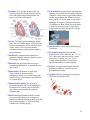
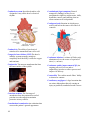
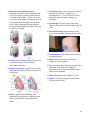
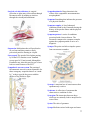
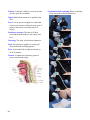
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download glossary - Cengage
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
GLOSSARY Abandonment Situation in which a Paramedic walks away from or discontinues care for a patient without turning over care to another provider who has the same or higher level of training. Accessory pathway A congenital abnormal cardiac electrical pathway that may be indicated by a short PR interval. Abnormal automaticity Spontaneous impulses generated in cardiac muscle that may interfere with the SA node’s contraction-regulating impulses. Abrasions An irritated area on the skin caused by wearing or rubbing away by friction. Abscess A localized collection of pus surrounded by inflamed tissue. Absolute bradycardia A sinus rhythm with a rate below 60 bpm. Acetylcholine The chief neurotransmitter released into the synapse from the nerve’s presynaptic membrane during neurotransmission. Acetylcholinesterase A chemical that breaks down acetylcholine. Acid A substance with a pH value less than 7; a molecule that has a proton that is not orbited by a paired electron. Abstract An abbreviated summary that hits a research study’s highlights. Accessory muscles Muscles recruited to assist with body functions when the normal muscles used for that task are inadequate. For example, in respiratory distress, accessory muscles may be used to help expand the rib cage, allowing the patient to inhale. Acid load Excessive amounts of acid in the tissues to the point that tissues are acidotic. Acidemia Condition in which the amount of hydrogen atoms in an arterial blood gas sample is below 7.35. Acidosis Excessive acid in a body system that can have a profound effect upon the body’s uptake, distribution, and the effectiveness of medications administered. Acknowledging Responding to a patient’s answer to a question with a positive reply, either verbal or nonverbal, that encourages further dialogue. Actionable Determination if a claim can be the basis for a lawsuit. To be actionable, a claim must generally have the four elements of a tort. 1 Action potential A stimulus that raises the resting membrane potential above a specific threshold. Acute myocardial infarction (AMI) Death of cardiac muscle tissue. Active transport The movement of a chemical substance through a gradient of concentration in the opposite direction to that used for normal diffusion, which requires an expenditure of energy. Activities of daily living (ADL) The everyday events people perform in the course of their life, such as eating, dressing, driving, performing personal hygiene, and generally caring for themselves. Act-utilitarianism An approach to ethical decision making in which the Paramedic weighs the outcomes or consequences of performing the act against not performing the act and then makes a decision that maximizes the intrinsic good. Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) A complex of symptoms associated with the continuum of cardiovascular disease, emphasizing its morbidity (and more importantly, its mutability) and not simply its mortality. Acute hemolytic reaction A serious bodily response to a transfusion that most often occurs as a result of an A-B-O blood type incompatibility, which leads to agglutination and hemolysis of the transfused blood. 2 Acute renal failure (ARF) The net effect of prolonged hypoperfusion, leading to a reduction in the kidneys’ ability to function. Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) A serious reaction to various injuries that involve the lungs. Acute respiratory failure Dysfunction within the lungs that impairs respiration. Acute traumatic stress An unexpected and sudden stressful event which is unlike the stress of day-to-day EMS and understandably requires a different approach to relieve. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) The chemical energy source in a cell used to power the rest of the cell’s functions. Administrative law judge (ALJ) One who decides cases involving violations of a department’s regulations. Adrenergic transmission The transmission of a nervous system signal using adrenaline as the neurotransmitter. Advanced directives Written declarations of patient intent during specific circumstances, which are designed to provide guidance when a patient is threatened with living in a persistent vegetative state or being afflicted with a terminal illness. Against medical advice (AMA) Situation in which patients refuse medical care in opposition to all logic when confronted with a clear and immediate danger to their health. Advanced emergency medical technician (AEMT) An EMS professional trained to administer a limited number of drugs and perform skills that have been shown to positively impact patient survival. Advanced life support (ALS) Additional skills and equipment offered by Paramedics over and above basic life support, such as intubation and ventilation. Adverse drug reaction An unwanted or harmful biological response to a drug that creates a subsequent negative impact upon the patient’s health. Aerobic metabolism The step in the metabolism process in which the cell uses oxygen to create ATP from glucose. Affidavit A sworn written statement which attests to facts that pertain to a legal case. Ageism A stereotypical view of the elderly as frail or feeble. Age of majority The legal age a person must be in order to consent to a medical procedure; 18 years of age in most states. Agglutination Clumping together of red blood cells. Agonist A drug or other chemical that can combine with a receptor on a cell to produce a physiologic reaction typical of a naturally occurring substance. Affinity An attraction to or liking of something. 3 Airlock A technique in which the Paramedic injects a small bubble of air into the injection, essentially sealing off the drug below from leaking out to the subcutaneous tissues above. Algorithm A logic tree in flowchart format that simply states: if this, then do that; if not this, then do this other thing. Algorithms can be useful during an emergency when time is of the essence. Akinetic State of being without motion. Alarm A signal on an ECG machine that indicates, via visible and/or audible signal, that a patient’s heart rate is above or below a certain rate. Alarm stage The first stage of the general adaptation syndrome, during which the body responds to the stressor via the central nervous system. Alert report A notification sent to the receiving medical facility about an incoming patient arrival. The information in the alert report is brief and concise: age, sex, chief complaint, mental status, vital signs, treatments in progress, and an estimated time of arrival (ETA). Algor mortis The body’s natural cooling. As the body’s metabolic processes cease, so does the production of heat. Alkalemia Condition in which the amount of hydrogen atoms in an arterial blood gas sample is above 7.45. Alkaloids Nitrogenous chemicals which are alkaline in nature and often chemically combined with acids to create water-soluble salts, such as morphine sulfate or atropine sulfate. Allergic reactions A bodily response that occurs when exposed to a certain substance, ranging from sneezing and rashes to severe complications. Alpha-adrenergic blockers Competitive blockers occupying the adrenergic receptor and preventing the catecholamine drug from attaching to the adrenergic receptor. Alphaadrenergic blockers can be divided as either long-acting and short-acting or competitive and noncompetitive. 4 Alpha1 adrenergic receptors Sympathetic neuroreceptors primarily involved with excitation. They are located in the peripheral vascular beds, on the arteriole side, and control the sphincters (round muscles) of the bladder, intestine, and the iris of the pupil. Anaerobic metabolism The phase of glucose metabolism that does not utilize oxygen, in which the cell changes glucose into pyruvate acid, which is in turn converted into lactic acid. Alpha2 adrenergic receptors Sympathetic neuroreceptors found in the gastrointestinal tract where they decrease bowel motility, via relaxation of the smooth muscles within the intestinal walls. Alternative hypothesis A result in a research study indicating the treatment is a plausible explanation for a change. Alternative medicine Techniques other than traditional western medicine people may attempt for a more natural treatment, such as use of megavitamins, therapeutic massages, chiropractic medicine, and acupuncture. Alveoli A large collection of small sacs in the lung that provides a larger surface area for gas exchange than if the lung were made up of a single large sac; singular is alveolus. Analgesia A condition where the patient does not feel pain yet remains conscious. More importantly, the patient retains his or her protective reflexes. Analgesics Medications that relieve pain by inhibiting the synthesis or release of prostaglandins or stimulating opiate receptors (opiate agonists). Anaphylactic response An exaggerated immune response that can lead to severe airway compromise and/or cardiovascular collapse secondary to relative hypovolemia. Anaphylatoxins Substances that increase the degranulation of mast cells and attract other white blood cells (leukocytes) to the site. Anasarca Total body edema. Ambulatory Able to walk. Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) A law that prohibits discrimination based on disability in hiring, promoting, training, and retiring. AMPLE A mnemonic used to determine a patient’s past medical history, consisting of questions about allergies, medications, past medical problems, last oral intake, and events preceding the incident. Amplitude modulation (AM) When modulating an audio signal, changing the wave’s height. Anemia Condition in which the blood is lacking red blood cells, hemoglobin, or volume. (How to check) Anemic hypoxia A low hematocrit, or other red blood cell abnormality, that can lead to oxygen deprivation at the cellular level. 5 Anesthesia A lack of sensation, painful or otherwise. Anesthetic drugs primarily induce anesthesia by interfering with or blocking nerve conduction. Apical pulse The pulse rate at the chest. Angulated Describes an extremity where the bone is obviously fractured and displaced at an abnormal angle. Anorexia nervosa A psychiatric illness involving problems with self-image characterized by self-starvation and bulimia. Anoxia Hypoxia of such severity that permanent damage results. Antagonist A drug or other chemical that interferes with the physiological action of another substance, especially by combining with and blocking its nerve receptor. Antecubital fossa (AC) A triangular cavity of the elbow joint that contains a tendon of the biceps, the median nerve, and the brachial artery. Apologize An admission of fault or error accompanied by a request for acceptance of that admission. Apoptosis A normal physiological process in which old or damaged cells are destroyed so new ones can take their place. Appeal A request for an appellate court to change the decision issued by a trial level court. Artifact A disturbance in the isoelectric line of an ECG as a result of outside interference with the signal. Anticholinergics Drugs that block acetylcholine from binding to either muscarinic or nicotinic receptors and stop parasympathetic activity. Antigens Foreign proteins found in bacteria. Antimetabolites Drugs that prevent enzymes from stimulating a cell’s metabolism. Antitussive A cough suppressant. Anxiolytics CNS depressants that reduce apprehension, fear, and anxiety. Arytenoid One of three separate cartilaginous structures in the aryepiglottic folds that are attached to each other and other structures by ligaments as well as the intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of the larynx. Aortic stenosis A condition in which the leaflets of the aortic valve become scarred over time and the pathway through the valve narrows. Ascites Accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity. 6 Assault An intentional tort involving a threat of violence, either physical or verbal. Asthma A chronic lung disorder marked by recurrent airway obstruction and labored breathing. Atrioventricular (AV) node A small mass of specialized cardiac muscle fibers, located in the wall of the right atrium of the heart, that receives heartbeat impulses from the sinoatrial node and directs them to the walls of the ventricles. Ataxia A disequilibrium in one’s walk that resembles a drunkard’s stagger. Atherosclerosis The underlying pathology of coronary artery disease, which starts as a streak of fat (cholesterol) on the walls of an artery. The fat infiltrates into the wall of the artery and forms a fatty lesion. Atropine A parasympathetic blocker that decreases vagal response. Augmented leads A modified unipolar limb type made from combining the lead type and the positive electrode location (i.e., augmented voltage right or aVR, augmented voltage left or aVL, and augmented voltage foot now called aVF). Atrial diastole State during the cardiac cycle in which the atria are at rest. Atrial kick The active contribution of blood to the ventricle by the atria during the cardiac cycle. Auscultation An assessment performed by listening, typically using a stethoscope. Atrial systole State in which the atria contract during the cardiac cycle. 7 Autoimmune response An immune response triggered by some infections that causes damage to the host. Bachmann’s Bundle A special pathway the SA node uses to communicate with the left atrium. Automatic answers Short, single-word responses such as “yes” or “no” given in reply to closed-ended questions. Bacterial contamination Infection of blood products often due to contamination during the blood collection process, which can lead to septic patients following transfusions. Automaticity A cell’s ability to generate its own action potential. Automatic transport ventilators (ATV) Mechanical devices that deliver a specified volume of respiratory gas. Balanced anesthesia Process of using a combination of anesthetic agents—some inhaled and some injected intravenously—to minimize the side effects that occur with using only one particular anesthetic agent. Barotrauma Physical damage to tissues, or an injury caused by an imbalance between pressures in the environment and those within the body. Autonomic nervous system The body system that maintains the involuntary, yet essential, life-preserving functions such as digestion. AV block An interruption of AV conduction that can be indicative of disease or ischemia at the level of the AV node. AVPU A technique used to report the patient’s general level of consciousness. A stands for alert, V stands for responsive to voice, P stands for responsive to pain, and U stands for unresponsive. Axis The major direction, or vector, of the energy of depolarization in the heart. Barrel The shaft of a syringe. Base Atoms that lack a proton and therefore want to accept protons from an acid in order to become electrically balanced; a substance with a pH value greater than 7. Baseline vital signs An initial set of vital signs taken from the patient against which all subsequent vital signs are compared to check for changes. Basic life support (BLS) The early assistance given to patients in the field, such as CPR, oxygen, and suction. Axis deviation Any situation in which the heart’s axis is not normal. 8 Battery An intentional tort involving unwanted touching. Behavioral emergency Abnormal or bizarre behavior that may include violence or threats of violence. Beneficence A belief that the physician’s actions are acts of mercy and charity, a good act performed for people at a time of need. Benign Something that will not harm or threaten health. Benzodiazepines Medicines that help relieve nervousness, tension, and other symptoms by slowing the central nervous system. These drugs are short acting, share the characteristics of the other benzodiazepines, and have been studied in the prehospital environment as a sole agent to facilitate intubation. Best practices Those actions which have led to the most desirable outcomes in the past. Beta1 adrenergic receptors Sympathetic neuroreceptors that cause the muscle of the heart, the myocardium, to beat harder and stimulate the heart to beat faster. Beta1 adrenergic receptors are also found in the kidneys where they cause the secretion of renin. Beta2 adrenergic receptors Sympathetic neuroreceptors that act upon the smooth muscles found in the bronchial walls, the level of the terminal bronchioles, and cause bronchodilation. Bilateral Relating to both the left and right sides. Bioavailability The difference between the amount of a drug administered and the amount that is bound and unavailable for use. For example, imagine an aspirin pill with 325 mg of active ingredient is swallowed, and then after various factors come into play, only 150 mg is free and unbound in the blood plasma. Thus, less than 50% of the medication is bioavailable. Bioethics A form of applied ethics—that is, ethics applied to the medical situation— which creates a set of guiding principles for the medical practitioner. Biological death Death associated with irreversibility, meaning that any efforts to prolong life would be futile. Biotransformation A detoxification process in the body that simply transforms a drug—by oxidation, hydrolysis, or reduction—into a water-soluble compound which can be excreted in the urine. Bipolar leads Use of two electrodes—one negative and one positive—to measure the electrical potential between the leads’ electrodes. Beta-blockers Medicines that block the sympathetic nervous system action at the Beta receptors. Beta-selective Drugs that preferentially targets either Beta1 or Beta2 receptors. Bevel An angled surface of a needle point designed to quickly pierce the skin with a minimum of pain. Bigeminy Condition in which an ectopic complex occurs at every other complex. Blastocyst A hollow, fluid-filled ball formed by the zygote. The cells inside of the blastocyst will form the human, whereas the cells on the outside will form a protective covering that eventually develops into the placenta. 9 Bleb(s) A small blister created when injecting medication, which is about the size of a mosquito bite; a change in the cell wall membrane. Body armor A form of personal protective equipment used to protect the Paramedic from thrown objects or projectiles like bullets. Blind insertion airway device (BIAD) An airway management tool that is placed blindly and provides an airway that is superior to face-mask ventilation, yet is not as protective as an endotracheal tube. Blocking behaviors Self-protective behaviors that inhibit free dialogue with the Paramedic. Many of these blocking behaviors are manifestations of psychological defense mechanisms. Blood bank Location where donated blood and blood products are evaluated and stored for future transfusions. Blood-brain barrier Tight slit junctions in the capillaries of the brain which prevent toxins and chemicals, including drugs, from easily passing into the brain. Blood chemistry A study of the blood’s chemical composition, such as its level of electrolytes. Blood pressure A measure of the pressure within the blood vessels that make up the circulatory system. The pressure will vary depending upon the type of vessel and the phase of heart contraction. Blood-typing Classifying blood as A, B, AB, or O based on antibodies. 10 Body habitus One’s physique or body build. Body language The transmission of a message by nonverbal visual cues. Experts suggest that 70% of any spoken message is conveyed by body language. Body substance isolation Protection worn to keep a patient’s body fluids from coming in contact with the Paramedic, such as latex gloves. Bronchial sounds Lung sounds auscultated over the larger airways that are louder and sound like air rushing through a hollow tube. Bronchoconstriction Narrowing of the airway’s lumen. Bronchodilation Widening of the airway’s lumen. Bronchospasm Temporary narrowing of the smaller air passages of the bronchi due to violent, involuntary contraction of the smooth muscle of the bronchi that sometimes accompanies a respiratory infection. Bolus A concentrated volume of fluid infused rapidly over several seconds or minutes. Bronchus Either of the two primary divisions of the trachea that lead into the right or left lung; plural is bronchi. Borrowed servant doctrine Situation in which the Paramedic in charge of an emergency is responsible for the actions of those Paramedics working in a subordinate role. Bounce A radio wave phenomenon that occurs whenever a short wave strikes a reflective surface and is redirected in another direction. Bradycardia A heart rate that is under 60 beats per minute for an adult or below the lower limit of normal for a child. Bradykinesia Extremely slow movement. Brain dead A state in which an electroencephalogram shows zero brain activity, indicating brain death. Breach of duty Situation in which a Paramedic fails to perform patient care in conformance with the standard of care. Buffered Actions taken to render an atom neutral (not to have an electrical charge). Bulimia Eating disorder characterized by bingeeating and then purging via laxatives or vomiting. Breakthrough seizure An unexpected epileptic seizure in a person who has had good seizure control, which occurs when the drug level in the plasma drops below the therapeutic level. 11 Bundle of His A wide, thick group of cardiac muscle fibers that conducts an electrical impulse to the interventricular septum. Capsule Medicinal powder placed within a gelatin casing that generally makes it easy to swallow and keeps it from easily dissolving in the water-based saliva of the mouth. Cardiac action potential The electrochemical activity of the heart’s individual cells. BURP technique A method to improve laryngoscopic view through backward, upward, and rightward pressure. Butterfly IV catheters A throwback to the days of steel needles, in which short steel needles are embedded into a plastic anchor device that has wings, like a butterfly. Calibration Process used to assess the accuracy of the ECG monitor, in which the Paramedic compares the ECG machine’s operation against standard settings. Cardiac cycle A single contraction (one heartbeat), during which blood flows through all four chambers of the heart. This contraction includes an entire sequence of events from atrial filling through ventricular filling and ejection. Cardiac monitor A device that shows the electrical and pressure waveforms of the cardiovascular system; the ECG oscilloscope. Capacity The mental ability to understand what one is being told. Capillary refill A measure of the patient’s ability to perfuse the extremities with oxygenated blood. Capnography The process of tracking the carbon dioxide in a patient’s exhaled breath, which enables Paramedics to objectively evaluate a patient’s ventilatory status. Capnometry The determination of the end-tidal partial pressure of carbon dioxide. 