Presentation Session Transport Network Data Link Physical Modbus TCP • The same Modbus data reliably transferred over a TCP socket connection. • Think of the socket connection like a complete modbus serial bus. • One Modbus TCP connection connects a master device to a slave device and/or a gateway. • Upto 247 modbus nodes can be communicated with over a single socket. Modbus TCP and the 5000 • The 5000 can simultaneously be – Slave to 4 Modbus TCP socket connections – Master to 16 Modbus devices (Serial, TCP or a mixture) – If configured for serial master communications with talk through enabled then it can act as a gateway to up to 246 serial slaves. – If configured as a serial slave it can still be a Slave to 4 Modbus TCP connections and master to 16 Modbus TCP devices. Modbus TCP Socket Sharing on the 5000 • Used to Improve timeout behaviour and reduce resource usage. – If we are talking to multiple serial slaves attached to a gateway they all share the serial bus. We will get better performance if they all share the socket. – If the gateway is also a modbus node (eg a 5000) we don’t need to access the serial wire to talk to it so we will get better communications by making this NOT share sockets. Modbus TCP - Error code B • Error code B allows a gateway to send a message back to indicate a timeout. – Some masters do NOT support it so it must be explicitly enabled. – If supported it gives much better support for timeouts from serial devices connected via gateways. Ethernet Serial Summary • Ethernet – Physical, MAC Addresses • IP – Address Classes, Subnets, Gateways, address assignment (static,BootP,DHCP), Routing • TCP – Connection Based, Ports & Sockets, firewalls • Other – DNS, Hubs, Routers, ping, nslookup, tracert • Modbus TCP