* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DCPS curriculum
Perspective (graphical) wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Rotation formalisms in three dimensions wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Compass-and-straightedge construction wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
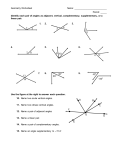
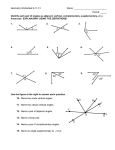
Curriculum Information SOL Reporting Category Measurement and Geometry Focus Problem Solving Virginia SOL 8.6 The student will a. verify by measuring and describe the relationships among vertical angles, adjacent angles, supplementary angles, and complementary angles; and b. measure angles of less than 360°. Essential Knowledge and Skills Key Vocabulary Essential Questions and Understandings Teacher Notes and Elaborations The student will use problem solving, mathematical communication, mathematical reasoning, connections and representations to: Measure and draw angles of less than 360° to the nearest degree, using appropriate tools. Identify and describe the relationships between angles formed by two intersecting lines. Classify the types of angles formed by two lines and a transversal. Identify and describe the relationship between pairs of angles that are vertical. Identify and describe the relationship between pairs of angles that are alternate interior angles and same side interior angles. Identify and describe the relationship between pairs of angles that are supplementary. Identify and describe the relationship between pairs of angles that are complementary. Identify and describe the relationship between pairs of angles that are adjacent. Use the relationships among supplementary, complementary, vertical, and adjacent angles to solve practical problems. Solve practical problems by using the relationship between pairs of angles such as vertical angles, alternate interior angles, same side interior angles, complementary and supplementary angles. Identify lines as parallel, intersecting, or perpendicular. Essential Questions and Understandings How are vertical, adjacent, complementary and supplementary angles related? Adjacent angles are any two non-overlapping angles that share a common side and a common vertex. Vertical angles will always be nonadjacent angles. Supplementary and complementary angles may or may not be adjacent. What are the relationships between the angles formed when two parallel lines are cut by a transversal? When two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, several pairs of angles are formed. Pairs of alternate interior angles, and vertical angles are congruent. Adjacent angles, and same side (consecutive) interior angles are supplementary. Teacher Notes and Elaborations Lines that have one and only one point in common are known as intersecting lines. When two lines intersect, four non-overlapping angles are formed. Parallel lines are lines that are in the same plane and never intersect because they are always the same distance apart. They have no points in common. The symbol || indicates parallel lines. Perpendicular lines are lines that intersect at right angles. Two angles are congruent if they have the same measure. A vertex is a common point to the two sides of an angle or a polygon. When two lines intersect two types of angle pairs are formed: vertical angles and adjacent supplementary angles. Adjacent angles are any two non-overlapping angles that share a common side and a common vertex. Vertical angles are all nonadjacent angles formed by two intersecting lines. Vertical angles are congruent and share a common vertex. The adjacent angles are supplementary. Nonadjacent angles do not share a common side. Complementary angles are any two angles such that the sum of their measures is 90°. When complementary angles are adjacent, they form a right angle. Supplementary angles are any two angles such that the sum of their measures is 180°. When supplementary angles are adjacent, they form a straight angle. A straight angle is an angle whose measure is 180º. A transversal is a line that intersects two or more coplanar lines in different points forming eight angles. Interior angles lie between the two lines. (continued) 46 Updated: 8-29-16 Curriculum Information SOL Reporting Category Measurement and Geometry Essential Knowledge and Skills Key Vocabulary Cognitive Level (Bloom’s Taxonomy, Revised) Remember – Classify, Describe, Identify Apply – Apply, Use, Solve, Measure Analyze - Draw Focus Problem Solving Virginia SOL 8.6 The student will a. verify by measuring and describe the relationships among vertical angles, adjacent angles, supplementary angles, and complementary angles; and b. measure angles of less than 360°. Key Vocabulary adjacent angles alternate interior angles complementary angles congruent intersecting lines nonadjacent angles parallel lines perpendicular lines protractor reflex angles same side interior angles straight angle supplementary angles transversal vertex vertical angles Essential Questions and Understandings Teacher Notes and Elaborations Teacher Notes and Elaborations (continued) Alternate interior angles are on opposite sides of the transversal. Same side (consecutive) interior angles are on the same side of the transversal. Exterior angles lie outside the two lines. Alternate exterior angles are on opposite sides of the transversal. If two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then alternate interior angles are congruent. If two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then same side(consecutive) interior angles are supplementary. Given parallel lines and the transversal (t), students should identify, classify, and describe angle relationships. 1 3 5 7 2 4 6 8 t Examples: 1 and 2 is a pair of adjacent supplementary angles. 4 and 6 and 3 and 5 are pairs of same side interior supplementary angles. 1 and 4 , 2 and 3 , 5 and 8 , 6 and 7 are pairs of vertical angles. 3 and 6 and 4 and 5 are pairs of alternate interior angles. Using angle relationships when two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, students are expected to determine angle measures given the measure of one angle. Problems should include algebraic expressions and equations (e.g., Given 3 3x and 6 x 30 , what is the value of x? What is the measure of 3 ?) Reflex angles measure more than 180° and less than 360º. The relationships of angles may be verified by measuring the angles with a protractor, a compass, or by physical direct comparison. When drawing angles, students should use a protractor and straightedge. 47 Updated: 8-29-16 Curriculum Information SOL Reporting Category Measurement and Geometry Focus Problem Solving Virginia SOL 8.6 Foundational Objectives 6.12 The student will determine congruence of segments, angles, and polygons. 5.11 The student will measure right, acute, obtuse, and straight angles. 5.12a The student will classify angles as right, acute, obtuse, or straight. Resources Text: Mathematics Course 3 VA Grade 8, ©2012, Prentice Hall, Pearson Education VDOE Enhanced Scope and Sequence Sample Lesson Plans http://www.doe.virginia.gov/testing/sol/sco pe_sequence/mathematics_2009/index.php Sample Instructional Strategies and Activities Use patty paper to trace angles and compare them with other angles to determine if they are congruent. Given quilt square patterns, students will identify supplementary and complementary angles. Students will verify measures of adjacent, vertical, complementary, and supplementary angles by using a protractor. Students will draw angles (given the degree measure less than 360º) using a protractor and straight edge. Virginia Department of Education Website http://www.doe.virginia.gov/instruction/ma thematics/index.shtml 48 Updated: 8-29-16