* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - singhscience
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
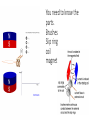
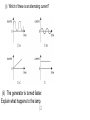
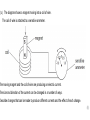
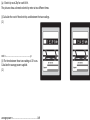
Foundation P1 – Part 5 Electricity AC – Alternating Current – The current flows one way then the other. DC – Direct Current – The current only flows one way. Producing electricity in this way is called induction or inducing a current. Moving a magnet through, or inside, a coil of wire induces a current. A bigger current can be generated by • Using a stronger magnet. • Using more coils of wire. • Moving the magnet more/faster. You need to know the parts. Brushes Slip ring coil magnet How you will be tested. The diagram shows a generator producing an alternating voltage. (a) Draw one straight line from each letter to its correct label. (2) (i) Which of these is an alternating current? (ii) The generator is turned faster. Explain what happens to the lamp. (2 ) *(c) The diagram shows a magnet moving into a coil of wire. The coil of wire is attached to a sensitive ammeter. The moving magnet and the coil of wire are producing an electric current. The size and direction of the current can be changed in a number of ways. Describe changes that can be made to produce different currents and the effect of each change. (6) More than one line from either P or Q (or both) loses the mark for that box B Answer Acceptable answers An explanation linking ‘fuses’ / ‘blows’ / gets the following hotter • increased brightness (1) • (due to) increased voltage (1) Transformers Transformers change the voltage. •A transformer that increases the voltage is called a step-up transformer. •A transformer that decreases the voltage is called a step-down transformer. Electricity is transferred at a High Voltage but low Current, this reduced loss due to heat. Non renewable Renewable Positive Negative Positive Negative Give lots of energy. Will run out will not run out Expensive to set up Cheap to build. Coal, oil and gas make carbon dioxide. no atmospheric pollution (except biofuels which are carbon neutral) Unreliable (not always windy, sunny) Nuclear makes radioactive waste. free/cheap to run. Visual pollution (doesn’t look good) Sounds pollution (wind turbines make noise) Waves and hydroelectric change the environment which is bad for wildlife. (dams need a reservoir) How you will be tested. Transformers are designed to use alternating current. Describe what change happens when a step-up transformer is used. (2) Explain why step-up transformers are used in the transmission of electricity in the National Grid. (2) *(c) The National Grid is supplied with electricity from large-scale electrical generators. These generators may be driven using different energy sources. Compare the use of a non-renewable energy source with the use of a renewable energy source to produce electricity for the National Grid. A description including the following • voltage (1) • increases (1) current decreases (ignore speed of current) Accept for 1 mark • increases current AND reduces voltage • voltage higher and bigger current/power • power decreases ‘it’ increases/decreases =0 A comparison including some of the following points Non- renewable sources · coal, oil, gas and nuclear · coal, oil, gas are fossil fuels · fossil fuels will run out · fossil fuels burn and produce CO2 · fossil fuels burn to produce atmospheric pollution · CO2 contributes to global warming · are a more expensive source · Nuclear power stations do not produce CO2 · Nuclear power produces radioactive waste · Radioactive waste is dangerous and difficult to store safely Renewable resources · Wind, waves, solar, biofuels, geothermal and hydroelectric · are a free/cheaper source · The energy source is unreliable · No (net) CO2 produced · No atmospheric pollution (except biofuels) · Waves and hydroelectric cause environmental changes · Wind farms and solar panels give visual pollution · Wind farms can be built off shore Comparison · Fossil fuel power stations are cheaper to build than wind farms for the same power output · Coal, oil, gas and nuclear fuel will run out, wind, waves and sun will always be available · Fossil fuel power stations produce CO2 which may increase global warming, renewable energy generators (wind farms) do not · Renewable energy generators have a free/cheaper source of fuel · fossil fuels have to be taken out of the ground · Nuclear power stations produce radioactive waste, which is dangerous, none of the other energy generators do this. Level 0 No rewardable content 1 1 - 2 ·a limited statement about either renewable or non-renewable e.g. Coal is non-renewable OR renewable energy will not run out OR oil will run out ·the answer communicates ideas using simple language and uses limited scientific terminology. ·spelling, punctuation and grammar are used with limited accuracy. 2 3 - 4 ·a simple comparison including 2 statements covering renewable and non-renewable e.g. Coal is nonrenewable and solar power is renewable OR renewable energy sources will not run out and non renewable sources do not pollute the atmosphere OR oil will run out, solar will not ·the answer communicates ideas showing some evidence of clarity and organisation and uses scientific terminology appropriately. ·spelling, punctuation and grammar are used with some accuracy. 3 5 - 6 ·a detailed comparison including at least 3 statements with a direct comparison between a renewable and a non-renewable source, at least one named e.g. Renewables will not run out but nonrenewables like coal will. OR Coal is non-renewable. When it is burnt carbon dioxide is produced. Wind farms do not produce any carbon dioxide. OR Carbon dioxide is produced when coal is used. Wind farms do not produce any carbon dioxide. Wind farms are noisy. OR Oil will run out, solar will not. Oil causes air pollution ·the answer communicates ideas clearly and coherently uses a range of scientific terminology accurately. ·spelling, punctuation and grammar are used with few errors. (a) Electricity costs 20p for each kW h. The pictures show a domestic electricity meter at two different times. (i) Calculate the cost of the electricity used between the two readings. (2) cost =...........................................................p (ii) The time between these two readings is 15 hours. Calculate the average power supplied. (2) average power =...........................................................kW (iii) It would cost the homeowner 15 p to buy 1.0 kW h of electrical energy from the National Grid. His generator has a maximum power of 2.0 kW. The generator produces energy at this maximum power for 3 hours. Calculate how much it would cost to buy the same amount of energy from the National Grid. (2) cost = ........................................................... p (b) An electric kettle is plugged into a 230 V mains supply. It has a power of 2.5 kW. Use this equation to calculate the current in the kettle. (3)