12 Cardiac output The volume of blood pumped out of the left ventricle with each contraction. Cardiac skeleton A fibrous matrix to which the muscles, valves, and rings of the myocardium are attached and that separates the atria from the ventricles. Cardiogenic shock Problems with the heart that lead to its failure to pump. Cardioselective Beta-selective drugs that only affect the heart. Carina Level of the 5th thoracic vertebrae; an anatomical part, ridge, or process. Case-control study An observational study method in which the Paramedic compares cases—those patients with the disease—to controls—those patients without the disease—and then examines the procedures performed on both to see if there was an association between outcomes. Catecholamines A classification of very potent adrenergic agonists that cause a direct response from the adrenergic receptor. Carotid bruit A whooshing sound heard in a carotid artery that has plaque buildup on the artery walls. Carotid pulse A measure of the beats produced by blood flow taken in the anterior neck. Cell An area that a mobile radio transmission tower services for cell phone calls. Cell-mediated immunity Immunity that results from the activity of T lymphocytes. Cellular telephones Low-powered wireless transmitters (radios) that work within close proximity to a radio tower. Cellulitis A skin infection. Cell wall membrane A porous semipermeable dual layer lipid–protein matrix that makes up the outside of a cell. Celsius scale A method of measuring temperature based on a system of 10 in which water freezes at 0°C and water boils at 100°C. Carrier squelch A type of squelch control that eliminates background static during pauses in a radio transmission, essentially muting the radio between transmissions and thereby improving the message’s overall quality. Case law Law established by previous judicial decisions. Case report An example of a descriptive study Paramedics use to report interesting or unique cases, which allow other Paramedics to gain insight into a problem. Central nervous system depressants Drugs that produce a state of reduced central nervous system activity. Central venous pressure (CVP) A measurement used to assess a patient’s hemodynamic status. Cerebellum The portion of the brain responsible for coordination of muscles and balance. Channel crowding Situation in which several agencies share the same radio frequencies. Chart audit A system of quality review performed retrospectively in which the Paramedics reviews the chart against care standards. 13 CHEATED A mnemonic for an EMS-specific, user-friendly documentation method highlighting chief concern/complaint, history, examination, assessment, treatment, evaluation, and disposition. Chemical hiatus Situation in which the drug level in the body drops below the therapeutic level before the infusion has assumed dominance. If left untreated, a potentially lifethreatening return ventricular ectopy could occur. Chemical name A description of a drug according to its elemental chemical makeup and molecular structure. Chemotactic factors Chemical messengers released by mast cells that attract specific leukocytes (white blood cells) to the injury site. Chemotherapy Use of drugs to combat infections and diseases, most notably cancer. Chevron Method for securing a catheter hub that involves slipping the inverted tape, sticky side up, under the hub until it adheres to the hub, then crossing it over the hub. Chief concern or complaint (CC) The main reason for which the patient is seeking medical care. Cholinergic transmission The transmission of a nervous system signal using acetylcholine as the neurotransmitter at the motor endplate. Chordae tendinae Strong cords of connective tissue that connect the mitral valve to the papillary muscle of the heart’s left ventricle. Chest leads Leads in which the exploring electrode is placed on the chest and the other is connected to one or more limbs. Choreography The ability to organize a team’s efforts in order to deliver appropriate interventions in a timely manner. Chromosomes A double helix of DNA that carries genetic information. 14 Chronotropy To make the heart beat faster. Circumflex (Cx) A minor branch of the left coronary artery that bends around to the left side of the heart and provides blood to the lateral wall of the left ventricle. Clock method Procedure used to determine the infusion rate in which the Paramedic mentally visualizes a clock with a sweep hand pointing out the drug infusion rate. When the sweep hand is at the 15 second point, it represents 1 milligram of drug at 15 drops per minute or 15 milliliters an hour. When the sweep hand is at the 30 second position, it represents 2 milligrams of the drug infusing at 30 drops per minute, and so forth. Civil law The legal system designed to handle cases not of a criminal nature, often involving business transactions, such as contracts, torts, estates, trusts, wills, real estate matters, commercial matters, and grievances against the government. Clarification Communication technique in which a Paramedic asks the patient to restate the message in other words. Climacteric An age-related decrease in sex hormone production that occurs in both men and women. Clinical death The absence of vital signs. Clinical death is characterized by unresponsiveness to loud verbal and painful stimuli, absence of breathing, and an absence of a central pulse. Clonic Repetitive muscle contractions during a convulsion. Closed-ended questions Questions that generally start with words like “do,” “is,” or “are” and require the answer to be a short, direct reply—usually just “yes” or “no.” Closed-ended questions are used when specific information is needed quickly. Clot tubes A red top blood sample tube that contains no additives or preservatives to prevent blood clotting. Coagulation The thickening process through which the blood makes clots. Clinical decision making The process of systematic analysis and critical thinking the Paramedic uses to make clinical decisions that will be incorporated into a patient’s treatment plan. Clinical trial Experimental medical research process in which subjects are assigned at random to either the treatment group or to the non-treatment group (i.e., those receiving standard care [control group]). 15 Coagulation cascade The process the body uses to manufacture fibrin and fibrinogen. Colloid Blood substitutes that contain proteins and are capable of both pulling fluids from within the interstitial space into the circulation (to help augment the circulating volume) and remaining within the bloodstream for a prolonged period of time (to help maintain the circulating volume). Colorimetric device Encapsulated pieces of litmus paper over which an exhaled breath flows. When carbon dioxide is in the presence of water, it forms carbonic acid; the pH sensitive litmus paper in the colorimetric device detects this acid and changes color. Coagulation factors Proteins which act to attract platelets to each other to build platelet plugs. Additionally, coagulation factors are key to the production of fibrin and fibrinogen, two materials that serve to solidify and stabilize the platelet plug, making it impermeable to liquid. Coagulative necrosis Condition in which muscle cells die, such as in myocardial infarction, the skeleton of the cell remains, and the tissue remains firm. Coded (or tone) squelch Sometimes called private line, a type of squelch control that permits the radio to receive only the intended signal by eliminating reception of nearby broadcast messages and only accepting signals with the correct code. Cognitive restructuring Action taken to reframe the brain’s interpretation of a stimulus so that it is nonthreatening. Cohort study An observational study method that examines patients who have been exposed to a treatment and compares them to a group that was not exposed to the same treatment. The patients are followed to determine outcomes. Cold maceration Process of letting medicinal herbs steep in cold water. 16 Combining forms Creating a word by placing two or more roots together, separated by a vowel, to explain a complex process. For example, the term “cardiomyopathy”, meaning disease of the muscle of the heart, is made up of “cardia-” (meaning heart), “my” (meaning muscle), and “patho” (meaning disease), with the letter “O” separating the roots “cardia”, “my”, and “patho.” Command presence The ability to present oneself as the person of authority. Commercial ambulance services For-profit EMS services that provide interfacility medical transportation as well as emergency medical services to patients. Many of these commercial ambulance services originated from the funeral homes that previously provided the service. Communications Act of 1934 A resolution which states that the President of the United States has control over all government radios and that the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has control over the civilian use of radios. Complete heart block Obstruction of electrical signals through the AV node or at the bundle of His, in which case pacemakers lower in the heart at the level of the bundle of His, bundle branches, or even the ventricular myocardium will take over as the pacemaker. Communications specialists (COMSPEC) Enhanced 9-1-1 staff that dispatch emergency responders to people who are unable to speak or who have lapsed into unconsciousness. Comprehensive Drug Abuse Prevention and Control Act of 1970 (Controlled Substance Act) A law that expanded the Drug Enforcement Administration’s authority to include schedules of potentially dangerous and addictive drugs that had special restrictions. Concealment Any object that blocks the pursuer’s vision of the Paramedic, although it does not offer physical protection. Community-based EMS Volunteer (nonprofit) EMS squads that operate independently of local fire departments or hospitals. Competency assurance The necessity of the Paramedic not only to maintain minimal skills and an adequate knowledge base, but to continue to remain current with updates to EMS. Concentration gradient The difference in concentration between two solutions in different areas (i.e., on two sides of a membrane). When a concentration gradient exists, the higher concentration will diffuse across the membrane to the lower concentration solution until a balance is reached. Concept formation The inductive logic process of forming ideas about what is causing a patient’s condition based on the patient’s history and the Paramedic’s knowledge base. Complementary medicine See Alternative medicine. Complete blood count (CBC) The quantity of each type of blood cell in a given sample of blood, often including the amount of hemoglobin, the hematocrit, and the proportions of various white cells. 17 Conduction system Specialized cardiac cells designed to carry on the heart’s electrical rhythm. Constitutional signs/symptoms General nonspecific findings, such as fevers, unexplained weight loss, night sweats, chills, headaches, nausea, and vomiting, that are often common to all sick patients. Contiguous leads Situation in which two or more leads look at the same wall of the left ventricle. Conductivity The ability of an electrical stimulus to be transmitted from cell to cell. Congestive heart failure (CHF) The heart’s inability to pump strongly enough to completely meet the body’s needs for oxygen and nutrients. Conjunctiva The mucous membrane that lines the inner surface of the eyelids. Continuous infusion A volume of fluid evenly administered over the course of a period of time (i.e., an hour). Continuous quality improvement (CQI) An ongoing process of review and reengineering, in order to refine a process and improve its delivery. Contractility The cardiac muscle fibers’ ability to shorten or contract. Contributory negligence A legal assertion that an action, although not directly causing an injury or problem, nonetheless made it worse. Conscious sedation The first stage of anesthesia where the patient does not feel pain but is awake enough to maintain protective airway reflexes. Constitutional examination An evaluation that assesses the patient’s general appearance. 18 Cormack-Lehane grading system A quantitative measure system that grades the view of the glottic opening by how much is occluded by the tongue— Grade I is a clear view of the entire glottic opening whereas IV is visualization of the tongue or soft palate only. Proper patient position and external laryngeal manipulation can improve the view by one to two grades. Cost–benefit ratio A classic economic analysis that asks the question of whether it is advantageous (i.e., cost-effective) to take a particular action or make a change in a procedure. Costal margin The lower edge of the chest (thorax) formed by the bottom edge of the rib cage. Costovertebral angle Area located over the lower ribs just medial to the posterior axillary line. Countermeasures Steps that could be effective in reducing injury. Couplets Situation in which two ectopic complexes occur together. Coronary artery disease (CAD) The series of events that leads up to and includes myocardial infarction. Cover Any object that cannot be penetrated by a projectile, from bullets to frying pans. Examples of cover include telephone poles and even fire hydrants. Coronary circulation A special set of arteries and veins that supplies blood to the muscles of the heart. Crenate Dehydration and collapse of a cell. Crepitus Crackling or popping sounds under the skin or near joints. Cortisol A glucocorticoid hormone that stimulates the production of glucogen from amino acids and fatty acids contained in lipids. 19 Cricoid pressure Also called the Sellick’s maneuver, a procedure that involves identifying the cricoid ring and gently applying approximately 10 pounds of pressure in a posterior direction throughout airway management; from the onset of ventilation until completion of intubation. Crowning Part of the childbirth process in which the infant’s head begins the passage into the birth canal, indicating delivery will occur within several minutes. Criminal law Laws dealing with violations of a person’s duties to the community and for which the written law requires the person to provide satisfaction. Critical incident response team (CIRT) Individuals called in during an acute stress situation to meet with the affected personnel, typically front-line responders. Critical incident stress debriefing (CISD) An intervention to defuse stressors in an acute stress situation, such as a line-of-duty death, serious injury of a coworker while on-the-job, and post-event suicide of a fellow responder. Cross-match Comparing a donor’s blood to a patient’s blood to determine compatibility of antibodies and type. Cryoprecipitate The protein portion of plasma made up of concentrated clotting factors. Crystalloids Electrolyte-containing fluids Paramedics use during trauma resuscitation that, when dehydrated, create crystals. Cultural competence A Paramedic’s ability to function effectively within the diverse populations that she serves. Culture The culmination of life experiences in a locality or region that affects the way a person thinks and behaves. Cyanosis A bluish hue that develops when the patient develops a decreased oxygen level in the blood. Cross-sectional survey A snapshot of a certain aspect of a population at a given moment in time that the researcher is interested in, obtained by means of observation. Cytopathic Manifestations of disease at the cellular level. Cytoplasm A fluid mixture inside a cell, primarily made up of water and organelles, which has a specific cellular function(s). 20 Decoction Process of bringing water to a boil then steeping medicinal herbs in the water (like one would steep a teabag), then drinking the resulting solution. Dangerous instruments Any object that could be used, under the right circumstances, to produce serious injury or even death, such as a broken bottle or box cutter. Decode To interpret and understand a message. Decubitus ulcers Also known as pressure ulcers, tender or inflamed patches that develop when skin covering a weight-bearing part of the body is squeezed between bone and another body part, or a bed, chair, splint, or other hard object, creating pressure or friction. Data and Safety Monitoring Board (DSMB) A group of individuals who are not directly involved in a research study but who can nonetheless make an objective decision about the research based on the merits of the data. Data dredging Sometimes called data mining, it means conducting research by searching through a database without a predefined scientific question in mind (i.e., without a predefined hypothesis). Dead airtime A period in which no radio transmissions are made on a particular channel. Deadly weapons Objects that are, by design, intended to inflict death or disability (e.g., a gun or a knife). Deep tendon reflexes (DTRs) Involuntary muscle contraction in the muscle associated with a tendon. Defasciculating dose A small dose of a nondepolarizing paralytic which, when administered before administering a certain drug, prevents the fasciculations associated with that drug. Defensive medicine The practice of a Paramedic performing a wide variety of random tests to limit liability or criticism from the medical director, rather than performing just those tests that benefit the patient. 21 Deontology Duty-based ethics in which the decision as to whether an action is right or wrong is based on principles and not upon the consequences. Defusing An immediate intervention intended to avert acute stress reactions among the emergency responders. Depolarization A cascade of ionic changes at a cell wall that occurs as electrolytes transfer across the cell in an attempt to balance (neutralize) the charge. Degranulate The process of breaking down or losing granules. Delirium A sudden change in mental function, usually associated with reversible metabolic derangements (e.g., hypoxia, or the toxic effects of medications). Deltoid An intramuscular injection site in the muscle that overlays the shoulder and extends downward toward the elbow, forming an inverted triangle in the process. Depolarizing neuromuscular blocker One of the two major classes of neuromuscular blockers; binds to the acetylcholine receptor and causes the muscle to depolarize or contract. Deposition Out-of-court testimony made under oath and recorded by an authorized officer for later use in court. Demobilization An opportunity to mitigate the effects of the acute stressors and to decrease the incidence of acute traumatic stress reactions. Denature To break down a protein’s complex folded structure. 22 Descriptive analysis Based on the Marriott method of analysis, a way to gather information for a thorough ECG interpretation consisting of review of the rhythm, rate, width of the QRS complex, and atrial activity. Descriptive study Documentation that simply states that a condition or situation exists without trying to offer an explanation. Detailed physical examination A more thorough evaluation given to low-priority patients with whom the Paramedic has more time. Developmental milestones The skills and abilities a child achieves at certain ages in his or her life, measured against the norms of other children. Dextrocardia Condition in which the heart and lungs in a body are opposite their normal position while the abdominal organs are in their usual position. Diagnosis Identification of a disease or disorder based on available symptoms and testing. Diagnosis-related groups (DRG) Groups of patient populations with the same or similar diagnosis, who may benefit from similar treatments. Diaphoretic To be profusely sweaty. Diaphragm A large, thin, dome-shaped muscle that divides the abdomen from the thorax. Diastolic blood pressure The minimum blood pressure measured during diastole when the heart relaxes and fills. Digital intubation An endotracheal intubation technique that uses the Paramedic’s hand to identify laryngeal structures and to guide tube placement. Diminished autonomy Standard that states any person who is mentally incapable of making an informed decision (e.g., by virtue of age or infirmity) cannot willingly consent to participate in research. Diphasic A wave that begins as a positive deflection then becomes a negative wave or vice versa; having two phases. Diplomacy To calmly and thoughtfully resolve issues without angering the parties in the dispute. Direct questioning An interviewing technique in which a Paramedic asks simple, unambiguous questions of the affected party about the situation at hand. Disclosure An open dialogue between patient and provider in which the provider tells the patient about the procedure, including its attendant risks, and recommends the procedure. Disease An abnormal change in the function of cells, tissues, or organs. An example of each is cancer in cells, emphysema in tissues, and acute myocardial infarction in organs. Disorder A physiological deviation from a normal homeostasis. Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) A condition in which, after initial blood clotting factors are partially consumed by massive coagulation throughout the body, the remaining clotting factors are insufficient to protect the body. 23 Distention An abnormal expansion, such as in a vein or the abdomen. Distracting injury Situation in which a pain (often dull visceral pain) is overshadowed by another more intense pain from another injury; for example, a fractured femur taking attention away from chest pain. Distress A negative response to stimuli that overcomes the body’s innate defenses and serves as the body’s maladaptive reaction to stress. Distributive shock The third category of the Hinshaw–Cox shock classification, which is descriptive of the problem of poor blood distribution. Distributive shock includes shock caused by the widespread vasodilatation seen with severe infections and during anaphylactic reactions, to name a few causes. Do-Not-Resuscitate (DNR) order Sometimes called a Do-Not-Attempt-Resuscitation (DNAR) order, a directive from the patient that artificial means of life support should not be used, generally in cases when a condition is terminal and artificial life support will just delay the inevitable. DOPE A mnemonic Paramedics use to help remember the causes of problem intubations. The D in dope stands for displaced endotracheal tube; the O stands for obstructions of the endotracheal tube, such as a mucous plug; the P suggests the possibility of a pneumothorax; and the last letter, E, indicates equipment failure. Dormant A state of biological rest a disease may stay in until favorable conditions exist for it to reanimate. Dorsalis pedis (DP) pulse A measure of the beat created by blood flow measured over the dorsum of the foot. Diuretics Medications that cause the increased loss of fluid and salts from the body. Divine command ethics Extrinsic ethics based upon a higher authority, such as the Bible’s Ten Commandments or Buddha’s Four Noble Truths and Eight Paths to Righteousness, in which that higher authority has predetermined what qualities a virtuous person would have and calls upon the person to display those virtues through correct action. Dominance A condition of superiority, as in when the actions of one bodily function are faster than or overpower the actions of another. 