* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geometry Lesson Plan Unit: 10 Circles Lesson Topic(s): Parts of a
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
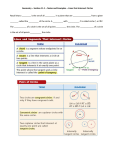
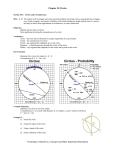
Geometry Lesson Plan Unit: 10 Circles Lesson Topic(s): Parts of a Circle Day: 1 Guiding Question(s): How many parts of a circle can you describe? How is a triangle inscribed in a circle? Lesson Plan Components Introduction How are circles utilized in real life (example: tire, ferris wheel, etc) Daily Review Solve the equation : (x+4)2= x2 + 62 Daily Objective/Essential Question The student will differentiate among the terms relating to a circle. Concept and Skill Development and Application Use the folding activity of a circle to identify the basic parts. Practice (Guided/Independent/Group) See Attached Notes Homework HANDOUT – SEE ATTACHED Closure Differentiate between a chord vs diameter Resources/Materials See Attached FIle Notes/Vocabulary See Attached Technology ELMO ELL/SPED/ Struggling Student Modifications Include instructional strategies/materials to meet the needs of all students. Geometry Lesson Plan Unit: Cirlce Lesson Topic(s): Segments and lines in a circle Day: 2 Guiding Question(s): How are the segments and lines in a circle related? Lesson Plan Components Introduction Warm up – Solve the following equations. 1. 2x = x + 5 x = 5 2. 3𝑤 + 4 = 5𝑤 − 8 w = 6 3. (𝑟 + 8)2 = 𝑟 2 + 162 r = 12 4. ℎ2 + 4 = 40 h = 6, -6 5. (𝑦 + 2)2 + 4 = 29 x = 3, -7 Daily Review Review previous day’s homework. Daily Objective/Essential Question The student will differentiate among the terms relating to a circle. (4.12.1) The student will solve problems involving tangent segments for a circle. (2.12.1, 4.12.1) Concept and Skill Development and Application See Notes. Practice (Guided/Independent/Group) See Notes. Homework McDougal Littell pg 599-600 #17 – 25, 37 – 38, 40 – 41, 46 – 48 Closure A line that is tangent to a circle touches a circle at exactly one point and is perpendicular to the radius of the circle at that point. Resources/Materials McDougal Littell Geometry Textbook pg 595 – 600 Notes/Vocabulary See notes. Technology Elmo, Smart Board ELL/SPED/ Struggling Student Modifications Guided notes, modified assignment Geometry Lesson Plan Unit: Circles Lesson Topic(s): Arcs and Chords Day: 3 Guiding Question(s): Sketch a pie chart. Ask students where they have seen pie charts, and explain finding arc measures of pie charts (arc addition postulate)? How many degrees in the arc of a semicircle? Lesson Plan Components Introduction Warm-up → Given a central angle of 700 for arc Daily Review AB how would we find the measure of the larger arc ACB ? Go over previous days assignment and the problems students may need extra assistance Review what is a minor and major arc and how we name and identify the two types of arcs including semicircles. Daily Objective/Essential Question Today the students will use the properties of arcs and chords… What is the difference between a major arc and a minor arc? How can determine which is present on a circle? How many degrees are in the arc of a semicircle? Sketch a pie chart. Ask students where they have seen pie charts, and explain finding arc measures of circles (arc addition postulate all sections combined equal 3600)? Use properties of chords of a circle and their theorems for arcs and perpendicular chords Two chords are congruent if and only if they are equidistant from the center Concept and Skill Development and Application See notes and review guide examples → Arc addition postulate of adjacent arcs is the sum of their measures →Two minor arcs are congruent if and only if their corresponding arcs are congruent →The diameter of a circle is perpendicular to a chord then the diameter bisects the chord and the arc →If one chord is perpendicular bisector of another chord then the first chard is a diameter Practice (Guided/Independent/Group) See notes and examples Homework Guided practice and applications page 607 Check for understanding 16, 22, 32, 38, 40, 42, and 46 Closure Find the length of a chord of a circle that passes through the center with a radius of 8? Given two central adjacent angles of 850 and 950 would this form a semicircle? Which is closer to the center of a circle? A longer chord or a shorter chord? Explain and use a drawing. Resources/Materials Textbook → Mcdougal Littell pages 603 to 612 Notes/Vocabulary Classify each arc as a major arc, minor arc, or semicircle given 620, 1800, 2400 . Intercepted arc measure of an arc Technology SmartBoard, Elmo, overhead ELL/SPED/ Struggling Student Modifications Have a hard copy of the notes available including figures of different types arcs and chords with examples Geometry Lesson Plan Unit: Circles Part I Lesson Topic(s): Inscribed Angles Day: 4 Guiding Question(s): How can we use the properties of inscribed angles of a circle to find missing measurements? Lesson Plan Components Introduction Define inscribed angle and intercepted arc then tell the students that we are going to find out today their relationship. Daily Review Review on solving equations with like terms. Daily Objective/Essential Question To use the properties of inscribed angles of a circle to find missing measurements. Concept and Skill Development and Application See notes Practice (Guided/Independent/Group) See notes Homework Mc Dougal Littell book p. 617 nos. 9-23 (odd numbers) Closure What are the properties of inscribed angles in a circle? Resources/Materials Textbook (Mc Dougal Littell) Notes/Vocabulary See attached notes Technology ELMO, Smart board etc. ELL/SPED/ Struggling