* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Routing
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
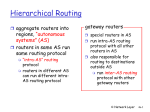
Topology of the Internet Autonomous Systems (AS) • The global Internet consists of Autonomous Systems (AS) interconnected with each other: - Collection of routers under same administrative control, all running the same routing protocol among themselves. - Stub AS: only one connection to another AS (small company) Mulithomed AS: multiple connections to other AS. No transit. (large corporation) Transit AS: hooking many AS together (provider) - Two-Level Routing Copyright © 2005 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. • • Intra-AS Routing (RIP/DV, OSPF/LS, IGRP/DV) - administrator responsible for the choice of routing protocol. Why are there different Protocols? 1- • Inter-AS Routing (BGP) • • Policy: - Inter-AS: control over how traffic is routed, and who routes through the network. Intra-AS: single admin, so no policy decisions needed. - hierarchical routing saves table size, reduced update traffic. - Intra-AS: can focus on performance Inter-AS: scalability and policy dominate over performance. Scale: Performance: IPv4 Addressing • An IP address is an identifier for a host/router interface. - IPv4 Address Structure • IPv4 Addresses: 32 bit • Human readable form: a.b.c.d Interface Addresses and Subnets Copyright © 2005 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. (where a,b,c,d are 8bit values) example: 130.238.8.176 • network/prefix host x bits 32-x bits Routing is only based on the network identifier. - Interface: connection between host/router and physical link Routers have several interfaces, hosts can have several interfaces. prefix = x MSB of the address (x: mask) we use the following notation for the prefix: a.b.c.d/x in Windows the mask has the form of e.g., 255.255.255.0 (=/24) A Router (layer 3) connects layer 2 networks. These networks are also called Subnet and have their own network id. 4- Routing Table Example Forwarding Policy • Routing Table at router R2 (simplified) subnet next hop L2 if 223.1.1.0/24 233.1.2.0/24 223.1.9.2 -* 3 1 223.1.3.0/24 223.1.7.0/24 223.1.8.0 223.1.8.0 2 2 223.1.8.0/24 223.1.9.0/24 -* -* 2 3 prefix check if destination address matches the prefix of the incoming network interface: - • • if it does: pass packet to transport layer (node is destination) else drop packet (the destination is on same network, no forwarding required) else, choose longest matching prefix in routing table. forward packet based on next hop information. 3 2 1 * this subnet is directly connected to the router. Default Router Copyright © 2005 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. • • Entry in the routing table of a host or router, specifying to which router a message that does not match any prefix should be forwarded to. Usually a gateway to other networks, e.g., the Internet. 4- Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) • • • • Translation between network-layer addresses and linklayer addresses. 130.238.8.100 > 49-BD-D2-C7-56-2A Resolution on same local link only (not-end-to end): “who has 130.238.8.100, tell 130.238.8.123” “reply 130.238.8.100 is at 49-BD-D2-C7-56-2A” Resolution at every router! Cache to avoid ARP request for every single packet (expires after ca. 20 minutes) Configuration on a Host Hierarchy - a Key to Scalability • network/prefix size: x bits • • • • host Address: network/prefix, host > identifyer Network mask > recognise prefix (network) Default router > router for traffic not on same netw. DNS server Hierarchical Addresses sunet.se 130.242.88.17/11 242: 11110010 uu.se student.uu.se 130.238.5.0/24 • - domain names: uu.se, it.uu.se fully qualified domain names: rama.it.uu.se, www.google.com Domain Name System Hierarchical Addressing - use of prefixes: 220.23.16.0/20, 200.23.16.0/23 IPv4 Addresses Hierarchical Routing - tightly related to addressing Autonomous Systems (intra-AS and inter-AS routing) Network Address Allocation Example without guarantee 130.238.0.0/16 238: 11101110 • Hierarchical Naming it.uu.se 130.238.8.0/24 Network Address Allocation More Addresses... • Allocation of prefixes is necessary for routing efficiency but inefficient in terms of address usage. • IPv6 • - Extended addressing capabilities (net|id, id unique) Streamlined header (40 Bytes) Flow labelling and priority - IP addresses have only a local scope 10.0.0.0/8 , 192.168.0.0/16 (“non routable” addresses) Typical home/student network. Network Address Translation (NAT) • How does an IPS get a block of addresses? ICANN: Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers Alternative Routing Approaches Copyright © 2005 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. • • Label Switching - Probabilistic Routing - • Hop-by-hop addresses (labels) Example: Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) The routing table indicates the probability to deliver to the destination based on prior experience. Forward a message if higher probability than previous hop. Example: Prophet routing protocol (Sami Network Connectivity) Content Routing - Finding information rather than a specific address. 4- Note: It is not the goal to improve address usage efficiency.