* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cell-transport-g9
Survey
Document related concepts
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
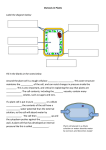
Topic 3- Cell Membranes, Transport & Response Start Mid End of of Way Topic topic 3.4: Membranes (cell and plasma) 3.4.1 Identify the structure of a cell membrane 3.4.2 Explain the importance of the membrane proteins to transport across the membrane 3.5 Transport of substances across membranes 1: Passive transport 3.5 Passive transport 1: Diffusion 3.5.1 Define diffusion as ‘the net movement of molecules from a region of their higher concentration to a region of their lower concentration down a concentration gradient, as a result of their random movement’ 3.5.2 Describe the importance of diffusion of gases, solutes (and water as a solvent) 3.5.3 Explain that diffusion is a dynamic process (always happening) 3.5.4 State that the energy for diffusion comes from the kinetic energy of random movement of molecules and ions 3.5.5 Investigate the factors that influence diffusion: limited to surface area temperature concentration gradient distance 3.5 Passive transport 2: Osmosis 3.5.6 State that water diffuses through partially permeable membranes by osmosis 3.5.7 State that water moves in and out of cells by osmosis through the cell membrane 3.5.8 Define osmosis as ‘the diffusion of water molecules from a region of their higher concentration (dilute solution) to a region of their lower concentration (concentrated solution), through a partially permeable membrane’ 3.5.9 Investigate and describe the effects on plant tissues of immersing them into solutions of different concentrations 3.5.10 State that plants are supported by the pressure of water inside the cells pressing outwards on the cell wall. 3.6: Active Transport 3.6.1 Define active transport as movement of ions in or out of a cell through the cell membrane, from a region of their lower concentration to a region of their higher concentration against a concentration gradient, using energy released during respiration 3.6.2 Discuss the importance of active transport as a process for movement across membranes: e.g. ion uptake by root hairs & uptake of glucose by epithelial cells of villi and kidney tubules 3.6.3 Explain how protein molecules move particles across a membrane during active transport 3.7 Cell Responses 3.7.1 Explain the effects on plant tissues of immersing them in solutions of different concentrations by using the terms turgid, turgor pressure, plasmolysis and flaccid 3.7.2 Explain the importance of osmosis in the uptake of water by plants 3.7.3 Explain the importance of osmosis on animals cells and tissues 3.7.4 Explain how plants are supported by turgor pressure within cells, in terms of water pressure acting against an inelastic cell wall