24 Dorsiflex The ability to raise toes above the horizontal toward the tibia. Dorsogluteal (DG) The most common intramuscular injection site, located in the gluteus medius. Dry powder inhalers (DPI) Respiratory device that uses a solid drug pulverized into microfine particles for inhalation. Duplex A radio that uses two frequencies—one to transmit and one to receive—so that an operator can talk and listen at the same time, permitting more rapid communications. Dose The amount of drug needed to produce the desired effect. Double-blinded randomized clinical trial (RCT) A prospective scientific study that controls known and unknown variables, leaving only one variable to be manipulated. Subjects are then chosen at random to be included in either the experimental treatment group or in the control group. Double-blind study A research study in which both the researcher and the participants are unaware of which group the subject is in. Downregulation A decrease in the number of cell receptors in a cell due to changes in hormone levels. Dress-up philosophy Technique in which Paramedics add barrier devices for protection as the situation warrants. Drug Any material which, when injected, ingested, inhaled, or absorbed into the body, is used for the diagnosis, treatment, or cure of a disease or condition. Drug decline The idea that while a drug moves through the body various forces and organs are weakening it, reducing its effectiveness. Drug reservoir A type of drug depot in the body, created when drugs bind to certain substances, that stores the drug until it is needed. The effect of a drug reservoir is to prolong the drug’s action within the body. Duration The length of a QRS complex wave. Duty to act An element of a tort that implies a Paramedic must act whenever called upon to perform patient care (i.e., the Paramedic is “on duty”). Dyskinesia Lack of ability to control body movements. Dysplasia Situation in which there are too many new, or immature, cells being produced that are not functional. Dysrhythmias An abnormality of the electrical activity in the heart. Ecchymosis Blood from ruptured vessels moving into other tissues; bruising. ECG interpretation A systematic approach used to rapidly and accurately analyze an ECG rhythm strip. ECG rhythm strip A printed hard copy from an ECG machine of at least one lead that shows the ECG complexes over a long period of time allowing Paramedics to analyze the rhythm. Echo technique Communication method in which the physician gives an order and the Paramedic, in order to ensure it’s been interpreted correctly, repeats the order back to the physician exactly as received. 25 Ecological study Sometimes called a correlational study, this type of research design serves to provide information about trends and rates of disease within a population, often cited as X number of cases of Y disease per 1,000 or per 100,000 of Z population. Elastic gum bougie A device made entirely of wound gum rubber, with a hard, smooth, and round plastic tip, that resembles a very long stylet. The device is directed through the vocal cords and into the trachea to serve as a guide for an endotracheal tube. Ectopic To occur in an abnormal or atypical position. Ectopic beats Aberrant cardiac beats resulting from abnormal automaticity. Ectopic focus Any complex that occurs outside of the sinus of the heart’s cavity. ED50 The dose of a drug that effectively creates the therapeutic effect in a majority of patients. Edema A dramatic fluid buildup in the body’s tissues. Edentulous A state of having no teeth. Efficacy The power to produce an effect; the ability of a drug to realize its full intended therapeutic effect. Ejection fraction The percentage of blood pushed and squeezed out of the heart, typically 60% to 75% of the end diastolic volume. Electrical alternans Situation in which every other ECG complex has alternating amplitude (i.e., the one QRS complex is smaller when compared to the next). Electrical storm Multiple recurrent episodes of ventricular fibrillation. Electrocardiogram A device used to monitor cardiac rhythm. Electromagnetic interference (EMI) Disruptions of an ECG signal caused by the flow of electricity through an electric device, such as a radio, cellular telephone, or television, which creates an electromagnetic field. Electromyographic signal (EMG) An electrical current recorded by the ECG any time a muscle contracts, appearing as narrow rapid spikes on the ECG monitor. Electroporation The effect of electrical current passing through the tissue. Elixir A sweetened tincture used for medicinal purposes. 26 Emancipated minors A special class of youths who are below the age of majority but are permitted to give informed consent, provided they are capable of understanding the consequences of their decisions and that they are not impaired by alcohol or drugs. These include married persons, single parents, the military, and youth living on their own. Embryo An unborn child at any stage of development between conception and birth. Emergency doctrine Policy invoked when family members or guardians are not present that states if a parent was present the parent would want the child treated and transported to the hospital. The emergency doctrine is usually invoked only in cases of life- or limbthreatening emergencies. Emergency exception A situation in which a care provider performs a procedure without fully explaining it to the patient because the delay created by a lengthy explanation might compromise the patient’s health. Emergency medical dispatch (EMD) A dispatch algorithm in which the communications specialist interrogates the caller, gives prearrival instructions, and uses preset criteria to make a response determination before dispatching the appropriate EMS responder units. Emergency medical responder (EMR) An EMS provider who is expected to render lifesaving care with minimal equipment; for example, a police officer or fire fighter providing rapid response. Emergency Medical Services (EMS) The field of medicine that involves transporting the sick or wounded to medical care and providing treatment to patients prior to their arrival at the hospital. Emergency Medical Technician-Ambulance A national standard curriculum established in 1969 for the training of ambulance drivers/attendants in new skills and lifesaving techniques. Emergency Medical Technician (EMT)–Basic Part of a team that responds to the emergency scene, typically aboard an ambulance, and is trained to provide initial care on scene as well as medical care to the patient while in transit to the hospital. Emergency vehicle operator (EVO) Any individual who operates a vehicle en route to a response call. Emergent An assessment classification in which the patient’s condition unexpectedly developed and is in need of immediate medical attention. Empathy An emotional understanding of the patient’s feelings; to be able to understand what it is like to walk in the other person’s shoes. Empiric therapy Treatment based on initial observations obtained during the primary assessment. EMS Act of 1973 Federal legislation that delineated the 15 aspects of an EMS system that needed improvement including education (both public as well as provider), improved communications (including public access), and system evaluation, but offered little money to help make those improvements. 27 EMS Agenda for the Future Overall framework which suggests that EMS will be more intimately intertwined with public health, as well as public safety, over time and continue to evolve along with health care. EMS Education Agenda for the Future The plans that emerged from the 1996 meeting of over 30 EMS organizations held with the intent of implementing the educational portions of the EMS Agenda for the Future. Emulsions Finely pulverized particles placed into oils, such as cod liver oil. Endotoxins Poisons produced by bacteria during an infection that stimulate chemical mediators to affect the hypothalamus. Endotracheal tube The basic tool of endotracheal intubation which provides a conduit for oxygenation and ventilation between the patient’s lungs and the ventilator (person or machine). End-tidal carbon dioxide (ETCO2) A standard method of measurement and monitoring carbon dioxide levels used for both confirming endotracheal tube placement and monitoring patient status, ventilation, and continuing tube placement. Endocardium A single-layer thick sheet of epithelial cells that act as a lining in the heart; the heart’s innermost layer. Enhanced excitability The ability to respond to a much weaker stimulus. Endocrine shock A fifth classification of shock, which recognizes the importance of hormones in maintaining homeostasis. The classic endocrine shock is hypoglycemic shock. Endogenous Originating within the body. Endorphins Neuromodulators that reduce the sensation of pain and affect emotions by attaching to opiate receptors on the neuron, which in turn inhibit neural activity. 28 Enteral Administration of drugs through the gastrointestinal tract, either through pills taken orally or through suppositories. Enteric coating A protective coating on a tablet that permits the tablet to travel, unaltered, through the stomach and into the intestine for absorption. Environmental risk Modifiable risk factors that are a function of one’s lifestyle or occupational choice, such as farmers developing respiratory issues from their exposure to dust. Epicardium The heart’s outermost part; a part of the pericardium that is closely adherent to the heart. Equity A concept of fairness or evenhandedness. To be accepted, any change must appear to be equitable to all parties concerned. Erythema Abnormal redness of the skin caused by capillary congestion. Epidemiology The study of the causes, distribution, and control of disease in populations. Epiglottis A “U” shaped structure in the upper airway attached to the anterior pharynx between the base of the tongue and the larynx that protects the lower airway from foreign body aspiration. Erythrocytes Red blood cells that transport oxygen and carbon dioxide through the blood. Epilepsy A neurological disorder characterized by recurrent seizures that occur without known cause. Epistaxis Nosebleed. Equianalgesic Drug characteristic in which a dose of a new medication formulation has the same ability to produce analgesia as 10 milligrams of morphine. Escape mechanism A form of backup pacemaker in the heart that will continue to prompt contractions (at a slower rate) if the SA node stops sending impulses. Equiphasic A flatline pattern on an ECG machine that occurs if the differences in the flow of electricity result in a zero net difference in direction. 29 Esophageal intubation detection devices (EDD) Devices used to confirm endotracheal tube placement. Two major styles of these devices exist: self-inflating bulbs and syringe style aspirators. Etomidate A sedative that functions primarily as a hypnotic, although it also is an excellent amnestic. Eustress A positive, manageable form of stress from daily activities. Eutectic mixture of local anesthetics (EMLA) A cream that helps to reduce the pain of needle insertion, consisting of lidocaine 2.5% and prilocaine 2.5%. Esophageal-tracheal Combitube (ETC) A rescue device placed into the esophagus that allows tracheal placement. The double-lumen design allows for endotracheal as well as esophageal intubation. Ethical relativism When a majority of Paramedics agree to a specific conduct or course of action, determining that it does more good than harm, which suggests the act is ethical. Ethics From the Greek “ethos” meaning character, a system of guiding principles that govern a person’s conduct. Ethics committee A group that can help individuals, including Paramedics, deal with common ethical concerns. Ethnocentrism A view that one’s own cultural practices and customs are superior. Etiology The origin of a disease. 30 Evaluation and Management Documentation Guidelines Standardized histories that permit the Paramedic to identify diseases, disorders, and syndromes, vis-á-vis, through symptom pattern recognition, and document the medical necessity of the therapeutic services provided to the patient. Event monitor A credit-card sized device patients may use to record abnormal ECG activity that occurs very irregularly (as in days or weeks apart). When the patient senses the abnormal activity, the monitor is placed on the chest for a preset period of time. Event report Documentation following a mass casualty incident that details the situation and conditions that occurred which led to the incident. Triage tags are attached to this report. Evidence-based practice A research approach based on observed experimental results, in hopes of making the results more reliable and valid than peer reviews. Exacerbation Periodic episodes in which a chronic disease returns, or flares up. Excitability The ability to respond to a stimulus. Excited delirium A physical state a restrained patient may reach if agitated and combative in which he becomes tachycardic, hypertensive, and has hyperpyrexia. Exercise A series of physical activities, both aerobic (e.g., walking or jogging) and strength training, which is considered optimal to perform for maintaining health. Exhaustion The final, recovery stage of the general adaptation syndrome, which occurs when the body’s response is insufficient to meet the challenge of the stressor. Exogenous Originating outside of the body. Exotoxins Proteins produced by bacteria that are released into the interstitial fluid. They are then absorbed, because they are highly soluble, into surrounding cells. Expanded scope of practice Assigning additional duties and responsibilities to Paramedics beyond the scope of practice to provide health care where scarce healthcare resources exist. Extrinsic trigger A stimulus prompting an airway spasm that originates outside the body, such as pollen, dust, and mold. Exudate A collection of white blood cells and fluids; whitish discharge. Facilitation Interviewing technique in which the Paramedic nods his head in acknowledgement and says “Go on,” as well as tries to make eye contact, which may encourage the patient to continue talking about a subject. Facsimile machine A device that, using digital technology, can transmit a high-quality copy of documentation from one location to another. Exposure Situation in which blood or bodily fluids from a patient are spilled, splashed, or dripped onto or injected into a Paramedic. Exposure report A special incident report completed after an exposure that details the circumstances that resulted in the Paramedic being exposed, in hopes that a future exposure will not occur in the same manner. Expressed consent During an emergency situation, an assumption that if a patient does not object to receiving care, consent for the procedure has been given. External laryngeal manipulation A technique used to improve visualization of the glottic opening in which the Paramedic performs direct laryngoscopy with his left hand while manipulating the larynx with his right hand. Once he has an improved view of the glottic opening, the Paramedic has an assistant take over the external laryngeal manipulation, holding the larynx absolutely still. Extracellular water The water that is outside of cells. Fading Progressive weakening of a radio wave as it encounters more and more obstacles. Fahrenheit scale A standard used to measure temperature based on freezing and boiling temperatures of a water and salt solution. In this scale, water freezes at 32°F, water boils at 212°F, and a person’s body temperature is 98.6°F. Failure to thrive Situation in which a child does not grow as expected, perhaps due to psychosocial or nutritional imbalances. Fallout Situation that occurs in the airway whenever large particles carried in the air current settle out as airflow velocity is lost. 31 False imprisonment A restriction of movement or a confinement that abridges the patient’s right to freedom, such as by the use of restraints. Fibrin An elastic, insoluble, whitish protein produced by the action of thrombin on fibrinogen and forming an interlacing fibrous network in the coagulation of blood. FarMedic© An EMS course specifically directed to the rural or farm emergency. Fibrinogen A protein in the blood plasma that is essential for the coagulation of blood and is converted to fibrin by the action of thrombin in the presence of ionized calcium. Fasciculations Transient fine muscle contractions, seen after administration of a depolarizing neuromuscular blocker. Febrile non-hemolytic reaction An elevation of the patient’s temperature of 1°C from baseline within two hours of the start of a transfusion which begins shortly after the initiation of the transfusion or a new unit. It is often secondary to minor antibodies present in the recipient’s blood that cause a mild reaction when exposed to the donor’s blood. Fick principle The process of getting oxygen to the cells, which can be summed up in five key concepts: oxygenation, ventilation, respiration, circulation, and cellular respiration. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) The agency with rule-making and enforcement responsibility for civilian radio frequencies. Feedback The mechanism by which the Paramedic can ensure the message sent was the message received and decoded; that is, the message heard was the message sent. Fee for service A “pay as you go” approach to health care, with a certain amount of medical care provided gratis to the poor or uninsured. Femoral pulse A count of the beats created by blood flow in the femoral artery that is measured at the patient’s groin. Fetal alcohol syndrome Umbrella term covering a variety of birth defects caused by a mother drinking during pregnancy. Fetal hydantoin syndrome (FHS) Birth defects such as cleft lip, cleft palate, and congenital heart anomalies seen in children born to mothers taking hydantoins during pregnancy. 32 Fidelity The physician’s obligation, and therefore the Paramedic’s obligation, to keep any promises made to the patient. Field A place to enter data on a chart or form. Field diagnosis See Paramedical diagnosis . Fight or flight The body’s instinctive response to a potential life threat, either to resist it or avoid it. This primitive stress response may have been critical to the survival of primeval man, but can be unhealthy today. Fire-based EMS Using the fire service, with their combination of trained personnel, lifesaving equipment, emergency vehicles, and strategically located stations, as the platform for delivery of EMS; the predominant means of delivering EMS in the United States. Flail segment Condition that develops when two or more adjacent ribs are fractured in two or more places, which produces an unstable area of the chest that impedes normal respiration. First-due report A brief synopsis of the scene size-up obtained by the first arriving responder. First pass metabolism A chemical degradation of a drug by the liver that markedly reduces the drug’s bioavailability. Fixed-post staffing The method of resource allocation in which EMS is stationed in centrally located standing facilities, from which ambulances respond to emergencies. Fixed-wing aircraft A traditional airplane, rather than a helicopter, used by flight Paramedics to transport patients. Flashback A return of blood that may be observed in the tubing when an IV solution bag is lowered below the level of the patient’s heart, which indicates that the IV access remains patent. Flight Paramedic The most highly trained level of EMS provider; this individual transports critically ill patients from emergency scenes or other facilities to definitive care. Fluori-methane A topical refrigerant, sometimes called vapocoolant spray, that numbs the skin at the injection site in as little as 15 seconds. Flush the line A procedure in which the Paramedic runs fluid through an intravenous administration set to remove any air bubbles in order to prevent an air embolism. Focused/vectored physical examination (PE) A more detailed evaluation following the primary assessment in which the Paramedic looks for observations that the physician will most likely request. Followership A willingness to follow a leader’s direction and to support the mission, putting aside personal ambitions. 33 Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act Law that prohibits the sale of new drugs before they go through safety testing. General adaptation syndrome The body’s predictable pattern of response to stressors. Foreseeable harm Risks that can reasonably be expected as a result of a medical procedure. Frequency modulation (FM) When modulating an audio signal, changing the wave’s speed. Fresh frozen plasma Blood component formed by removing the red blood cells and platelets from whole blood. The remaining liquid component of the blood is still rich in several of the clotting factors needed as part of the coagulation system. Functional job description Tasks described in a job description that are needed to perform the functions of the job, excluding rare or marginal job functions. Functional syncytium A group of myocardial cells that act as a unit. Gain Enlargement in the size of the tracing shown on the ECG monitor screen. Gait The way a patient walks. Gallop The combination of the normal and extra heart sounds that occur with changes in ventricular filling. This produces a galloping rhythm, similar to hearing a horse gallop. Garbage can diagnosis An imprecise and overgeneralized field diagnosis the Paramedic might make that lends little direction to patient care. Gene A sequence of nucleotides in DNA on a chromosome that determines an individual’s physical characteristics. General impression A Paramedic’s overall evaluation of the patient, in which she assesses the patient’s mental status, airway, breathing, and circulation, to determine which patients require immediate transport. Generation A span of time used to differentiate advancements (e.g., the next generation of drugs). Generic name A simple name given to a drug, often listed by the manufacturer in the United States Pharmacopeia (USP). Genetic make-up Those physical characteristics that make up a person, including appearance, disposition, and so on. Genotype An individual’s genetic make-up. Gestalt A decision-making process in which the Paramedic comes to a conclusion not through a summation of symptoms but rather from patterns observed in similar situations in past practice and experience. Also referred to as the Paramedic’s “gut feel.” Glottis The space between the vocal cords. Glucagon An enzyme that breaks down glycogen into individual glucose molecules. 