* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Micro Ch 21-Presentation 3 Price Determination
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
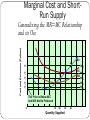
Micro Chapter 21-Presentation 3 Efficiency Productive Efficiency: Price = Minimum ATC Allocative Efficiency: Price = MC Pure Competition Has Both in its Long-Run Equilibrium Short-Run Supply Curve Firms will supply the product at prices above its AVC curve MC curve above AVC is the SR S curve Marginal Cost and ShortRun Supply Cost and Revenues (Dollars) Generalizing the MR=MC Relationship and its Use e P5 P3 P2 P1 MR5 d P4 ATC c AVC b a This Price is Below AVC And Will Not Be Produced 0 Q2 Q3 MC Q4 Quantity Supplied Q5 MR4 MR3 MR2 MR1 LR Equilibrium In the LR, equilibrium is where MR = MC and Price and Minimum ATC are = At this point there is no incentive to leave the industry or for more firms to join Entry of New Firms When consumer demand increases, existing firms receive economic profits This entices new firms to enter, driving P down back to equilibrium and ending profits Increasing-Cost Industry An industry with a positively-sloped long-run supply curve. average cost of production increases as industry grows. With rapidly increasing average cost, a relatively large increase in price is needed to get firms to produce more output. Long-Run Supply Curve Increasing-Cost Industry P S P2 $55 P1 $50 Y2 Y1 P3 $40 Y3 D2 D1 D3 0 Q3 90,000 Q1 100,000 Q2 110,000 Q Decreasing Cost Industry In a decreasing cost industry, the long-run supply curve for that industry is downward sloping. Over time, the price of the good to the consumer is decreasing (increased productivity) Examples: Over time, the price of personal computers has fallen for quality and features. Televisions, DVD, MP3, computer software