* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download FINAL EXAM REVIEW
Participatory economics wikipedia , lookup
Non-monetary economy wikipedia , lookup
Fiscal multiplier wikipedia , lookup
Nominal rigidity wikipedia , lookup
Economic planning wikipedia , lookup
Criticisms of socialism wikipedia , lookup
Economics of fascism wikipedia , lookup
Long Depression wikipedia , lookup
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
Production for use wikipedia , lookup
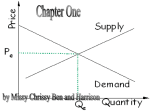
Economics FINAL EXAM REVIEW ______________________ 1. characteristic of wants (limited/unlimited?) ______________________ 2. characteristic of resources (limited/unlimited?) ______________________ 3. the basic economic problem Identify the four factors of ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ production defined below: 4. natural resources/raw materials 5. machinery/equipment/the factory 6. human resource: mental and physical efforts 7. human resource: initiative; risk taking; more important in capitalism than in any other type of economic system Identify the three basic economic systems as defined below: ______________________ 8. decisions (what, how, for whom) are made through the interactions of individual buyers and sellers (supply and demand) in the marketplace) ______________________ 9. decisions (what, how, for whom) are made by government ______________________ 10. economic decisions (what, how, for whom) are determined on the basis of custom – what has always been produced ______________________ 11. type of economy that mixes command (government) and market (free enterprise) List the three basic economic questions: ______________________ 12. ______________________ 13. ______________________ 14. Identify the terms defined or explained below: ______________________ 15. what is given up when making a choice; forgone opportunity; next best alternative not taken ______________________ 16. a good used to produce another good: i.e., machinery, equipment ______________________ 17. total revenue – total costs = ____________ ______________________ 18. lower prices, greater variety and better quality are benefits of? ______________________ 19. # of unemployed + # of employed = _____________ ______________________ 20. a minimum price imposed by government below which the price cannot fall; located above Pe, it creates a surplus ______________________ 21. a maximum price imposed by government above which the price cannot rise; located below Pe, it creates a shortage ______________________ 22. occurs when the price rises above Pe and QS > QD ______________________ 23. occurs when the price falls below Pe and QD > QS ______________________ 24. relationship between price and QD (inverse or direct?) ______________________ 25. relationship between price and QS (inverse or direct?) Identify the market structures characterized below: ______________________ 26. many firms; homogeneous product; low concentration of economic power; high degree of competition; a price taker – no control over price; no barriers to entry into market 1 ______________________ 27. many firms; heterogeneous product; low concentration of economic power; competition; some name brands can corner the market and raise their prices; few, if any barriers to entry ______________________ 28. few firms; high concentration of economic power; less competition; significant barriers to entry; some control over price ______________________ 29. one firm; total concentration of economic power; no competition; entry blocked; price-setter Identify the types of business organization based on ownership characterized below: ______________________ 30. one owner; disadvantages: unlimited liability; limited life, limited capital; advantages: pride in ownership; keep all profits; no double taxation; own boss, etc. Disadvantage: It is very difficult to raise money for business ______________________ 31. two or more owners; disadvantages: unlimited liability, limited life; advantages: owners can specialize in different aspects of the business; pride in business ownership, etc. ______________________ 32. many owners (stockholders); advantages: limited liability; unlimited life; greater access to capital; disadvantages: double taxation, etc. Identify the terms defined/explained below: ______________________ 33. means government should “let do” – stay out of the economy ______________________ 34. modern economic theory based on a market economic system; also called free enterprise system ______________________ 35. economic model that illustrates the exchanges taking place between consumer households and business firms within the markets (resource and product) of the economy ______________________ 36. market in the circular flow model (CFM) in which resources (L, L, C, E) are provided by consumers and purchased by business firms with a payment of rent, wages, interest, and profit ______________________ 37. market in the CFM in which goods and services are sold by business firms and purchased by consumers ______________________ 38. income earned for labor ______________________ 39. income earned for capital ______________________ 40. income earned for land ______________________ 41. income earned for entrepreneurship ______________________ 42. part of economics that studies the economy as a whole (macro or micro?) ______________________ 43. part of economics that studies the individual parts of the economy ______________________ 44. the sum of the # of employed + # of unemployed ______________________ 45. = (the # of unemployed/the labor force) X 100 ______________________ 46. = direct cost (tuition, etc.) of going to college + the work given up types of mergers (combination of two or more businesses): ______________________ 47. same product; same stage in production process ______________________ 48. same product line; different stage in production process ______________________ 49. unrelated products production possibilities curves: ______________________ 50. a point on the curve represents (full or less than full?) use of resources ______________________ 51. a point under the curve represents (full or less than full?) use of resources ______________________ 52. a point outside the curve is (possible or impossible?) given resources ______________________ 53. movement along a PPC curve results in a _______? 2 ______________________ 54. to get something, one must give up something (identify term) Identify the four phases of the business cycle described below: ______________________ 55. high point in economic activity (maximum employment and production; increase in price level) ______________________ 56. increasing AD, decreasing unemployment, increase in store orders, etc. ______________________ 57. rising unemployment; decreasing production; decreasing AD ______________________ 58. lowest level of economic activity ______________________ 59. problem associated with peak phase of business cycle Identify the term defined or explained below: ______________________ 60. total responsibility for business debts; disadvantage of sole proprietorship and partnership ______________________ 61. type of production cost (i.e., cost of pollution) that must be paid by society if government does not regulate business ______________________ 62. a gap between potential output and actual output; develops during a recession when cyclical unemployment is occurring types of unemployment: ______________________ 63. in between; first time job seekers; quit job to find better one ______________________ 64. caused by change in demand for products/skills of workers; foreign competition; or automation ______________________ 65. caused by too little AD in the economy; recession; GDP gap characteristics of capitalism: ______________________ 66. freedom of economic choice ______________________ 67. individual ownership of property resources ______________________ 68. self interest guides economic decision making (i.e. desire for profit) ______________________ 69. economic rivalry ______________________ 70. role of government in capitalism (stay out!) identify economic goals: ______________________ 71. freedom of economic choice/decision making ______________________ 72. getting the most of scarce resources through competitive markets ______________________ 73. fairness in economic decision making ______________________ 74. 94-95% of labor force employed ______________________ 75. increases in GDP; increase in productive potential ______________________ 76. cushion against economic risk (social security) ______________________ 77. absence of serious inflation or deflation 78. government policies expansionary policy: fight _____________________ monetary policy (FED): ____ MS (money supply) ____ reserve requirement; ____ discount rate ____ securities fiscal policy (Congress/President) ___ government spending ____ taxes contractionary policy: fight ____________________ monetary policy (FED): ____ MS (money supply) ____ reserve requirement; ___ discount rate ____ securities fiscal policy (Congress/President) ____ government spending ____ taxes 3 Drawing supply and demand curves increase in demand: causes: (NPD) ____ buyers ____ price of complement ____ price of substitute ____ tastes decrease in demand: causes: (NPD) ____ buyers ____ price of complement ____ price of substitute ____ tastes increase in supply: causes: (NPD) ____ resource prices ____ technology ____ costs of production ____ gov’t regulation decrease in supply: causes: (NPD) ____ resource prices ____ technology ____ costs of production ____ gov’t regulation PPC: illustrate the condition or event unemployment increase in resources decrease in resources trade-off You will also need to be able to interpret PPC, circular flow, supply and demand, and budget line models. Be familiar with the term “There is no such thing as a free lunch,” TINSTAAFL. A durable good is one that lasts more than three years when used regularly. 4