34 Glycogen A dual molecule in the liver and muscles that stores any glucose which is not needed immediately by the body. Glycolysis An aerobic process during which the body uses eight different enzymes to divide glucose and create a chemical called pyruvate. Glyconeogenesis The production of glucogen from amino acids and fatty acids contained in lipids. Glycoside Any of a group of organic compounds, occurring abundantly in plants, that yield a sugar and one or more nonsugar substances on hydrolysis. Good Samaritan statutes Laws that protect well-meaning people who, although they have no duty to provide care to an injured person, do so nonetheless. Governmental immunity Also called sovereign immunity, a practice in which the government is exempt from liability for torts committed by its employees except to the extent that it has consented by statute to be sued. Haddon matrix An easily understood concept map of injury causation and prevention. Using a model similar to the one used for disease, Haddon plotted the factors that cause injury across a horizontal X-axis and the stages of an injury process along the Y-axis. The result was an injury prevention matrix. Half-life (t1/2) The point when the decline of the amount of a drug in the bloodstream due to metabolism reaches 50%. Hands-off The process in which one mobile radio tower switches the transmission to another tower so that there is no interruption in transmission. Hanger Hook-like device an IV bag is hung from. Hanging the bag Process of suspending an intravenous solution for delivery to the patient. Hard-wire Use of physical transmission lines for communication rather than radio waves, i.e., wireless. Gross negligence Intent to willfully, or with reckless disregard for a patient, cause harm to a patient. Hard wire monitoring Devices that feature electrodes running from the device to the patient, causing limited mobility for the patient. Ground wave High-frequency (HF) radio transmissions that are capable of being transmitted over the land. Harrison Act A law established in 1914 that made it illegal to obtain “narcotics” (e.g., morphine) without a prescription. Guidelines General rules that provide the Paramedic with direction while also permitting use of her knowledge and experience to shape clinical decisions. Whenever guidelines are in use, the Paramedic must be willing to discuss and defend the clinical decisions. Head elevated laryngoscopic position (HELP) A patient position that places the head in extension along the atlanto-occipital joints, bringing the pharyngeal, laryngeal, and oral axes into alignment using an elevation pillow. It can also be used in patients who are unable to lay flat (i.e., CHF patients or morbidly obese patients) or to help clear secretions. Gum Sometimes called resin, a complex sugar in plants, a polysaccharide, that when moistened becomes a gelatinous material. 35 Healthcare proxy This person has a responsibility to review the medical record, consult with healthcare providers, and give consent to either initiate or to refuse care for the patient. Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) Federal legislation that has placed conditions upon all healthcare providers that protect patient privacy during claims processing, data analysis, utilization review, quality assurance, and practice management. Health maintenance organization (HMO) A managed care system that provides payments to healthcare providers at a negotiated annual per capita rate. These rates are based on practice history of the insured patients and helps to prevent fluctuations in payments, thus making expenses, costs, and budgets more predictable. Heart failure Situation in which an impaired heart cannot meet the body’s demands for perfusion. Heave To cause to swell or rise. When referring to the heart, a heave indicates the heart is beating so forcibly that the chest wall is felt to move by the Paramedic assessing the patient. Heel stick Puncturing an infant’s heel with a lancet then drawing the blood off with a capillary tube to acquire a sample. Hematocrit The volume of red blood cells in the blood expressed as a percentage. Hematoma A mass of clotted blood that forms in a swelling as a result of a broken blood vessel. Hematopoiesis The manufacturing process the body uses to create the three main solid components of blood: red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Hemicorporectomy Amputation at the waist. 36 Hemocytoblast The generic stem cell from which all other blood cells (red, white, and platelets) develop. Hemoglobin The molecule in red blood cells that accepts oxygen in the lungs and carries it to the body’s tissues to allow cellular respiration. Hemolysis The disintegration of red blood cells, resulting in a release of hemoglobin. Hemostasis The stoppage of blood flow through a blood vessel or body part. Hemothorax Collection of blood in the pleural cavity which can cause lung collapse. Heparin sulfate An anticoagulant released from the endothelium of the walls of the arteries that temporarily prevents blood clot formation in the narrowed coronary arteries. Heparin well An intermittent infusion device filled with heparin to prevent clot formation in the device. Hepatectomy The surgical removal of a portion of the liver. Hepatojugular reflux An elevation of venous pressure visible in the jugular veins when firm pressure with the flat hand over the liver. Hermeneutics The Paramedic’s ability to put himself in the patient’s situation, with all of the accompanying physical and cultural influences, in order to understand the patient better. Hernia Openings in the muscle and tissue layers that allow the an organ to protrude through the opening into another cavity. Hertz A unit of frequency measured in cycles per second. Hexaxial reference system An artificial construct created to help conceptualize the heart’s normal axis and to help determine if there is any axis deviation. Histoxic hypoxia The inability of the cells to accept or use oxygen, such as in cyanide poisoning. Holter monitoring A continuous type of ECG monitor that records the ECG activity while the patient goes about his routine work and play activities, which is often used on patients with sporadic dysrhythmia problems. Homeostasis The processes a body undertakes to try to maintain a constant state of balance or equilibrium. High-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) An advance in nasal cannula technology in which, by humidifying and warming the oxygen and using membrane technology, up to 40 LPM is comfortably delivered to the patient through a nasal cannula. High priority patients Patients with the most serious, yet treatable, conditions. They are generally transported to the hospital immediately, with further assessment being performed en route. History of present illness (HPI) A chronological description of the development of the patient’s present illness, including symptoms the patient is currently displaying, which may help the Paramedic make a diagnosis. This can be determined by asking when, where, why, and how type questions about the problem. History taking Medical questioning to determine the disorder, syndrome, or condition affecting the patient that resulted in the call for assistance. Horizontal equity Injury prevention strategy in which standards are broadly applied to all individuals equally, such as the level of a legal blood alcohol content. Horizontal leadership A leadership style that “flattens the pyramid” so Paramedic leaders work toward linking, or networking, with the members of a public safety team. Horizontal leadership emphasizes an “out and back” line of communication instead of an “up and down” line of communication and can be visualized more like a wagon wheel. Hormones The chemical messengers that stimulate the body’s organs and help to maintain the body’s internal environment. Hospice A concept of care focused on providing for the physical, emotional, and spiritual needs of a terminal patient. Hospital-based EMS An EMS system design where a hospital provides EMS services in the form of a flycar or ambulance. Hotline A telephone number dedicated to providing the caller with immediate assistance. Huber needle A beveled needle intended to pierce a stopper without coring it, thereby preventing leakage of the contents within the catheter from leaking out of the stopper when the needle is withdrawn. 37 Human dignity The right of every person to be treated respectfully, regardless of his or her station in life. Hypercarbia Condition in which the amount of bicarbonate ions in an arterial blood gas sample is greater than 30. Human rights Rights based on a commonly desired human condition (i.e., freedom from want, freedom from pain, and freedom from suffering). Human rights involve universally accepted standards of justice. Hyperlipidemia An abnormally high level of triglycerides and cholesterol which, when uncontrolled, can lead to atherosclerosis. Humoral immunity The component of the immune system involving antibodies that circulate as soluble protein in blood plasma. Hydrostatic pressure Pressure created by the force behind the volume of water in the body. Hyoid The only bone in the body that does not directly articulate with another bone. Instead, it serves as a common point of attachment for a number of muscles and ligaments that function in swallowing and airway maintenance. Hyperoxia Condition in which partial pressure of oxygen dissolved in the arterial blood gas sample is greater than 100. Hyperplasia An abnormal increase in the number of cells due to frequent cell division/reproduction which causes the tissue or organ to increase in size. Hyperpnea Deep breathing. Hyperreflexive Reflexes that are significantly more brisk than normal. Hyperresonant Percussion notes that sound similar to striking a drum, indicating an increased amount of air in the chest. Hypertension A systolic blood pressure that is above the upper limit of normal. Hyperthermia A condition that occurs if too much heat builds up in the body’s core; a body temperature above 38°C (100.4°F). Hyperacute T wave An increase in the amplitude of T waves in the leads facing cellular damage. Hypertonic Fluid that has less water and more salt (electrolytes) than the solution on the other side of a semipermeable membrane. Hypertonic fluid on the other side of a semipermeable membrane will pull fluids into itself. Hypercapnia Condition in which the partial pressure of carbon dioxide dissolved in an arterial blood gas sample is greater than 45; increased carbon dioxide levels. 38 Hypertrophy An increase in either the weight or functional capacity of a tissue or organ beyond what is normal. Hyperventilation A deeper than normal respiration that may be caused by respiratory distress, a metabolic condition, or drug overdose. Hypotonic Fluid that has more water and less salt (electrolytes) than the solution on the other side of a semipermeable membrane. In an effort to balance concentrations, the water from the hypotonic solution will cross the membrane until the two solutions are balanced. Hypnotic state A sleep-like condition often induced by a large dose of CNS depressants. Hypocapnea Condition in which the partial pressure of carbon dioxide dissolved in an arterial blood gas sample is less than 35. Hypocarbia Condition in which the amount of bicarbonate ions in an arterial blood gas sample is less than 22. Hypoglycemia Condition in which blood sugar (or blood glucose) concentrations fall below a level necessary to properly support the body’s need for energy and stability. Hypoventilation Shallow respirations that can be caused by drug overdose, head injury, or another condition. Hypokalemia The development of low sodium potassium in the blood serum. Hypovolemic A state of decreased circulating blood volume. Hyporeflexive Reflexes that are significantly less brisk than normal. Hypovolemic shock The first category of the Hinshaw—Cox shock classification, which includes shock that arises from trauma (hemorrhagic shock) but also includes other etiologies where there is a loss of circulating blood volume. Hyporesonant Percussion note that is dull in character and often indicates fluid in the lung. Hypotension A systolic blood pressure below the lower limit of normal. Hypothermia A condition that occurs if there is too little heat in the body’s core; a body temperature less than 35°C (95°F). Hypoxemia A decreased oxygen level in the blood. Hypoxia Condition in which partial pressure of oxygen dissolved in an arterial blood gas sample is less than 70; low oxygen concentration that causes cells to redirect their metabolic processes to anaerobic respiration in an effort to sustain the cell. Hypoxic hypoxia Lack of oxygen, due to an oxygen poor environment, which can lead to hypoxia. 39 Iatrogenic Adverse effects or complication that results from a medical intervention. Idiosyncratic reaction Situation in which a drug produces an unpredictable reaction that is not allergic in nature or due to overdose and resultant toxicity, but often due to the patient’s genetic make-up. Immune complex Situation in which an antibody has attached to an antigen and stimulates the complement system. Immunocompetent Capable of providing immunity. Immunoglobulins A type of protein globulin. Five types of immunoglobulins have been identified: IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG (gamma globulin), and IgM. Each immunoglobulin fits into the surface of an antigen in a key and lock fashion, linking them together. Implanted vascular access device (IVAD) A central venous catheter that has the port buried in a subcutaneous pocket under the skin’s surface. Implanting the entire device affords the IVAD the skin’s protection, which decreases the rate of infection, as well as protects the port from physical trauma. Implied consent An assumption that an unconscious patient in danger would consent to a life saving procedure if awake and capable of consenting. Incidence The number of new cases of a disease per standardized group per time. An example would be 1 case per 100,000 per year of x disease. 40 Incision and drainage (I&D) A minor surgical procedure used to release pus or pressure from a site such as an abscess. Indirect statement A question that asks for an explanation that is not constrained by the question. An example of an indirect statement would be, “Please tell me about your pain.” In extremis An appearance of grave illness or mortal injury. Infarction A large area of necrosis in a tissue or organ. Inflammation A protective reaction of tissue to irritation, injury, or infection, characterized by localized pain, redness, swelling, and sometimes loss of function. Initial assessment See Primary assessment. Initial impression A global patient assessment made on initial contact with a patient based on a myriad of factors such as patient presentation, environmental factors, gross observation, and resources on-scene. Injury Something that damages or harms. Injury prevention See Prevention; Injury prevention strategies. Injury prevention strategies Techniques used to go about implementing Haddon’s countermeasures, which include engineering safety into products or processes, educating people about the dangers, increasing or improving enforcement of laws and regulations which promote safety, and providing economic incentives for people to use safer products or processes. Inotropy To make the heart beat harder. Insensible loss The volume of fluid that is lost from the body in the form of perspiration off the skin (1.1 liters/daily) and the vapor in the breath. Insight An understanding of the patient’s current or chronic medical condition, as well as the consequences of inappropriate treatment; the ability to make reasonable decisions. Inspection A physical examination technique that involves looking closely at the patient. Internal locus of control The idea that one has the ability to remain in control of a given situation. International unit (IU) A standardized measurement that reveals the quantity of a biologically active substance, such as a hormone or vitamin, required to produce a specific response. Interpretation An interviewing technique in which the Paramedic tries to determine the meaning of a message based on what is said and the speaker’s nonverbal cues. Interstitial fluid The fluid between cells. Interval A segment and an ECG wave together. Inspiratory capacity The total of the tidal volume plus the inspiratory reserve volume, which is a measure of the maximum air that can be inspired. Institutional Review Board (IRB) An independent ethics committee consisting of experts from the fields of theology, sociology, psychology, and medicine, which is responsible for reviewing all aspects of a proposed research project in terms of the potential psychosocial impact and to ensure that all human subject research is ethical. Integrity A personal commitment to a code of moral or ethical behavior which serves as a foundation for the patient–provider relationship. Intended biological effect The modification a drug is designed to have on the function of a tissue or an organ, such as reduce fever, eliminate pain, and so on. Interference Extraneous electromagnetic energy heard on the radio as crackles and dead spots. Intimate space In the theory of proxemics, an area about the size of a beach blanket where patients feel most vulnerable. Entry into that space is only permitted to those people whom the patient trusts. Intracellular water The water that is within cells. Intradermal Injections that place a small quantity of medicine just under the epidermis and in close proximity of the subcutaneous tissue. Intramuscular injection Injection deposited between the layers of muscle, which is a common method of medication administration. 41 Intraosseous (IO) An injection into the bone marrow. Intravascular fluid A type of extracellular water found in the blood, which is primarily made of plasma and constitutes about 4% of the total body weight (3 or 4 L). Intrinsic rate The rate at which the pacemaker cells of the heart depolarize. Intrinsic trigger A stimulus prompting an airway spasm that originates within the body, such as through stress or exercise. Inverted T waves A negative T wave that’s normally positive and upright, which may indicate coronary ischemia. Isoelectric line A line on the ECG that extends from the end of the T wave to the start of the ventricular depolarization represented by the QRS complex. This line indicates the period of time when the myocardium, particularly the ventricular mass, has been repolarized and awaits depolarization. An isoelectric line on the monitor and on the rhythm strip should appear as a fl at line between ECG complexes. Isometric Exercise using free weights. Isotonic In terms of exercise, resistance exercises. In terms of fluid management, a balanced solution (equal water and salt on both sides of a membrane). Involuntary consent Situation during a life or limb emergency in which an officer can provide consent for a person in custody (e.g., a prisoner). Involuntary consent is usually reserved for true emergencies; the police power to provide consent is not generally invoked for minor emergencies or elective procedures. Ions An atom that has a positive or negative charge due to a gained or lost electron. Ischemia A deficient supply of blood going to a body part due to an obstruction of the inflow of arterial blood. Ischemic hypoxia Problems of circulation that can lead to oxygen deprivation at the cellular level. Ischemic patterns Changes in an ECG as the result of abnormal repolarization. 42 IV bags Soft plastic solution containers that collapse as the solution is withdrawn, eliminating the need for venting. These create a closed system that helps to decrease the risk of outside contamination. IV push Procedure in which a Paramedic administers medication by attaching a syringe filled with the medication to an infusion device and rapidly injects the medication. Jaundice A yellowish hue of the skin, which can indicate liver failure or obstruction of the bile duct. Justice The application of the concept of fairness, which implies impartiality in the administration of rewards. In terms of research, the belief that one group of people should not bear all the risks of research when the benefits of said research would benefit all persons in the larger society. J-wire A special tightly wound spring wire with an open hook at the end to prevent it from puncturing soft tissues, which is inserted into the hub of a needle during the Seldinger technique. Joule heat Heat caused by the buildup of thermal energy as a result of electricity overcoming resistance from the tissues. Kaizen Japanese concept of continual self improvement that emphasizes process and system thinking. J point The start of the ST segment found at the juncture of the QRS and the ST segment, the point where the angle from the QRS changes. Keep the vein open (KVO) A slow infusion of fluid designed to be just enough to keep the veins from occluding. Jugular venous pressure The force at which blood flows throughout the venous system, which can help diagnose issues in the lung and heart. Kefauver-Harris Act A 1962 amendment to the Federal Food, Drug and Cosmetic Act that required all drugs to undergo an extensive review that not only ensured the public’s safety, but also reassured the public that a drug would do what it claimed to do. Ketamine A dissociative anesthetic that provides excellent amnesia, analgesia, and anesthesia during procedures and intubation. Most notably, however, it has minimal respiratory depression even at very high doses. Kinematics The branch of dynamics that studies motion apart from mass and force considerations. Junctional tissues A long strip of tissue below the AV node connecting the atria and the ventricles that is capable of independently initiating a stimulus if the SA nodal impulse should fail to depolarize one first. Kinesics The study of nonverbal behavior in interpreting communications. Knowledge base The Paramedic’s previous experiences, anecdotal information, and formal medical education. Jurisdiction The court having authority to decide a legal case, typically based on location. 43 Korotkoff sounds Sounds heard during the inflation and deflation of the cuff that are caused by the change in the nature of blood flow through the artery. Labor Uterus contractions which signify the start of the childbirth process. Lacerations A torn or ragged wound. Landline A hard-wired telephone. Laryngeal mask airway A blindly inserted airway device designed to be used in situations where face-mask ventilation was inappropriate but the invasiveness of endotracheal intubation was not necessary. Lead Any of the conductors connected to the electrocardiograph, each comprising two or more electrodes that are attached at specific body sites and used to examine electrical activity by monitoring changes in the electrical potential between them. Lead I An electrode point that measures the voltage change between the right arm and the left arm. The negative electrode is on the right arm. The positive electrode is on the left arm. Lead II An electrode point that notes the change between the right arm and left leg and provides a view of the inferior wall of the heart. The positive electrode is located on the left leg. Lead III An electrode point that measures change between the left arm and left leg. The positive electrode is on the left leg. Laryngoscope The primary, compact, and selfcontained device healthcare providers use to visualize the larynx. Leading question A question that may direct the patient toward an answer that might not necessarily have been given if asked in another manner; for example, asking “Was the pain crushing?” rather than “Tell me what the pain in your chest was like.” Left anterior descending coronary artery (LAD) A coronary artery branch that provides blood to the anterior wall of the left ventricle. Larynx Also known as the “voice box,” the upper group of structures of the lower airway that contains the vocal cords. LD50 Shorthand for lethal dose 50%, the drug dosage where 50% of the test animals given that dose died. Left bundle branch A division of the bundle of His that lies within the septum and serves as a further passageway for electrical impulses into the left ventricle. 