* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Em Waves
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
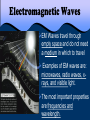
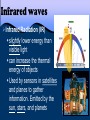
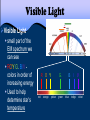
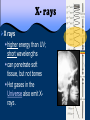
197 Waves and the EM Spectrum 2/22-25/2013 3/01/2017 EQ: How can patterns be used to describe the universe? Waves and the EM Spectrum 198 2/22-25/2013 3/01/2017 Practice/Application: Notes Starter/Practice: When looking at the night sky, Shrek tells Donkey, “The stars don’t tell us our future, but our past.” Do you agree or disagree? Why? Please explain your thoughts on this. Use what you learned in your notes!!! Connection: WS Exit: Describe what you have learned about the EM spectrum. Please write 3-4 sentences!! March 01, 2017 AGENDA Objective 8.8C Explore how different wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum such as light and radio waves are used to gain information about distances and properties of components in the universe by completing notes. 1. Starter 2. Activity 3. Notes 4. Exit Table of Contents Date 2/28 3/1 Lecture/ Activity/ Lab Big Bang Lab Waves and the EM Spectrum Page 195-196 197-198 TEKS 8.8C explore how different wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum such as light and radio waves are used to gain information about distances and properties of components of the universe How Do Astronomers Gather Information About Space? Most of the information we have about the universe comes from radiation. Objects in the universe, such as stars and galaxies, emit radiation. This radiation travels as waves. Different kinds of radiation have differing wavelengths and energies. We cannot see most of the radiation, but telescopes are used to collect the radiation for astronomers to study. The entire collection of different kinds of radiation is called the Electromagnetic Spectrum. The electromagnetic spectrum is a continuum of waves divided into regions based on wavelengths. At one end of the spectrum are radio waves, which allow you to listen to your favorite radio station. In the central portion is the only part of the spectrum you can see with your eye, the visible region. Most of the visible region comes from the Sun. When light is passed through a prism, it bends and separates into its different wavelengths. Spectroscopy is the study of the spectrum. A spectroscope is used to separate light into its component wavelengths so that they can be studied. The pattern of wavelengths and colors is called a spectrum. By obtaining and analyzing the spectrum from a distant object, astronomers can determine the object’s temperature, density, direction of motion and composition. Each element composing a star has a unique spectrum. Just like a fingerprint….. Astronomers use the spectral patterns from stars and other objects to determine what elements compose the object. Electromagnetic Waves EM Waves travel through empty space and do not need a medium in which to travel Examples of EM waves are: microwaves, radio waves, xrays, and visible light. The most important properties are frequencies and wavelength. Radio Waves & Microwaves Radio waves Long wavelengths; low energy. Radio and television stations broadcast using radio waves. Microwaves Shorter wavelengths and more energy than radio waves. The waves cause water to vibrate; this energy gives off thermal energy. Infrared waves Infrared Radiation (IR) slightly lower energy than visible light can increase the thermal energy of objects Used by sensors in satellites and planes to gather information. Emitted by the sun, stars, and planets Visible Light Visible Light small part of the EM spectrum we can see ROY G. BIV colors in order of increasing energy Used to help determine star’s temperature red R O Y G. orange green yellow B blue I indigo V violet Ultraviolet Rays Ultraviolet Radiation (UV) slightly higher energy than visible light Types: • UVA - tanning, wrinkles • UVB - sunburn, cancer • UVC - most harmful, sterilization X- rays X rays higher energy than UV; short wavelengths can penetrate soft tissue, but not bones Hot gases in the Universe also emit Xrays . Gamma Rays Gamma rays highest energy EM radiation; shortest wavelengths emitted by radioactive atoms used to kill cancerous cells Radiation treatment using radioactive cobalt-60. 197 Waves and the EM Spectrum 2/22-25/2013 3/01/2017 EQ: How can patterns be used to describe the universe? Waves and the EM Spectrum 198 2/22-25/2013 3/01/2017 Practice/Application: Notes Starter/Practice: When looking at the night sky, Shrek tells Donkey, “The stars don’t tell us our future, but our past.” Do you agree or disagree? Why? Please explain your thoughts on this. Use what you learned in your notes!!! Connection: WS Exit: Describe what you have learned about the EM spectrum. Please write 3-4 sentences!!