* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 16-6 How do astronomers measure distance?
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Archaeoastronomy wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy on Mars wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
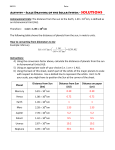
Name Class Date 16-6 How do astronomers measure distance? Lesson Review Write true if the statement is true. If the statement is false, change the underlined term to make the statement true. ____________________ 1. A light-year is equal to the distance that light travels in one day. ____________________ 2. One light-year is equal to a distance of about 10 trillion kilometers. ____________________ 3. An astronomical unit is equal to the distance between Earth and the Moon. ____________________ 4. Proxima Centauri is the closest star to Earth other than the Sun. ____________________ 5. A light-year is a smaller unit than an astronomical unit. ____________________ 6. The distance from the Sun to Earth is one light year. ____________________ 7. Light travels at a speed of about 300,000 km/sec. ____________________ 8. Light from the Sun takes about 8 minutes to reach Earth. ____________________ 9. The apparent change in the position of a distant object when seen from two different places is an astronomical unit. ____________________ 10. Distant stars have a larger angle of parallax. Skill Challenge Skills: analyzing, calculating, sequencing Use the table to answer the questions. DISTANCES OF PLANETS FROM THE SUN IN ASTRONOMICAL UNITS 1. How far is Earth from the Sun in AU? ___________________________________________________ Planet Distance Mercury 0.4 Venus 0.7 Earth 1.0 Mars 1.5 Jupiter 5.2 Saturn 9.5 than Neptune? _____________________________________ Uranus 19.2 5. Is Earth’s orbit closer to that of Venus or to that of Mars? Neptune 30.1 Explain. ___________________________________________ Pluto 39.4 ___________________________________________________ 2. How far is Mercury from the Sun in AU? ___________________________________________________ 3. How much closer to the Sun is Jupiter than Saturn? ___________________________________________________ 4. On average, how much farther from the Sun is Pluto ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ Concepts and Challenges in Earth Science, Teacher’s Resources CD-ROM (c) by Pearson Education, Inc./Globe Fearon/Pearson Learning Group. All rights reserved. The Exploration of Space: CHAPTER 16, page 9