44 Legitimate interest A determination of which individuals need access to a patient’s confidential medical information, and the extent of the information they are entitled to view. Legitimization The process in which a Paramedic listens and seeks to understand the patient and the patient’s concern, regardless of how seemingly insignificant the problem. This process supports the patient and demonstrates caring. LEMON law A rapid mnemonic used to predict a difficult airway when evaluating a patient. The elements of the LEMON law are to: ■ L—Look externally for anything that will hinder ventilation or intubation ■ E—Evaluate the 3-3-2 rule to assess the airway anatomy ■ M—Mallampati classification Leukocytes White blood cells, which help the body fight off disease. Leukotrienes Slow acting substances of anaphylaxis that produce chemical effects similar to histamine and help to prolong the inflammation. Libel Situation in which a falsehood damaging to a person’s reputation is written or printed and then disseminated to the public. Lidocaine A common local anesthetic and antiarrhythmic drug. Life-long learning The commitment made by all Paramedics when they attain their first certification to remain current with the state of the profession. Lighted stylettes Malleable stylettes with a bright light source at the distal end and a power source at the proximal end. When placed in the trachea, a bright, wellcircumscribed light is seen in the midline of the trachea. ■ O—Obstruction, either new or chronic, should be evaluated ■ N—Neck mobility should be determined if not contraindicated (contraindicated in suspected C-spine injury) . Les ambulance volutes Light two-wheeled carriages used by the French military in the early 1800s that carried an attendant as well as a driver, often viewed as the precursor to the modern ambulance. Line of sight (LOS) The path that radio transmissions take over land, which ideally are free of obstructions that will impede the radio waves. Line-out To place a single diagonal line across any open areas of a document in order to prevent the addition of new content to a PCR by others after the Paramedic has completed the PCR. Lipid-soluble A substance that is able to be dissolved in lipids (fat). 45 Lipophilic Characteristic of being attracted to lipids. Liquid oxygen (LOX) Concentrated oxygen in liquid form. Liquifactive necrosis Process in which cells that are largely lipid in content, such as the neurons of the brain, simply liquefy upon death and leave a pool in their place. Literature Published reports of research. Livor mortis A condition caused by relaxation of the vascular bed and a pooling of blood in dependent portions of the body. Loco parentis Legal doctrine that states if a child has been left in the custody and care of another adult (e.g., a schoolteacher) then that adult has the authority to provide consent for medical care. Lotions Topical medications mixed in water. Lower esophageal sphincter (LES) A functional portion of the esophagus where its walls contract inwardly, forming a physical barrier to the reflux of stomach contents up the esophagus. Lymphocytes Almost colorless cells found in the blood, lymph, and lymphoid tissues, constituting approximately 25 percent of white blood cells and including B cells, which function in humoral immunity, and T cells, which function in cellular immunity. Lysosomes Tiny sacs in a cell that contain enzymes which can break down proteins. Macintosh blade A curved laryngoscope blade with common sizes from 1 to 4 with a large flange and flat surfaces to control the tongue. Macro-drop Administration set with a short, straight line that has few obstructions, such as filters or medication portals. It is used when volume replacement is needed (e.g., during a trauma resuscitation). Low priority patients Patients with relatively minor conditions who can typically be treated in a more focused manner on-scene. Lozenges Medicines intended to dissolve in the mouth. Luer lock A needle adaptor that attaches to the syringe hub by use of a twist connection, where the adaptor on the syringe is grooved and will mate with a flange on the needle hub. Lymphangitis Inflammation of the lymphatic channels in the skin that occurs when there is spread of an infection from a site distal to the channel. Lymphedema The swelling of tissues on a limb due to lymphatic obstruction. 46 Macroglossia A state of having an abnormally large tongue. Magmas Powdered drugs with particles so large that they are visible when they are mixed, or suspended, in water. Malfeasance Wrongdoing or misconduct; for example, if the Paramedic performed an inappropriate procedure (e.g., gave a fluid bolus to a hypertensive head-injured patient). Malignant Cancerous; something that will cause harm or damage health. Mechanism of action The way a drug specifically works upon a cell. Malignant hyperthermia A skeletal muscle disease that leads to a life-threatening reaction to succinylcholine and some other inhaled anesthetics. Mechanism of injury (MOI) A description of the forces applied to a patient with the potential to cause injury, such as a motor vehicle collision (MVC) or a fall. Malpractice Failure to exercise an appropriate degree of professional skill during a service, resulting in injury, loss, and damage. Managed health care A financial system where a large corporation or the government obtains health insurance for its workers via private sources, who then gather groups of healthcare providers and obtains a reduced rate in exchange for a guaranteed client base. The managed healthcare insurance plan then mandates that patients seek treatment from this preferred medical group, in essence managing the care that the patient will receive by providing medical care for the lowest price. Mandatory reporting A situation in which one is required by law to report a crime, such as child abuse, sexual assaults, gunshot wounds, certain communicable diseases, and animal bites. Mason–Likar modification Adjustment in the placement of electrodes to help Paramedics obtain a more accurate 12-lead ECG, which involves moving the electrodes to the shoulders and the hip rather than the ankle and wrist. Masses A large, firm area of considerable size in the body. Master problem list In a POMR recordkeeping system, a list of the medical conditions for which a patient had been, or currently was, receiving treatment. Medical command An immediate and direct physician involvement in patient care. The physician’s authority can be exercised either on-scene or over-the-air at the time of an emergency. Medical ethics The way Paramedics behave in regard to patients. Medical intelligence The healthcare provider’s process of learning from experience and past medical practice and then coming to a decision. Medical lines Sometimes called lifelines, a means of adding medications directly into the circulation. Medical oversight When a physician is involved in the quality assurance/quality improvement process and provides direction, either in the form of protocols or education, to Paramedics. Medical Priority Dispatching™ A classification system designed to ensure the right response gets to the right person at the right time. Mean arterial pressure (MAP) The average blood pressure in the arterial system over time, typically about 60 to 80 mmHg. 47 Medical record Documentation about the patient’s condition that will be used in the future by other physicians and allied healthcare professionals for patient care. As a part of the medical record, the patient care report often provides vital information to physicians about the origin of a condition or disease. Menopause An age-related cessation of a woman’s menses for an entire year, generally indicating the end of the woman’s reproductive abilities. Medical restraint Any device used to immobilize a patient for both the patient’s and the care provider’s safety; may include straps, jackets, and so on. Meta-analysis A technique used when it is difficult to obtain a large population of study subjects, or the event being studied is relatively rare. The results of several similar small studies are combined and a statistical hypothesis test is applied, taking into account differences in subjects and methods used before a conclusion is made. Medical self-help Instructions provided to patients by 9-1-1 on self-rescue actions they can take during the time before responders arrive. Medical utility An assumption that those with the best medical prognosis should be treated with the medical provider’s limited resources. Medication-facilitated intubation The use of adjunctive medications during intubations, either to provide sedation or cause muscular paralysis to protect patients and improve their quality of care. Medulla oblongata The part of the brain responsible for controlling involuntary vital functions; the brainstem. Membrane attack complex (MAC) In cases where the body does not recognize the bacteria and cannot mount an effective antigen—antibody defense, a complex created by the complement system which attaches itself to the cell’s walls and forms a tube from the outside to the inside. The tube allows water to enter the cell, the cell to swell, and the cell to lysis. Memory cells Clone cells that have a memory of the make-up of the original cell. Meniscus A concave-curved shape liquid assumes due to tensions within a syringe. 48 Mentors Experienced master Paramedics who take on graduate Paramedics as their protégés to teach them paramedicine. Metabolic acids Acids formed during anaerobic metabolism and amino acids formed by the breakdown/oxidation of proteins. Metabolism Biochemical reactions that need to occur for life processes to go on. Metabolite A chemical produced by degradation of a medication into subcomponents that may be active or inactive. Metaplasia Replacement of one adult cell type with another type of adult cell. Metered dose inhaler (MDI) Portable and simple to operate respiratory device that delivers a specific amount of aerosolized medication to the lungs. Micro-drop Administration set with fine control of the infusion stream, used when careful titration of medicated fluid is desired (e.g., when a medical patient needs a slow infusion of a drug). Misfeasance To perform a legal action in an illegal manner; for example, if the Paramedic performs the correct procedure but does so incorrectly. Mitochondria The largest organelle in the cell, found outside a cell’s nucleus, which produces energy. Mitosis The process of cell division. Micrognathia A state of having a small jaw. Milieu An environment where an action can occur. Military emergency medicine The largest and oldest EMS service, consisting of those who provide emergency medical care to members of the armed forces. Miller blade A straight laryngoscope blade with common sizes from 00 to 4 with a small and curved flange designed to open a conduit to the larynx on the right side of the mouth and hold the tongue in the midline to the left side of the mouth. Mobile data terminal Laptop or handheld computers inside a vehicle a Paramedic can use to create a downloadable document for transmission over a telephone line, via modem, over the Internet, or by using wireless technologies. Mobile subscriber units (MSU) The various varieties of cellular phones for use within a cellular radio system. The three main varieties are the portable cellular telephone, the transportable cellular telephone, and the mobile telephone. Modified chest Lead 1 (MCL1) An alternative ECG lead Paramedics may use to monitor patients instead of/in addition to Lead II. MCL1 simulates the precordial lead V1, one of the six precordial leads of a 12-lead. Minimum data sets Certain fields with requested information that must be completed on a PCR or other form. Morality A personal code of conduct. Minute ventilation A measure of the total volume of gas that passes through the lungs in a minute. It equals the respiratory rate (RR) times the volume per breath (Tidal Volume, or TV). Moral obligations Certain mores that go beyond the basic human rights which every patient enjoys; for example, an off-duty Paramedic’s moral obligation may be to provide care when coming in contact with an injured person. 49 Morbidity The incidence of disease. Morphology The shape of a QRS complex wave. Myocardial ischemia A condition that occurs prior to myocardial cell death in which the heart tissue is slowly or suddenly deprived of oxygen and other nutrients. Mortality The state of death. Motion A request sent to a judge for some action (i.e., dismiss the case, order a party to do something, postponement, cease and desist orders, etc.). A motion can be verbal, but is most often a written request that contains pertinent points for the judge to consider. Mucolytics Drugs that thin mucous secretions and physically break down the viscosity of mucus by breaking apart the mucoprotein structure. Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) A failure of two or more organ systems. Multiplex Radios that permit the transmission of audio signals as well as data. Municipal EMS service A governmentfinanced and administered EMS system that may exist as an independent entity or crosstrained with the police or fire department. Murphy’s sign Right upper quadrant tenderness that worsens when the patient takes a deep breath while the quadrant is palpated. A Murphy’s sign indicates gallbladder inflammation . Muscarinic receptors Parasympathetic neuroreceptors that are slower than nicotinic receptors and indirectly open ion channels that cause depolarization. Muscarinic receptors, by definition, are more sensitive to muscarine, a naturally occurring chemical found in mushrooms, than to nicotine. Mutation A change in the DNA sequence of one gene. Myocardial infarction The death of myocardial cells. 50 Myocardium A muscular layer that actually performs the heart’s work by contracting forcefully and ejecting blood from within the heart’s chambers. Myoglobulinuria A condition in which the protein products of muscle breakdown clog the kidneys. Narcotic The hallucinogenic effects of opiates, thought to be the result of stimulation of the sigma receptors located in the limbic system. Narcotics A class of drugs known for their ability to induce a profound state of sedation. Nares The openings to the nose; nostrils. National EMS Education Program Accreditation A designation that assures students their EMS education will meet national standards and assures the public that graduates of those educational programs will be competent providers. Nasogastric tube A single-lumen tube passed through the nose into the stomach to evacuate air from the stomach. Nasotracheal intubation The process of aiding respiration by placing an endotracheal tube through the patient’s nostril and into the trachea. National Association of EMTs (NAEMT) A professional organization, founded in 1975, whose mission is to represent the views and opinions of all prehospital care providers. National Centers for Injury Prevention and Control A federal agency tasked with injury surveillance. National EMS Core Content Created under the leadership of the National Association of EMS Physicians (NAEMSP) a curriculum that defines the entire universe of disorders, diseases, syndromes, and skills that an EMS provider might encounter and for which he would be expected to provide emergency care. National EMS Education Standards Created under the leadership of the National Association of EMS Educators (NAEMSE), the basis for EMS instruction that provides direction for EMS educators regarding both the core content and the scope of practice. National EMS Scope of Practice (NEMSSOP) Created under the leadership of the National Association of State EMS Officials (NASEMSO), an organizational plan that clearly defines four levels of EMS providers and identifies the knowledge and skills required for each level. National Formulary (NF) A drug reference manual that lists medications which are approved for prescription. It contains specific chemical information that is more helpful to the pharmacist and manufacturer than the physician. National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians (NREMT) An organization that provides a process of practical testing and written examinations for the certification of Paramedics, providing proof that the individual being licensed is minimally competent to provide a specified level of care. The majority of states currently accept National Registry certification for state licensure. National Standard Curriculum (NSC) A seminal document that defines the scope of practice for many EMS providers distributed by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA). Nature of illness The history of the present patient’s illness, often reported by the patient himself or the patient’s family. 51 Necrosis A physiological process in which living cells die, often due to disease, injury, or some other pathological state. Needle cricothyroidotomy A type of surgical airway performed by piercing the cricothyroid membrane with a large bore needle and catheter, allowing rapid access to an otherwise obstructed airway. Neuromuscular blocking agents (NMBAs) Medications that block transmission of nerve impulses to skeletal muscle at the neuromuscular junction. Negative pressure ventilation A mechanical ventilation technique in which a negative pressure environment is created around the patient’s chest, thus sucking air into the lungs. An iron lung is an example. Negligence A failure to exercise the degree of care that a prudent person would exercise. Negligence per se Situation in which a Paramedic commits a criminal act, and the patient is injured as a result of that criminal act. The assumption is that the Paramedic’s negligence flows from the criminal act. Neuroreceptor A chemical receptor that receives messages from the neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitter A chemical messenger that transmits a nervous signal across the synapse. Neuroleptics Major tranquilizers that prevent nausea. Nicotinic receptors Chemical receptors from the parasympathetic nervous system found in the central and peripheral nervous system as well as the neuromuscular junction with skeletal muscles. Cholinergic stimulation of nicotinic receptors is quick in onset and short in duration, causing a sodium influx and local depolarization. Neuromodulator Substances that inhibit the transmission of painful sensations to the brain and spinal cord by adjusting, or modulating, the rate of a neuron’s discharge. Nitric oxide (NO) A colorless, poisonous gas involved in oxygen transport to the tissues, the transmission of nerve impulses, and other physiological activities. Neostigmine An acetylcholinesterase inhibitor that can be used to reverse the effects of the competitive (non-depolarizing) NMBAs. NKDA Acronym that stands for “no known drug allergies.” No apparent distress (NAD) An appearance of not having difficulty. Nociceptors Pain receptors in the body that respond to chemical, mechanical, or thermal stimulus. Noisy Characteristic of an ECG signal that is of poor quality and produces an unreadable tracing. 52 Non-depolarizing neuromuscular blockers One of the two major classes of neuromuscular blockers; competes with acetylcholine for the receptor but does not cause the receptor to fire. Nonfeasance A failure to perform the correct or required procedure, which would be an error of omission; for example, if a Paramedic were to arrive on-scene of a cardiac arrest and the defibrillator failed because of a dead battery, which the Paramedic should have checked during routine maintenance. Norepinephrine The chief neurotransmitter used in the sympathetic nervous system. Normal saline (NS) A solution of 0.9% sodium chloride in sterile water (0.9% NaCl) that contains the same amount of salt as does blood. NSS has become an EMS standard solution in many systems because it is compatible with all medications as well as blood. Normal sinus rhythm An optimal rhythm to provide adequate filling of the ventricles and sufficient ejection of blood for perfusion. Nonjudgmental Providing services based upon human need, with respect for human dignity, unrestricted by consideration of nationality, race, creed, color or status. Non-malfeasance A concept suggesting that no act of harm will be done during a medical treatment. Nonrebreather face masks (NRB) Oxygen masks with an oxygen reservoir that can deliver up to 80% FiO2; they do not deliver 100% FiO2 because there will always be some room air mixing through the open side port. Normocardiac A heart rate between 50 and 100, which is considered to be normal. Nosocomial A hospital-acquired infection. Notary public A public officer recognized by the court who can verify the Paramedic’s writings to authenticate them as evidence. Null hypothesis When considering the results of a research study, the supposition that the treatment did not create changes (i.e., any changes are purely random and coincidental). The purpose of the study is to determine if the null hypothesis is true or false. Nonspecific ST changes Situation in which the ST segment changes do not fit a pattern of ischemia, nor are they contributory toward another diagnosis. Causes of nonspecific ST changes include improper lead contacts, electrolyte abnormalities, drug-induced changes, hyperventilation, and even a drink of cold water. Nutritional flow The daily process of excretion and reabsorption of approximately half the nutrient-laden fluids in the body that is essential to the body’s sustenance. Nystagmus A fine tremble of the eye when holding a lateral gaze; unequal movement or oscillating eye movements that are usually involuntary. 