* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
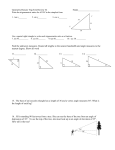
Download When you see the triangle below on the left and someone asks you
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
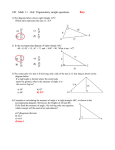
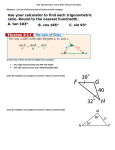
Name: _________________________________ Common Core Geometry – Honors Date: _______________ Law of Sines AIM: What is the Law of Sines and how do we use it to solve problems with triangles? Do Now: In ABC, AB = 14, AC = 9, and m<A = 48º. Find the area of ABC, to the nearest tenth of a square unit. Homework: Worksheet When you see the triangle below on the left and someone asks you to find the value of x, you immediately know how to proceed. You call upon your friend the Pythagorean Theorem because you see the right angle. But what do you do when you see the triangle on the right? There is no indication of a right angle. Now, with our knowledge of trigonometry, we are armed to attack any of these perplexing problems! Let's see how to apply trigonometry to working in triangles which do not contain a right angle. In this diagram, notice how the triangle is labeled. The capital letters for the vertices are repeated in small case on the side opposite the corresponding vertex. side a is opposite <A side b is opposite <B side c is opposite <C working together as partners! The ratios of each side to the sine of its "partner" are equal to each other. Law of Sines or These ratios, in pairs, are applied to solving problems. You never need to use all three ratios at the same time. Mix and match the ratios to correspond with the letters you need. Remember when working with proportions, the product of the means equals the product of the extremes (cross multiply). Example: In the accompanying diagram of mB 70, mA 65 , mB 70 , and the side opposite vertex B is 7. Find the length of the side opposite vertex A, and find the area of ABC . Class Work: 1. In triangle ABC, a = 8, b = 9, and m C=135o. What is the exact area, in square units, of triangle ABC. 2. In triangle ABC, sinA = 0.8, sinB = 0.3, and a=24. Find the length of side b. 3. In the accompanying diagram of triangle RST, What is the length of to the nearest integer? , , and . 4. Gregory wants to build a garden in the shape of an acute isosceles triangle with one of the congruent sides equal to 12 yards. If the area of the garden will be 55 square yards, find to the nearest tenth of a degree, the measures of the three angles of the triangle. 5. A ship at sea heads directly toward a cliff on the shoreline. The accompanying diagram shows the top of the cliff, D, sighted from two locations, A and B, separated by distance S. If , , and , what is the height of the cliff, to the nearest foot? 6. The angle of elevation from a ship at point A to the top of a lighthouse at point B is 43º. When the ship reaches point C, 300 meters closer to the lighthouse, the angle of elevation is 56º. Find, to the nearest meter, the height of the lighthouse. (Draw a diagram) 7. In the diagram, a = 55, c = 20, and m<A = 110º. Find the measure of <C to the nearest degree.