Student Modifications Provide a copy of the notes Geometry Lesson Plan Unit: Circles Lesson Topic(s): Use the angles formed by segments and lines that intersect a circle to find missing measurements Day: 5 Guiding Question(s): What is the relationship between an inscribed angle in a circle and the intercepted arc? What will be the relationship between an angle formed by a tangent and a chord that intersect at a point on a circle and the measure of the intercepted arc? Lesson Plan Components Introduction Warm-up → Given a tangent and a chord that intersect on the circle, what is the measure of the linear pair of angles formed? If one angle is 1300, then what is the measure of the adjacent angle? Are the two angles supplementary? Daily Review Go over the previous day’s assignment for specific problems that students need extra assistance. Review the measure of an angle inscribed in a circle is half the measure of the intercepted arc. When two intersecting lines intersect a circle, there are three places where the lines can intersect; inside, on, or outside the circle. Daily Objective/Essential Question Students will use the properties of tangents, chords, and secants and their relationship with the angles and arcs formed in a circle to solve problems. Concept and Skill Development and Application See notes and review guide examples → Tangent -Chord Angle Theorem → Chord-Chord Angle Theorem → Tangent-Secant Angle Theorem → Tangent-Tangent Angle Theorem → Secant-Secant Angle Theorem Practice (Guided/Independent/Group) See notes and examples Homework Guided practice and applications page 624 Check for understanding 8, 16, 18, 22, 24, 28, and 40 Closure Find x and y X = 750 Y = 800 30 80 x y 120 Describe how can you find the measure of an angle formed by a tangent and a chord that intersect on a circle? Resources/Materials Textbook → Mcdougal Littell pages 621 to 627 Notes/Vocabulary Tangent, secant segments and lines, chords Technology SmartBoard, Elmo, overhead ELL/SPED/ Struggling Student Modifications Have a hard copy of the notes available including figures of different types lines with tangents, secants, and chords with examples Geometry Lesson Plan Unit: Circles Lesson Topic(s): Find the lengths of segments of chords, tangents, and secants of a circle. Day: 7 Guiding Question(s): What is the relationship of the lengths of segments of chords, tangents, and secants of a circle? Lesson Plan Components Introduction Warm up – Solve the following equations. 1. 4x = 12(4) x = 12 2 2. 8(12 + 8) = 6(𝑏 + 6) b = 20 3 3. 42 = 𝑥(𝑥 + 6) x = -8, 2 Daily Review Go over any questions on previous day’s assignment, then grade. Daily Objective/Essential Question Today we will determine the lengths of segments of chords, tangents, and secants of a circle. Concept and Skill Development and Application See Notes. Practice (Guided/Independent/Group) See Notes. Homework Page 632# 10, 12, 14, 15, 16-24 even, 28, 30 Closure Explain other ways you could use the lengths of tangents, secants, and chords of a circle in a real life situation. Resources/Materials Textbook (McDougal Littell) – pages 629 – 635 Handouts Notes/Vocabulary See attached notes. Technology Elmo, Smartboard ELL/SPED/ Struggling Student Modifications Have a hard copy of the notes printed off for the students. Geometry Lesson Plan Unit: Circles (Part II) Lesson Topic(s): Equations of Circles Day: 8 Guiding Question(s): How to write and use the equation of a circle in the coordinate plane in problem-solving? Lesson Plan Components Introduction Recall the relationship of the center and the radius of a circle. Daily Review Review distance formula. Daily Objective/Essential Question To write the equation of a circle in the coordinate plane and use the equation of a circle and its graph to solve problems. Concept and Skill Development and Application See notes Practice (Guided/Independent/Group) See notes Homework Mc Dougal Littell textbook pp. 638-639 nos. 19-40 (odd numbers) Closure What is the standard form of the equation of a circle? Resources/Materials Textbook (Mc Dougal Littell) and graphing papers Notes/Vocabulary See attached notes Technology ELMO, Smart board, etc. ELL/SPED/ Struggling Student Modifications Provide a copy of the notes Geometry Lesson Plan Unit: Circles Lesson Topic(s): Construct a circle using a straight edge and compass Day: 9 Guiding Question(s): How can you inscribe a regular triangle inside a circle? Lesson Plan Components Introduction Using manipulative activity show how the altitude drawn to the hypotenuse of right triangle forms three similar triangles. (See lesson plans.) Identify the different parts of the circle and the different segments and lines related to the circle. Daily Review Review construction techniques Daily Objective/Essential Question The student will perform constructions involving special relationship within circles. NS 3.12.3, 4.12.8 Concept and Skill Development and Application Construct circles using a straight edge and compass to include inscribed polygons and tangents. Practice (Guided/Independent/Group) See notes. Homework None Closure How would you use a compass and straight edge to construct a circle with an inscribed regular triangle? Resources/Materials Compass Straight edge (ruler) Elmo Smartboard Notes/Vocabulary Review inscribed, circumscribed, tangent, secant, concentric circles Review the use of a compass in geometric constructions Technology Smart board could be used to demonstrate constructions. ELL/SPED/ Struggling Student Modifications A copy of the notes could be made available. Modify the length of the assignment. Model constructions and provide guidance as necessary.