53 Obesity A growing health crisis when an individual’s body mass index is 30 or greater; a common layperson definition of morbid obesity is 100 pounds over ideal weight. Ointments Topical medications placed in either lanolin, an oil from sheep’s wool, or petroleum jelly. Oliguria An decreased output of urine, below 20 mL per hour. Omega loop Creation of a stress loop when securing an intravenous administration set tubing to the patient. Initially, a strip of tape is laid across the adaptor and against the skin. Then a loop of tubing is taped across the first strip of tape, which will absorb any tension on the tubing and potentially prevent the IV catheter from being displaced. Observational study In contrast to the descriptive study, a study that asks a question and poses a simple explanation or hypothesis. To have a scientifically valid result from an observational study, one must control extraneous confounding variables that could account for the desired change. Oncotic Caused by swelling (e.g., oncotic pressure). Obstructive shock The final category of the Hinshaw–Cox shock classification, which deals with the physical impairment of forward blood flow despite an effective pump, an adequate blood volume, and a normal vasculature. Examples of obstructive shock include massive pulmonary clots, embolism, and a collapsed lung (pneumothorax), which proceeds to crush the heart as well. Open-ended questions Questions that allow the patient to express himself without restriction, with answers that can be used as a springboard to other questions. Open-ended questions usually begin with words like “how,” “what,” or “could” and ask for an explanation. Ockham’s razor A theory that simply states that if all things are equal, the simplest solution tends to be the best one. In other words, common things occur commonly. Oils Substances that have been extracted from plants for centuries for their use as food additives as well as medications. 54 On-line medical control Medical command technique in which physicians can give medical direction and exercise medical command via the base radio. Operational competence A Paramedic knowing how the various team members interact, knowing an organization’s policies and procedures, and possessing situational awareness. Opsonization A process in which the plasma proteins mark resistant bacterium by attaching fragments of themselves to the bacterial cell wall, thus enhancing the impact of the leukocytes. Otitis media A middle ear infection marked by pain, fever, or hearing loss. Optic Pertaining to the eyes. Orientation A person’s awareness of himself in terms of place and time. Orogastric tube A single-lumen tube passed through the mouth into the stomach to evacuate air from the stomach. Outcomes evaluation A matter of comparing the level of injury or illness before and after an injury prevention program. Orotracheal intubation The most common technique used to intubate patients, in which a laryngoscope is used to visualize the larynx and the vocal cords, and an endotracheal tube is observed to pass through the vocal cords. Over-the-counter (OTC) Nonprescription medications that can be purchased by the public without a prescription so patients can self-treat minor illnesses. Orphan drugs Drug therapies for rare or uncommon diseases, which generally are unprofitable for manufacturers to produce because the drugs are so rarely used. Orthostatic hypotension An abnormal decrease in blood pressure that occurs when someone stands up. Orthostatic vital signs Vital signs that change with position. For example, when an individual changes position from lying down to standing, the blood pressure normally has a tendency to drop due to gravity. Oscilloscope An electronic instrument that produces an instantaneous trace on the screen of a cathode-ray tube corresponding to oscillations of voltage and current, used in some cases to measure electrocardiograms. Osteoporosis A loss of calcium from the bones secondary to a decrease in hormones. Ovum A female gamete; the egg in a female fertilized by a sperm cell to create an embryo. Oxygenation The ability to move oxygen from the air in the lungs into the blood. p value The probability of random chance causing the changes in a clinical trial, rather than the treatment. An acceptable p value is arbitrarily assigned by the researcher prior to the start of the study and is symbolized as α. Packed red blood cells (PRBC) Blood component formed by removing nearly all of the plasma from a unit of blood and adding a small volume of preservative to the unit. Pain threshold The amount of stimulus required to elicit a pain response in a person. Palliative care Measures used to increase comfort and reduce pain, such as medication. Otic Pertaining to the ear. 55 Palpation Evaluation that involves the provider placing his hands or fingers on the patient’s body in an effort to detect any abnormalities. Palpitations The sensation of one’s heart having an irregular and/or rapid heartbeat. Pandemics Outbreaks of diseases that spread throughout a country or a region, which may reach disaster proportions if not prevented or controlled in an appropriate fashion. Papillary muscle Muscles that stabilize, open, and close the valve leaflets with each myocardial contraction. Paramedic field diagnosis See Paramedical diagnosis. Paramedical diagnosis A broad and comprehensive identification of a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms that suggest a disease, or a primary disorder of homeostasis, such as hypoxia, in a patient upon assessment by the Paramedic. Paramedicine A special subset of medicine that Paramedics provide in the out-of-hospital setting. Parasympathetic nervous system The portion of the autonomic nervous system responsible for the body’s involuntary vegetative functions including digestion, heart rate, and the like, largely controlled by the vagus nerve. These functions are summarized as “feed and breed.” Paradigm blindness The attitude that “we have always done it this way.” Paradigms can sometimes become barriers to innovation and improvement. Paradoxical respiration A disruption in normal respiration in which, during inhalation, the flail segment is drawn inward by the negative pressure in the chest rather than expanding outward with the rest of the chest wall. During exhalation, the opposite occurs due to the increased pressure in the thorax during exhalation. Paraglossal approach An intubation technique that involves inserting the entire length of the laryngoscope blade blindly into the esophagus and then slowly withdrawing the blade under direct visualization. Paramedic The highest level of EMS provider, whose skill level and education includes advanced assessment and diagnosis of syndromes and disorders and the treatment thereof. 56 Parasympathomimetic A chemical agent that mimics the action of acetylcholine. Parenteral A method of drug administration that bypasses the gastrointestinal system, such as injection, which is preferred during an emergency because of the rapidity of onset of the medication’s action as well as predictability of the drug levels. Past medical history (PMH) Significant historical information necessary to determine the nature and potential severity of the patient’s illness or injury. All patients should be questioned about issues like chronic illnesses, medications taken, allergies, and use of tobacco, alcohol, or other drugs. Pathogen An organism that causes an infectious disease. Pathogenesis The sequence of events—at the molecular and cellular level—that leads to organ dysfunction. Pathologic Physical changes as a result of disease. Pathophysiology The study of the causes of suffering in the normal human condition. Patient advocate An individual who fights for the rights and wishes of the patient in terms of health care. Whenever a Paramedic acts to help a patient obtain needed health care, he is acting in the advocacy role. Patient autonomy The patient’s ability to control her person and her personal destiny through decision making. Followed to its logical conclusion, patient autonomy implies that patients could decide to do nothing about a fatal illness, a decision that might lead to their own demise. Patient care report (PCR) Documentation completed by the Paramedic indicating the care provided to a particular patient. Patient concordance The process of shared decision making between the healthcare provider and patient. Pattern recognition A tendency to quickly label an ECG rhythm because it looks like another ECG rhythm seen previously, which is poor practice because it negates nuances that differentiate one wave from another. PCR audits A careful review of the patient care report documentation for specific data that allows healthcare managers, EMS administrators, and EMS physicians to ensure that acceptable patient care is provided to all patients equally. Peak expiratory flow The maximum velocity of gas movement during exhalation. Peak-load staffing EMS practice in which, during predictable hours of high demand, additional ambulances are placed in-service at strategic locations. 57 PEARLS A mnemonic (partnership, empathy, apology, respect, legitimization, and support) that includes the qualities needed to provide for a strong Paramedic–patient relationship. Peer reviewed An article or research study that was critically appraised by experts in the field for validity. Penumbra A predictable pathway of cell changes leading to cell necrosis and myocardial infarction. Percutaneous central venous catheters (PCVC) A central venous access device inserted into the deep veins via the subclavian vein (in the chest), the internal jugular vein (in the neck), and the femoral vein (in the groin). Percutaneous cricothyrotomy A surgical technique used to gain entry to the trachea through placement of a needle, then guidewire, then a small bore tracheostomy tube in a rapid fashion with less bleeding than a traditional surgical cricothyrotomy. Pericarditis An inflammation of the pericardial sac that surrounds the heart. Pericardium The membranous sac filled with serous fluid that encloses the heart as well as the roots of the aorta and other large blood vessels. Percussion The act of lightly but sharply tapping the body surface to determine the characteristics of the underlying tissue. Percussion note The sounds that result from the act of percussion. Air-filled structures will produce a hollow, tympanic percussion note similar to that of a drum. Fluid-filled structures will produce a dull percussion note. Solid structures will provide a loud, welldefined percussion note. 58 Peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC) A very long central venous access catheter placed within a vein in the antecubital fossa that is threaded into the vena cava while under fluoroscopy. Peritoneum The inner lining of the abdomen. Persistent vegetative state (PVS) A permanent state of unconsciousness. Personal digital assistants (PDA) Personal palm computers Paramedics can use as they move about the patient compartment at will, all the while transmitting and receiving critical patient information. Phagocytosis A process in which neutrophils destroy bacteria by engulfing them. Personal space In the theory of proxemics, the area where a patient would engage in a oneon-one conversation. This personal space, about one and one-half feet to four feet, is the distance within which most Paramedics initially interview patients for a history. Pertinent negatives Those symptoms which, if present in a patient, could indicate a more serious underlying problem. pH scale A measure of the differing degrees of acidity or alkalinity in a substance. The range of pH is from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral. Values lower than 7 are acids, values higher than 7 are bases, and pure distilled water is neutral (pH is an abbreviation for potential hydrogen). Pharmacodynamics The study of how drugs come to create their therapeutic effect. Pharmacogenomics A combination of pharmaceutical research with the study of the human genome. Pharmacokinetics The study of how drug absorption, distribution, detoxification, and elimination affect a drug’s therapeutic value. Pharmacological effect A new or different effect a drug generates in the body other than what was expected. Pharmacology The study of drugs. Pharynx The area of the airway composed of the spaces behind the nose (the nasopharynx) and the oral cavity (the oropharynx). Phenotype The visible outward expression of the chromosome, which is the result of the genetic influences of both parents. Phlebotomy The act of drawing or removing blood from the circulatory system in order to obtain a sample for analysis and diagnosis. 59 Physical examination Also called an exam, an assessment of the patient from head to toe in an effort to detect signs associated with a disease or condition. Physiology The study of the body’s functions, in its normal human condition, which focuses on the physical, mechanical, and biochemical processes that go on inside the body every day (i.e., how the body works). PIER A model public education system developed by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHSTA) which stands for public information, education, and relations. Piggyback infusion The process of administering a medication infusion by attaching the secondary intravenous line containing the medication to a primary intravenous line to eliminate the need for a second intravenous line. Physician extenders Allied health professionals who work under the license granted to the physician. Physician’s Desk Reference (PDR) A reputable source of information about prescription and over-the-counter medications; a compendium of manufacturer drug-prescribing information which is usually found in a package insert required by law to accompany all medications. Physician’s Order of Life-Sustaining Treatment (POLST) A more detailed description than a DNR order of the patient’s wishes, placed in the form of a physician’s order. These forms are generated through a discussion between patients and their physician that addresses specific situations including utilizing artificial hydration, nutrition, intubation, antibiotics, and other medical therapies. Physiologic A physical loss of cells as a result of the normal changes of aging or simple disuse; a natural development of cells. 60 Pitting edema The amount of indentation produced when the edematous limb is pressed over the tibia by the examiner’s finger. Placebos Inactive drugs used in research trials that appear similar to the actual drug in order to create blinding for the participants. Placenta The vascular organ that connects the unborn child to the mother’s uterus, providing safety and nutrition during its development. Plain English transmissions The use of everyday speech to transmit information rather than using codes or jargon. Plantarflexion The ability to push the toes downward and away from the tibia. Point of care Testing done in the field by the Paramedic, such as capillary blood draws, which enhance the Paramedic’s ability to provide immediate emergency services while still in the field and to transmit critical information to the emergency department. Plaque Fatty lesion formed in the artery as a result of atherosclerosis. Plasma cells Cells that generate antibodies. Point of service (POS) A managed care system with qualities of both an HMO and a PPO. The patient is allowed to choose a healthcare provider from among a list of preferred care providers (PCP) but may elect to see another “out of system” provider, without a referral, at a substantially higher copayment and/or deductible, similar to a fee-for-service arrangement. Polarity The direction of a QRS complex wave. Platelet See Thrombocytes. Portable radios Radio devices that can be carried from place to place. Platelet plug A concentrated mass of platelets that serve as a short-term fix to a plaque rupture. Pleura The delicate serous membrane that lines each half of the thorax and is folded back over the surface of the lung on the same side. Pleural effusion Excess fluid that builds up in the fluid-filled space that surrounds the lungs, which can cause difficulty breathing. Pneumothorax Condition in which air or another gas is present in the pleural cavity as a result of disease or injury. Point The end of a needle, often cut obliquely in such a fashion that a sharp leading edge is created. Positional asphyxia Situation in which a patient in excited delirium develops hypoxia and goes into cardiac arrest when restrained prone, particularly if hobble restrained. Positive pressure ventilation A mechanical ventilation technique in which the pressure in the patient’s airway is increased, thus forcing air into the lungs. Intubation or a bag-valve mask are examples. 61 Postmortem Specific changes within the body that are associated with death. Post-traumatic stress disorder (PSTD) According to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual, the development of “characteristic symptoms following exposure to an extreme traumatic stress involving direct personal experience of an event that involves actual or threatened death or serious injury, or other threat to one’s physical integrity; or witnessing an event that involves death, injury or a threat to the physical integrity of another person.” Prefix An affix placed at the beginning of a root word to modify that root word; for example, adding the prefix “un-” to the root word “do” makes “undo,” the opposite of do. Potable infusions Process of boiling water over the top of medicinal herbs and immediately drawing off the solution. Potent Chemically or medically effective; strong. Potentially infectious materials (PIM) Any substance with the ability to transmit bacteria to another material. Potentiation Situation in which one drug increases the effectiveness of another drug. Power The ability to attribute the changes in a research study to the treatment rather than chance. Predictable injury pattern Characteristic injuries associated with a particular mechanism of injury. Preferred provider organization (PPO) A managed care system that serves as a modified fee-for-service schedule, permitting patients to choose their healthcare provider from among a roster of approved physicians. Pre-induction agents CNS depressants administered as a premedication before the introduction of anesthesia to decrease the incidence of fear or panic (anxiolysis) or combativeness (sedation) in the patient. Preload The volume of venous blood entering the heart during diastole. Prescription drugs Drugs that cannot be dispensed by a pharmacist without the written or verbal order of a physician or a mid-level healthcare provider, such as a physician’s assistant. Pressured speech Condition characterized by a patient speaking so fast it appears she has an urgency or pressure to speak quickly. Preventative maintenance (PM) A program that forestalls the incidence of failure, thereby decreasing the incidence of injury and potential litigation. 62 Prevention The steps taken to avoid illness or injury. Primary assessment The Paramedic’s initial evaluation performed to find and manage any life threatening injuries or conditions the patient might have by assessing for (and correcting, if possible) any threats to airway, breathing, and circulation. Primary infusion A continuous intravenous set to which other medications may be added as supplements. Primary rhythm The main heartbeat. Prime wave The first wave in a QRS complex in a situation where a wave repeats itself. The prime wave is represented by a capital letter and the second wave is represented by a lowercase letter. For example, a proper notation of a QRS might read RSr. Primum non nocere The duty to “first, do no harm.” PR interval The distance from the beginning of the P wave to the start of the QRS complex. Problem-oriented medical recordkeeping (POMR) Recordkeeping system in which a master problem list records the medical conditions for which that patient had been, or currently was, receiving treatment. Indexed as such, new entries in the medical record would be placed into the patient’s file under the problem listed. All healthcare professionals, from physicians to nurses to dieticians, would place their entries into the patient’s record. This system provides some order to the records needed by hospitals, medical specialties, and allied healthcare providers— all of whom need the same information. Process evaluation A measurement of the means used to carry out a program and how successful it was. Process server A person hired by an attorney to deliver a summons and complaint to the defendant in a case. Prodrugs A precursor of a drug that is converted into its active form in the body by normal metabolic processes. For example, heroin is a prodrug that, when acted upon by the liver, metabolizes into morphine. Product liability The responsibility a manufacturer has to ensure a drug (or other product) is not defective (unfit for its suggested use or results in harm to the consumer). Privacy officer An officer at a healthcare agency responsible for providing patient record security and recording security awareness training of all employees, as well as implementing a privacy protection plan within the agency. Private line (PL) See Coded (or tone) squelch. Professional development Steps a Paramedic may take to continue advancement of his or her EMS skills, which may include attendance at state and national EMS conferences or regional workshops, consultation with medical directors for guidance and education on new technologies, and review of EMS trade journals. Prognosis The expected outcome from a disease, determined by a culmination of modifiable risk factors, nonmodifiable risk factors, and the availability of treatments. 63 Progress notes In a POMR recordkeeping system, new entries in the medical record. Pronator drift An indicator of upper motor neuron weakness that is tested for by asking the seated patient to hold her arms out with the palms facing the ceiling and then close her eyes. The test is positive if one arm drifts away from the starting position. Protocols A written set of mandatory instructions for the Paramedic to use in specific situations in the absence of the physician. Protocols, almost by definition, assume that one patient’s situation is the same or similar to another patient’s condition in the same situation. Proxemics A theory based on the concept that four spaces surround a person—intimate space, personal space, social space, and public space—which provide varying levels of comfort when people move within them. Prospective research The most scientifically valid research, in which an attempt is made to account for all predictable or known confounding variables, to control those variables, and then add a treatment. If change occurs, then it may be reasonable to conclude that the treatment may have caused that change. Prostaglandin A chemical mediator released from the mast cell that creates the sensation of pain, although its primary function is to increase vascular permeability and smooth muscle contraction later in the inflammatory response. Protected health information (PHI) Facts from a patient’s medical record that are not to be dispersed to the public without authorization. Protective custody Situation in which a law enforcement officer assumes temporary custody of a child in order for the child to receive medical care after the parent refuses to give consent. 