* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is it? The retina is a thin film of light
Survey
Document related concepts
Keratoconus wikipedia , lookup
Contact lens wikipedia , lookup
Visual impairment wikipedia , lookup
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension wikipedia , lookup
Fundus photography wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial optic neuropathies wikipedia , lookup
Vision therapy wikipedia , lookup
Dry eye syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Eyeglass prescription wikipedia , lookup
Cataract surgery wikipedia , lookup
Photoreceptor cell wikipedia , lookup
Macular degeneration wikipedia , lookup
Retinal waves wikipedia , lookup
Retinitis pigmentosa wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
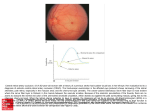
Retinal Detachment Web: cnib.ca Email: [email protected]/ontario CNIB Contact Centre: 1-800-563-2642 What is it? The retina is a thin film of light-sensitive cells inside the back of the eye. As we age, the vitreous (the thick fluid inside the eyeball) shrinks and pulls away from the retina, which sometimes pulls the retina away with it. Retinal detachment can also happen after a blow to the eye or an infection, or (less commonly) due to tumours or complications from diabetes. Retinal detachment is a serious problem that can lead to total vision loss if not treated promptly. Symptoms Retinal detachment is painless and cannot be seen simply by looking at the outside of the eye. See your eye doctor as soon as possible if you notice: Sudden spots or flashes of light in your visual field. Sudden “wavy” or “watery” vision. A shadow in your peripheral (side) vision. Risk factors and prevention You are at risk for retinal detachment if you are very nearsighted or if you have a family history of retinal detachments. Protect your eyes from injury by wearing CSAapproved safety goggles when playing sports or using tools. Regular examinations by an eye doctor can detect changes in your retina and vitreous and help prevent detachment. Diagnosis A dilated eye examination can be used to diagnose retinal detachment. In this test, drops are placed into the eye to widen (dilate) the pupils to allow a direct view of the retina. A special magnifying lens is used to examine the retina and the optic nerve. seeing beyond vision loss Treatment If your retina is torn or detached, you will require surgery to repair it. Procedures include: Placement of a scleral buckle to push the outside wall of the eye firmly against the retina. Use of a laser to seal tears or holes in the retina. Cryopexy: freezing the wall of the eye behind a hole or tear in the retina to seal the damaged area. Vitrectomy: removal of shrunken or damaged vitreous and replacement with air, or a special gas meant for this purpose or silicone oil, to preserve the eye’s shape and press the retina into position. In more than 90 per cent of cases, surgery to repair retinal detachment is successful and most patients have good vision within six months. But if the retina has been detached for a long time, if scar tissue develops or if central vision has been affected, overall vision may be partially or completely lost.