64 Proximate cause The immediate or direct reason why something occurred. In legal terms, the action that created an injury or reason for a claim. Prudent layperson standard An approach to defining an emergency that simply estimates if another citizen, not a physician, who was in the same or similar circumstance would think it appropriate to call EMS. Public Health Model A framework showing the connections between host, agent, and environment in preventing injury. Public Health Service A federal program which makes up a key portion of the Department of Health and Human Services. With 5,700 commissioned health services officers and 51,000 civilian employees, all led by the Surgeon General, the current United States Public Health Service provides support to county and state Public Health Departments as well as health care to medically underserved areas. Public information officer (PIO) An EMS agency employee whose responsibility is to interface with the news media and provide public information. Public safety access point (PSAP) A centralized communications center which runs 24 hours a day, seven days a week, and contains the entire 9-1-1 operation; a place where a service callback or additional emergency information would be available. Public space In the theory of proxemics, the area one would occupy with a stranger without fear but with an ability to flee if danger should arise. Public trust An understanding between the patient and the Paramedic that the patient will be treated with dignity and respect in the same manner a physician would treat the patient. Pulse oximetry A noninvasive measurement of the percentage of hemoglobin in arterial blood that is bound to oxygen molecules. Pulse pressure The difference between the systolic and diastolic blood pressures. The pulse pressure can provide the Paramedic with an indication about the blood volume status or compensation for illness in a given patient. Pulseless electrical activity (PEA) A situation in which the patient displays electrical activity in the heart but no signs of contraction; an electrical rhythm without a pulse. Punitive damages Money paid to reimburse an individual for more than just the actual damages suffered that prompted a court case; a monetary fine designed to “punish” the loser of the case. Pure Food and Drug Act of 1906 A law that prohibits the use of false or misleading claims about medicines. The law further stipulates that if a medicine contains any of the 11 “dangerous” drugs, then the drug(s) have to be listed on the label. 65 Purkinje fibers Cardiac muscle fibers that connect directly with the ventricular myocardium, allowing the ventricles to contract nearly simultaneously with the atrioventricular node, creating a functional syncytium. Pyrogen Chemical mediator that produces fever. Pyrogenic reaction A devastating systemic complication of intravenous therapy that occurs when a contaminated fluid, or fluid run through a contaminated administration set, is infused and leads to nearly immediate sepsis. QRS complexes A combination of two or more ECG waves, which combine in predictable ways to describe other cardiac events and are the basis for ECG interpretation. Pursed lip breathing A sign of increased work of breathing, in which the patient puckers his or her lips while exhaling, providing some resistance to exhalation that provides pressure to keep the alveoli open. Quadrageminy Situation in which ectopic beats occur every fourth beat. Quality assurance (QA) Verifying a program’s compliance with established standards. Quarantine The practice of isolating diseased individuals from the larger community. Putrefaction A process of decomposition within the body characterized by greenish discoloration, secondary to hemolysis of blood, and slippage of the skin from the skeleton, due to breakdown of subcutaneous fat. Pyelonephritis An infection of the upper urinary tract and kidney. Pyrexia A fever that makes the body’s environment hostile to bacteria. 66 Quickening Fetal movements during the second trimester that serve as the first signs of life. Q waves Pathologic waves on an ECG that indicate electrical silence (i.e., no depolarization) in a certain portion of the ventricular wall. Reception The process of interpreting a sent message, which may be influenced by both physical and cultural factors. Receptor The portion of a cell that attracts a certain molecule. Reciprocal changes ST-segment depressions seen on the 12-lead ECG in leads that face the wall opposite of those with ST-segment elevations. Recovery For cells, a return to a former functional capacity. For a person, a return to health. Radial pulse A measure of the beats created by blood flow taken at the wrist over the radial artery. Radio head A small remote radio control panel placed in the driver’s and/or patient compartment of an emergency vehicle. The actual transmitter is usually placed in a different location in the vehicle. Range A certain set of acceptable physical parameters the body uses to try maintaining a normal equilibrium. Rate counter A digital readout on some ECG monitors that measures the number of ECG complexes that pass in a minute, usually counting the tallest, or deepest, wave on the ECG. Reasonable accommodations Actions taken by an employer to make a workplace more accessible for a person with special needs, such as adding ramps or elevators. Rebound tenderness Tenderness that becomes worse when the pressure is suddenly released during palpation that may indicate irritation of the peritoneum. Reentry phenomenon The reexcitation of a region of the heart by a single electrical impulse, which may cause ectopic beats, tachyarrhythmia, or an abnormal conduction mechanism. Refereed A review process in which an editor will typically distribute an article to a panel of expert Paramedics, who offer input and edit the article. The article is returned to the author, who revises the article based on the edits. Reference librarian A librarian trained in research techniques who can help researchers develop a search strategy to identify which resources, such as articles, will be most helpful in a study. Referred pain Pain from one source transmitted to other parts of the body, via common nerve pathways. Reflected path When using the radio wave phenomenon of bounce, using enough reflective surfaces so that the redirected radio transmission will roughly result in the intended direction of travel. Recanalization The process of re-opening an artery to restore blood flow. 67 Reflection An interviewing technique in which the Paramedic repeats the patient’s words, which may encourage additional responses. Reflection is helpful because it typically doesn’t interrupt the patient’s train of thought. Refractory Unable to respond to a new stimulus. Relative bradycardia A sinus rhythm with a rate that is too slow for the patient’s metabolic needs. Release of information A written authorization allowing documents to be given to an attorney. Reliable Giving the same result on multiple trials. Refusal of medical assistance (RMA) A situation in which a patient can consent to a medical procedure, and yet still refuses care. Remission Situation in which the body’s defenses, or medical treatment, may force the disease into a non-active state. Remission does not mean the patient has been cured, but rather means the disease has been stopped. Remodeling To change the shape of something, such as the interior chamber of a ventricle. Repeaters Radios that pick up, amplify, and then retransmit a radio transmission, which can extend the range of a VHF almost indefinitely. Repolarization The restoration of a polarized state across a membrane, as in a muscle fiber following contraction or the recovery of the myocardial cell. Regulations Rules established by a government department to regulate the conduct of citizens. Regurgitation A backflow of blood into the atria. Rehabilitation Steps such as taking a rest break, eating some food, drinking fluids, and using lavatories that help EMS responders handle stress more effectively while at the scene of a prolonged incident. 68 Rescue devices Airway management tools used when intubation is not successful, such as a blind insertion airway device. Residual Physical or chemical changes that remain in a patient after an encounter with a disease, such as scars or hemiplegia. Resistance The second stage of the general adaptation syndrome, during which the body attempts to reestablish homeostasis, utilizing the endocrine and/or the immune system. Rib retractions Situation in which the work of breathing increases and more effort is needed to generate the negative pressure in the thorax required for inspiration. When this happens, the skin between the ribs is pulled inward because of this negative pressure in the chest. Respect High regard based upon a nonjudgmental attitude toward the patient. Respiratory acid Acid in the body formed when excess carbon dioxide reacts with water to form carbonic acid (H2CO3) before conversion into bicarbonate, which is the intermediary step in carbon dioxide transport. Resting membrane potential A difference in the electrical potential between the outside of the cell and the inside of the cell while in a resting state. Right Something to which a person is entitled based on society’s sense of fair play. Right bundle branch A division of the bundle of His that lies deep within the myocardium and serves as a further passageway for electrical impulses to the right ventricle. Reticular activating system (RAS) A complex network of interconnected reflexes in the brainstem that maintains wakefulness. Retrospective research Research technique in which a Paramedic looks at past practice, typically from patient care reports, to determine how to resolve a current issue or question. Re-uptake The reabsorption of a neurotransmitter by a neuron following impulse transmission across a synapse. Reverse R wave progression The loss of an R wave progression, which is suggestive of an anterior wall AMI. Right chest leads ECG recording technique in which the V4 to V6 wires from the left chest electrodes are switched over to the same relative position on the surface of the right chest and the ECG is rerecorded as V4R, V5R, and V6R. Reverse use- (rate) dependent Drugs that prolong the repolarization of normal myocardial tissues, as electrographically demonstrated by a prolonged QT interval. Rhabdomyolysis A breakdown of skeletal muscle releasing cell contents including myoglobin. 69 Right coronary artery (RCA) Cardiac artery that provides blood to the right atrium and ventricle and the inferior portion or wall of the left ventricle. Root A word, often supplemented with prefixes or suffixes, that relates to the main idea and often describes the organ involved or the key symptom. Rigor mortis A stiffening of the muscles, which often occurs after death. Risk The likelihood that a situation could lead to harm. Risk factors Traits or practices that tend to make a person more or less vulnerable to a disease as compared to another person. Risk management A plan that emphasizes safety and whose goal is to reduce Paramedic injury in an effort to promote a culture of safety in an organization. Risk manager An individual in an organization who identifies known hazards and then tries to mitigate those hazards. Rovsing’s sign Pain in the right lower quadrant that occurs when the left lower quadrant is palpated, which is often associated with appendicitis. Rub A low-pitched, soft scratching sound that occurs at any time during the cardiac cycle. Rules out A deductive process in which the Paramedic eliminates all explanations for the patient’s condition that don’t match the symptoms, thereby leaving the correct diagnosis. Runaway infusions An out-of-control drip infusion that results in the patient being overmedicated. Running the line out The process of clearing intravenous administration tubing of any air and running fluid freely from the end. Run of ventricular tachycardia Nonsustained bursts of ectopic ventricular beats that occur three or four at a time. 70 R wave progression A series of changes in the primary deflection of the QRS from negative in V1 to positive in V6 in a normal 12-lead ECG. SAFE-R A crisis intervention model consisting of five steps: stimulation reduction, acknowledgement, facilitation, explanation, and return or restoration. Safety officer In a large emergency situation, an individual assigned to maintain scene safety for the responders. Saline locks Process of filling the intermittent infusion device with saline to seal, or lock, the device and prevent thrombus formation. Scientific method The acquisition of knowledge through objective observation and considered reasoning. Sclerosis An inflammation, thickening, or hardening of a body part. Scope of practice The duties and responsibilities that fall under a particular Paramedic’s experience and skill level. Scored Adding a depression across the middle of a tablet that makes dividing the tablet in half easier. Script An idea in the Paramedic’s mind about a set of symptoms that has an associated symptom complex and an associated field diagnosis and treatment plan. Sedative Medications used to decrease a patient’s level of consciousness, lessen irritability, decrease excitability, or cause muscular relaxation. Salvo see Run of ventricular tachycardia. Satellite phones Satellites that radio waves are sent to, in which they literally bounce off the satellite and return back to Earth, bypassing obstructions such as mountains. Scanners Multiband radio receivers that monitor several radio frequencies, including those used by cellular telephones. Scene safety Steps taken to ensure the Paramedic’s well-being when responding to an emergency situation, such as rerouting traffic, assessing for threats, securing unstable areas, and the like. Schizokinesis A physiological theory that suggests past painful experiences, unconsciously recalled by trigger words, can elicit an autonomic nervous system response. In some cases, this response could be harmful to the patient. Segment The space between ECG waves. Seldinger technique A catheter-over-the-wire technique used to cannulate the femoral vein. Self-awareness Possessing a conscious understanding of one’s life influences and prejudices. Semantics The meanings of words. Senescence A breakdown in the body’s ability to monitor for organ system failure and to repair those organs, which is inherent in the concept of being elderly. Senile dementia Altered mental status caused by irreversible damage to the brain that typically is manifest over a long period of time (e.g., a series of brain attacks, such as strokes). Sensitivity A measure of how often a medical field test gives a correct positive result. 71 Sepsis A toxic condition resulting from the spread of bacteria or its toxic products from a focus of infection. Septal hematoma A form of nasal trauma that results in a bruise or bleeding. Shock–liver A form of liver failure. Shunting A displacement of blood volume to the core circulation. Side effects Unintended reactions one may have to a medication in addition to its therapeutic effect, such as drowsiness or nausea. Sign Indication that appears during a physical examination that suggests the cause of a disease or injury. Septic shock Condition in which the patient develops a potentially serious drop in blood pressure from a systemic infection in the blood. Serial vital signs All vital signs taken after the baseline vital signs that are useful to illustrate trends in vital sign changes. Serotonin A neurotransmitter found primarily in the gastrointestinal tract that causes arterial and venous constriction. Serve In legal terms, to cause to be delivered, as in a summons or other document. Settlement A sum of money paid to the plaintiff in order to conclude a case without going through a trial. Shams Ineffective devices used in research trials that appear similar to the actual device in order to create blinding for the participants. Shared decision making Collaborative medical practice in which the patient is seen as being interdependent with, rather than dependent on, the Paramedic. In a shared decisionmaking model, the patient is consulted about clinical decisions, empowering her with current information about her state of health. Shared practice The knowledge that both physicians and Paramedics are responsible for the patient’s care. 72 Sign-out An authentication measure in which the Paramedic writes the time, date, and initial after the last entry. The sign-out indicates that the PCR was written and completed by the person listed “in-charge” at the time and date listed. Simplex A radio system that only allows communication in one direction at a time, such as a walkie-talkie; the simplest radio system. Sim’s position A modified left lateral position used when administering medication rectally in which the patient is asked to bring her right knee to the chest as far as practical. This position provides optimal access to the anus while minimally compromising the patient’s dignity. Simulcast The ability to interact with several departments of an organization at once. Single-blind study A research study in which the subjects do not know which group they are in, although the researcher does. Sinoatrial node (SA) The initial portion of the conduction system, located just beneath the epicardium on the posterior wall of the right atrium near to the end of the vena cava and at the junction of the sinus of Valsalva and the atria. Sinus bradycardia A sinus rhythm with a rate below 60 bpm, although most patients are not symptomatic until the heart rate falls below 50 bpm. Small volume nebulizer (SVN) An alternative platform for the delivery of inhaled medications in which the medication is suspended in a stream of air which is then smashed against a round surface in the SVN, creating micro-fine particles that are ideal for inhalation. Sinus dysrhythmia An irregular heart rhythm characterized by alternating increases and decreases in the heart rate. Sinus of Valsalva An area adjacent to the aortic valve that creates a space between the aortic wall and each semilunar wall. Sinus tachycardia A sinus rhythm with a rate greater than 100 bpm. Situs inversus A condition characterized by complete reversal of all thoracoabdominal organs, such that they are positioned the mirror opposite of normal. Skip A radio wave transmission technique to overcome the problem of obstacles to line of sight, in which the high-frequency radio antenna is directed toward the sky. The radio signal then rises until it strikes the ionosphere, a layer of atmosphere where the sun’s ultraviolet rays ionize the gasses, and the signal is reflected back to Earth. Sky wave A radio wave transmitted into the atmosphere for a return to Earth rather than being transmitted across land. Slander Situation in which defamatory lies about a person are told to others. SOAP notes One of the earliest standardized documentation formats, which contains subjective (S) information obtained from the patient or the patient’s family, objective (O) information obtained during physical examination, an assessment (A) of the patient’s problem, and a plan (P) for action. Social norm A rule of conduct that regulates the interaction between people but is not specific to one individual. Social space In the theory of proxemics, an area of relative safety where strangers can enter, with certain expectations of conduct. A dining room in a restaurant is an example of the use of social space. Somatic pain Acute sharp, burning pain that often arises from the skin, ligaments, muscle, fascia, bones, or joints. Unlike visceral pain, somatic pain can be localized to a specific area. Slip-tip A syringe adaptor that simply slides inside the needle hub. 73 Spacer A device attached to a metered dose inhaler that allows a more controlled inhalation of smaller, ideal-sized drug particles suspended in the vapor within the chamber than are possible with the metered dose inhaler alone. Special incident reports (SIR) Documentation completed by the Paramedic that is not directly related to patient care but is instead used for administrative purposes or as a part of a court proceeding. Specialty Care Transport (SCT) A growing subspecialty in EMS, in which Paramedics perform critical care interfacility transportation by transporting sick and injured patients from outlying clinics and critical access hospitals to tertiary care centers. Specificity A measure of how often a patient with a negative medical field test truly does not have the condition the test is designed to detect. Spike Sometimes called a bayonet, a very sharp point on an administration set which is used to pierce the fluid container. Spirits Liquid medications brewed from various materials that have a volatile oil that evaporates at room temperature and leaves a distinctive odor in the air. Spontaneous abortion Situation that occurs in about 30% of pregnancies in which the zygote fails to implant and the pregnancy prematurely ends; often referred to as a miscarriage. Squelch control A static-reduction technique in radio transmissions that reduces the amount of signal received between transmissions, narrowing the reception of radio waves and eliminating background interference. 74 Standard leads The 12 leads used in a standard electrocardiogram, comprising the standard bipolar limb leads I–III, the augmented unipolar limb leads, and the standard precordial leads. Standard of care Care and treatment that another Paramedic with the same or similar training would have rendered in the same or a similar situation. Standing orders Preauthorized medical orders often given to Paramedics by physicians. Star of life The symbol of EMS as represented by six points: detection, reporting, response, on-scene care, care in transit, and transfer to definitive care. Starling’s law A cardiac theory that states the heart’s stroke volume increases in response to an increase in the volume of blood filling the heart (the end diastolic volume). The increased volume of blood stretches the ventricular wall, causing cardiac muscle to contract more forcefully. Static Radio interference caused by unshielded electrical devices emitting 60 cycle interference, lightning in the atmosphere, bursts of radio waves from sunspot activity, and even the spark plugs in an automobile. Status asthmaticus Persistent bronchospasm that is resistant to routine treatments. Status epilepticus A condition of unremitting convulsions interspersed with brief instances of coma. Statute A law enacted by legislation rather than previous case decisions. Statute of limitations The time allowed from the occurrence of an incident during which a lawsuit can be filed. The statute of limitations simply states that a plaintiff (usually the patient) cannot commence a lawsuit after a certain amount of time has passed. Sternal notch An anatomical position near the base of the neck. Sternal retractions Situation in which the work of breathing increases and more effort is needed to generate the negative pressure in the thorax required for inspiration. When this happens, the skin at the top of the sternum is pulled inward because of this negative pressure in the chest. Strain Signs of fatigue often seen when the body is repeatedly overstimulated, perhaps by constant bombardment by stress-inducing stimuli. Stress The body’s reaction to stimuli; a disruption in homeostasis. Stress management A process of coping with chronic stress in an effort to recover from its effects. Stress reduction Actions an individual takes to eliminate the source of stress. Stethoscope A medical instrument used to listen inside the body, consisting of hollow flexible tubes connected to ear pieces that join to a piece placed against the area to be evaluated. Stewardship To uphold the noble traditions of medicine while caring for patients. Stigma A negative connotation attached to participation in a program, such as labeling and public embarrassment. Stressors Stimuli that cause stress. Modern stressors include psychosocial pressures from family, coworker complaints, and supervisors’ demands, as well as such things as unrealistic expectations and noise pollution. Strike-out A method of error correction on the patient care report in which the Paramedic crosses through the mistake with a single line, leaving the content below the strike-out legible. Next to the strike-out, the Paramedic should place the date and initial the strike-out to indicate authorship. ST-segment depression A reduction of the ST segment, which is a >1 mm depression below the J point from isoelectric baseline. ST-segment elevation A rise in the ST segment, which is a >1 mm depression below the J point from isoelectric baseline. Stochastic effects Long-term complications from ionizing radiation exposure. Stock solution A standard concentration of a solution that may be diluted to weaken its potency for certain patients. 75 Stylet A commonly used adjunct to oral intubation that provides rigidity to the endotracheal tube. Subcutaneous emphysema The presence of air between the layers of the skin that indicates a leak in the respiratory system. Subcutaneous injection Injection in the layer of skin directly below the dermis and epidermis, which is the slowest and least dependable means of obtaining therapeutic drug levels in the bloodstream. Subendocardial ischemia Condition that occurs during myocardial ischemia in which the deep myocardial tissues becomes ischemic first, since coronary perfusion occurs from the surface (or epicardium) inwardly. Subpoena A legal command or direction issued by the court to appear at a certain place, such as the office of the plaintiff’s attorney or the courthouse, at a particular time. Substituted judgment Situation in which a surrogate decision maker has the responsibility to know the patient’s preferences and must place the patients’ wishes before the surrogate’s wishes. Succinylcholine A depolarizing neuromuscular blocker composed of two acetylcholine molecules hooked back to back. It offers a rapid onset of action (30 to 60 seconds) and rapid termination of effect (3 to 12 minutes) with return of sufficient ventilation to sustain life in 8 to 10 minutes. Succinylcholine produces muscle fasiculations at onset of action. 76 Suffix An affix placed at the end of the root word to modify that root word; for example, adding the suffix “-less” to the root word “help” makes “helpless,” meaning something different than “help.” Summarization Communication technique in which the Paramedic takes the patient’s own words, then paraphrases the patient’s words to ensure that the message sent was correctly received. Summary dismissal A request by the defendant’s attorney to end a court action based upon the facts in the case, stating that the facts of the case are clear and without dispute. Summary judgment Determination by a judge to dismiss or decide a case solely on the preliminary evidence without conducting a trial. Support Assistance that promotes another’s interests. Suppositories Medication within a wax carrier that melts at body temperature and is typically given internally for a local effect; often administered in the vagina, urethra, or rectum. Supraventricular rhythm A cardiac rhythm originating above the ventricles, indicated by a narrow QRS. Surfactant A fluid that decreases the alveoli’s surface tension and prevents the alveoli from collapsing during expiration. Surgical anesthesia A near-coma state of sedation in which the patient loses protective reflexes in a head-to-toe (cephalocaudal) direction. Surgical cricothyroidotomy A surgical procedure to gain entry to the trachea through the anterior neck by making an incision through the cricothyroid membrane. Sympathomimetics Drugs that mimic the effects of the sympathetic neurotransmitter norepinephrine. Symptom Something that indicates the presence of a physical disorder. Symptom complex A list of abnormal conditions found by the Paramedic during the history of the present illness and the physical examination. Suspension Medications that will not dissolve in a solvent and thus remain as finely pulverized particles floating in a liquid. Symptom pattern A series of conditions associated with a known disease. The Paramedic compares the symptom complex against the symptom pattern to arrive at a diagnosis. Synapse The point at which an impulse passes from one neuron to another. Sweep speed The speed of the rhythm passing by on the ECG monitor screen. Standard sweep speed is 25 mm/second, although the Paramedic may alter this speed to get a closer look at certain features of an ECG. Sympathetic nervous system The portion of the autonomic nervous system responsible for those emergency responses that are at “standby,” ready to provide the person with the ability to flee (flight) or fight. Syncope A transient loss of consciousness that spontaneously resolves. Syndrome A collection of symptoms that characterize a condition or state. Synergism The interaction between drugs which can occasionally lead to unexpected or extra effects. Syntax The rules of grammar. Syrups Medicines mixed with sugar and water. 77 System architecture The arrangement of radio components. Currently, two radio architectures exist in EMS: traditional land mobile radio (LMR) architecture and cellular system architecture. Systemic Pertaining to more than one internal organ system. Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) Localized infection leading to systemic infection leading to sepsis, then on to septic shock and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Systemic pathology Illnesses and ailments of humans related to specific organs. Systems review A head-to-toe approach to history gathering in which the healthcare provider starts at the head, questioning about issues/concerns that may be present at the nervous system level (stroke, seizures), and moving downward to cover the cardiovascular system, respiratory system, abdomen, genitourinary system, extremities, and behavioral disorders. System status management (SSM) A dynamic alternative to fixed-post staffing in which ambulances are “on the road” and moving to new locations to improve response times. Systole Ventricular contraction. Systolic blood pressure The maximum blood pressure measured during systole when the heart contracts. Tablet A dry medicinal powder that is compressed into a pill shape. Tachycardia A heart rate that is over 100 beats per minute for an adult or above the upper limit of normal for a child. Tachypnea Rapid breathing. 78 Tactical EMS (TEMS) EMS providers working with police SWAT teams trained on how to provide care to the wounded while in hostile surroundings as well as maintain the health of the SWAT team members during prolonged operations. Tactile fremitus Vibrations palpated on the chest wall that occur with speech. Tamponade Compression performed to control bleeding. Tardive dyskinesia A neurological disorder characterized by involuntary movements of the extremities often caused by long-term use of certain drugs (antipsychotic or neuroleptic). Teachable moment The time when the patient has a heightened awareness of a problem and is receptive to information. Telemetry The process of transmitting measurements and recordings to another location, where they are interpreted; a monitoring device connected to a patient by two or three wires that collects data and sends it via radio waves to an antenna. Teleological A model of ethics that simply states the end justifies the means. This approach implies that, even though some harm may occur, in the end if the outcome is good then the behavior is ethical. 10-codes A system from the 1920s in which police departments that only had one radio frequency used abbreviated messages designed to minimize airtime. Plain speech is preferred over 10-codes to avoid confusion and improve interoperability. Tenderness A soft or yielding texture; physically weak. Tentative field diagnosis A determination of what’s causing the patient’s problems performed upon initial evaluation. Teratogen Toxic substance or agent such as an illegal drug or an infection such as rubella (measles) or toxoplasmosis that could lead to fetal malformation. Teratogenic effect Exposure to ionizing radiation that can cause birth defects and cancer in subsequent generations as a result of changes in the structure of DNA. Tertiary care Highly specialized care provided in areas such as trauma centers and cardiac centers. Thrombin A protease in blood that facilitates blood clotting by converting fibrinogen to fibrin. Thrombocytes Platelets; blood cells that aid in clotting. Therapeutic effect See Intended biological effect. Thrombophlebitis An inflammation of a vein that may develop at an IV insertion site. Therapeutic index The ratio of the difference between a drug’s median effective dose (the ED50) and the median lethal dose (the LD50). Thrombus A mature clot made of platelets cross-linked with fibrin and other blood cells in a firm meshwork; a blood clot. Therapeutic level (t) The point when the drug levels attain the targeted value, as manifested by observation of the therapeutic effect. Therapeutic touch Intentional touching that mimics earlier comfort experiences (such as a mother stroking an infant’s cheek) and telegraphs reassurance, understanding, and caring to the patient as a means to heal. Third spacing A process that occurs when colloidal osmotic pressure is low, in which fluid leaks from the intravascular space and into the interstitial space. 3-3-2 rule A simple method for rapidly evaluating a patient’s anatomy, in which a Paramedic should be able to place three fingers between the tip of the chin and the hyoid bone, place three fingers between the upper and lower teeth at the maximal mouth opening, and place two fingers between the thyroid notch and the floor of the mouth. Thrill Vibration of the chest associated with heart contraction. Thyroid gland A highly vascular, “H” shaped structure that lies along the sides of the larynx and upper trachea. Tidal volume The volume of a normal breath, approximately 5 to 7 cc/kg of ideal body weight. Tincture Medicinal substance that is dissolved in alcohol. Tincture of benzoin Medication often applied to skin before applying tape or another adhesive bandage, used to both prevent allergic reactions on the skin from the bandage and to help the tape or bandage adhere longer. To keep open (TKO) The minimal infusion rate needed to keep veins from becoming occluded by a clot. Tolerance Resistance to a drug over time, which prompts the patient to take larger doses of the drug to acquire the same effect. Tonic A series of whole body contractions that often precede a seizure. 79 Tonicity A solution’s ability to exert an osmotic pressure upon the membrane. Tracheobronchial suctioning Direct suctioning of the secretions in the bronchial tree. Topical Medications meant to be applied to the skin. Tort A civil or private wrongful act, other than a breach of contract, resulting in some type of injury or harm (not necessarily physical injury). Total body clearance The sum of all drug excretion from the kidneys, skin, lungs, and liver. Toxicology The study of poisonous substances. Toxin Any substance capable of causing cell injury and death, including poisons. Trace A horizontal left-to-right movement on an ECG monitor. Trachea A conduit for respiratory gasses to pass to and from the lungs. 80 Trade name Drug name manufacturers give a patented drug to distinguish it from other similar drugs. Transdermal Pertaining to topical medication absorption, in which medicines are applied to the skin and absorbed into the body. Transtracheal jet ventilation (TTJV) Ventilation of the lungs using special highpressure devices through a large bore catheter placed through the cricothyroid membrane, which is a commonly taught and performed emergent oxygenation technique. Transfusion-associated circulatory overload (TACO) Situation that occurs when the patient receives more volume of blood products than can be handled by the circulatory system. Transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI) A new acute lung injury that occurs within six hours of a transfusion and is directly related to the transfusion. Translaryngeal illumination Using a lighted stylet during endotracheal intubation to take advantage of the larynx’s proximity to the anterior surface of the neck. Trauma Mechanical injury due to abrupt and sudden physical forces acting upon the body, such as friction, blunt force, or penetrating force. Translocations Gross breaks in some chromosomes with subsequent rejoinings at new locations. Transmission The process of conveying a message, which can be either a true and accurate representation of the sender’s thoughts or may be conveyed in such a way that the meaning is misconstrued by the receiver. Transmural ischemia The stage of myocardial ischemia when the ischemia affects the entire thickness of the myocardium, from the endocardium to the epicardium. Trauma line Intravenous access inserted into the vascular space so that intravascular volume can be replaced quickly. Treatment pathway The continuum of patient care which starts with the primary assessment and is continued in the emergency department, critical care units, rehabilitation floors, and homecare services. Triage tag A form of documentation tag used in mass casualty incidents to quickly prioritize patients based on how quickly they need assistance (i.e., immediate treatment vs minor injury). Trigeminy Situation in which ectopic complexes occur every third complex. 81 Tripod position A position patients may assume when in respiratory distress to help with breathing, in which they place their hands on their knees or legs and lean forward in a sitting position, creating a tripod. This position allows the overworked accessory muscles to work better, although most patients begin to tire when they are in such severe respiratory distress. Type I error A common error made in an experiment in which the researcher rejects the null hypothesis and accepts the alternative hypothesis when in fact it is not supported. Type II error A common error made in an experiment in which the researcher incorrectly fails to reject the null hypothesis; a failure to observe the change created by the treatment when one did occur. Umbilical cord A connection between the mother’s placenta and unborn child (at the navel) used to transfer nutrition, respiratory gasses, and wastes in the months prior to the child’s birth. Unilateral Relating to only one side. Unipolar lead The use of a single positive electrode, using Wilson’s central terminal, to record differences in electrical potential. Troches Lozenges that dissolve and are absorbed in the mouth through the oral mucosa. Trunking A technique whereby, using computers, multiple users can communicate over fewer frequencies, with the computer selecting the frequency to be used based on availability. Turgor A distended state of tension in living cells. Turned over to A process of transferring a patient to another care provider with equal or greater skill. Tympanic membrane Sometimes called the eardrum, a thin membrane that separates the external ear from the middle ear. Type and crossed Donor blood that is successfully matched to recipient blood. Type and cross-matched See Type and crossed. 82 United States Pharmacopeia (USP) A drug reference created by an independent nongovernmental science-based public health organization called the United States Pharmacopeia. The United States Pharmacopeia is made up of over 1,000 scientists, practitioners, and representatives from various colleges of medicine and pharmacy who set the standards for medication manufacturing in the United States. Universal donor Name given to Type O blood, since it can be given to any of the A-B-O blood types without adverse reactions. Type O blood does not have surface proteins that incite the immune response, which ends in hemolysis. Universal law A situation that demands action by any person in that situation, as a matter of duty. Universal recipients Name given to individuals with Type AB blood, since they can receive blood from any donor. This is because people with Type AB blood do not have antibodies against A or B proteins present in the plasma. Upregulation An increase in the number of cell receptors in a body cell due to changes in chemical levels. Urgent An assessment classification in which the patient’s condition is not emergent, suggesting further assessment and evaluation is needed before treatment is initiated. Use- (rate) dependent Drugs which act upon the ionic channels during the open/active state and preferentially will be attracted to rapidly depolarizing ectopic pacemakers. Uvula A fleshy lobe that typically hangs in the midline of the pharynx. Vagus nerve The major parasympathetic nerve which originates in the medulla, exits the skull at the base of the brain, travels down the neck (proximal to the larynx), branches into the heart and lungs, innervates the stomach, passes through the digestive tract, and ends in the anus. Valecula The space formed between the anteriorsuperior surface of the epiglottis and the posterior base of the tongue. Valid Logically correct and accurate. Value judgment A Paramedic’s decision as to which course of action is the correct course of action in terms of right or wrong. Vapocoolant spray See Fluori-methane. Vasopressor A chemical that causes vasoconstriction, particularly on the arterioles. Vastus lateralis (VL) An intramuscular injection site on the anterior thigh. The Paramedic mentally divides the vastus lateralis muscle into three equal portions. Choosing the middle section of the VL, the Paramedic prepares the intended injection site with an alcohol-soaked pad. Vector The sum of electrical events which makes up the common direction of the electrical wave front. Vecuronium A non-depolarizing neuromuscular blocking agent commonly used by Paramedics in the prehospital setting. 83 Venous cannulation The process of threading a catheter into a vein. Venturi masks Special masks with a restricted intake that permits an exact percentage of oxygen. These can be used to deliver oxygen, although their use in the prehospital environment is generally limited to specialty care services. Veracity An adherence to truthfulness. When a Paramedic practices being truthful with all of her patients, then that Paramedic can be said to have veracity. Ventilation A measure of how well a patient is moving air in and out of the lungs during inhalation and exhalation. Ventricular diastole Condition after a contraction when the ventricles of the heart are in a relaxed state. Ventricular rhythms A heartbeat originating from the ventricle, indicated by a wide QRS. This is usually, but not always, dangerous because the origin of the beat is in the last pacemaker in the ventricles. Ventricular systole Condition in which, with the pressure elevated in the ventricles, the ventricular muscle fibers contract forcefully and generate sufficient pressure to force open the aortic and pulmonary valves to eject blood out of the heart. Verbal consent A spoken request for permission to perform a procedure, accompanied by a simple explanation, which can improve patient compliance and decrease the risk of misunderstanding. Vertical equity Injury prevention programs where the people most affected receive the major emphasis. For example, if statistics demonstrate a higher number of accidental shootings among children in low-income households, then public health programs could be justifiably organized to emphasize prevention within that population. Vesicular sounds Lung sounds auscultated over the peripheral, smaller airways that sound like leaves rustling in the wind. Vicarious liability Based on the legal principle respondeat superior (“let the master answer”), the basis that a person is accountable for the actions of others. Ventricular tachycardia A rhythm experienced when the ectopic focus is ventricular and the ventricular pacemaker becomes dominant. With ventricular tachycardia, the rhythm is regular, the rate is fast, and every beat is wide. Virtue ethics A somewhat middle ground approach to ethics that does not depend on consequence-driven decisions or duty-driven decision making, but upon virtues. The virtue ethics approach suggests that a “rightthinking” person will make the best decision for the patient based upon a predetermined set of virtues. Ventrogluteal (VG) An intramuscular injection site located on the lateral thigh proximal to the hip. Visceral pain Poorly localized pain that arises from the internal organs and is usually described as pressure-like, dull, or aching. 84 Vital signs Objectively measured characteristics of basic body functions, such as temperature, pulse, respirations, and blood pressure. Vital signs provide the Paramedic with an indication as to how well the patient’s body is functioning or compensating for an injury or illness. Volume overload A potentially devastating complication of intravenous infusions that occurs when a positional IV access is inadvertently adjusted and the infusion flow is unrestricted. V/Q mismatch A mismatch between the amount of the lungs that are filled (alveolar ventilation) and the capillary circulation (pulmonary perfusion). Walked on Suppression of a radio signal. Wellness A state of physiologic equilibrium free of disease. More than an absence of illness, it is an active process of becoming aware of, and making choices toward, a more successful existence. Wide open (WO) A rapid infusion of intravenous fluid. Wilderness EMT (WEMT) An EMS provider in rural and woodland areas with special training that fosters critical thinking as well as creativity when working in an environment where supplies may be limited and patient transport to definitive care prolonged. Witness A person who can confirm testimony or evidence presented in a case, or authenticate information provided. Working diagnosis A presumptive conclusion the Paramedic makes based on the available signs and symptoms. World Health Organization (WHO) The most prominent and influential international public health agency. Z-track An injection technique in which the Paramedic holds the drug-filled syringe in the dominant hand, bevel up, and pulls gentle traction on the injection site with the nondominant hand as a means to prevent leakage. Zygote A fertilized ovum. 85