* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1. (a) state Law of multiple proportion (2) (b) A compound contains
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Density functional theory wikipedia , lookup
Bremsstrahlung wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Coupled cluster wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital wikipedia , lookup
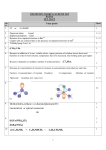
CHEMISTRY HSE-I Maximum marks: 60 Time: 2hrs Cool of time: 15mintes 1. (a) state Law of multiple proportion (2) (b) A compound contains 40% C, 6.66% H and the rest of oxygen. Find its empirical formula. (2) 2. (a) Name the charge less particle and find its number in the following mulei 16 56 8O , 26 Fe (1) (b) Sketch the shape and orientations of 2p orbitals. (1 ½) (c) An atomic orbital has n=3. (i) What are the possible values of l and m (ii) List the quantum number (m and l ) of electrons for 3d orbital . (iii) Which of the following orbitals are possible 1p, 2s, 2p and 3f (2 ½) 3. (a) Arrange the following halogens in the increasing order of their electron Gain enthalpy F, Cl, Br, I (1) (b) The graphical representation of Ionisation energy against atomic number of certain elements are given below. (i) How Ionisation energy varies along a period (1) (ii) How will you explain the unexpected values of Boron and Oxygen (2) 4. (a) Out of NH3 and NF3 which has higher dipole moment and given reason (b) (c) 5. (a) (b) (1) Discuss the shape and hybridization of the following molecules using the VSEPR theory (i) Becl2 (ii) NH3 (iii) C2H2 (iv) PCl5 (2) Using molecular orbital theory, explain the paramagnetic behaviour of O2 and find its bond order (2) Dalton’s law of pastial pressure is not applicable to gaseous mixture Of NH3 and Hcl gases. Give reason (1) In an examination one student wrote that ‘Real gases be have ideally at low temperature and high pressure. (i) Is the above statement correct or not? (ii) Why do real gases deviate from ideality? (iii) Write Vander waal’s equation for ‘n’ moles of an ideal gas. (2) (c) Analyse the graphs given below .Which graph represents charle’s law? Explain. (2) 6. (a) Classify the following properties in to intensive and extensive property Volume, density, work, enthalpy. (1) (b) Calculate the enthalpy change of the reaction CO (g) + ½ O2 (g) CO2 (g) from the following data. (i) C(S) + O 2 (g) (ii)C(S) + ½ O 2 (g) CO2 (g); 4H= -394.9KJ CO (g); 4H = -110.5KJ 7 (a) Sate Le chatelier’s principle (b) Describe the effect of (i) Addition of H2 (ii) addition of CH3OH (3) (1) (iii) Removal of CO and (IV) removal of CH3OH on the equilibrium of the reaction 2H 2(g) + CO (g) CH3 OH (g) (2) (c) The species H2O, HCO3-, HSO4- and NH3 can act both as Bronsted Acids and bases. For each case give the corresponding conjugate acid and base (2) 8 Assign the oxidation number of the underlined elements in each of the Following species H2O , CaO 2, Hcl O4 , K2MnO4, Na H, NaBH4 (3) 9. Permanent Hardness is due to the presence of chlorides and sulphates of Calcium and magnesium in water. (a) Give one method for the removal of permanent Hardness (2) (b) H2O2 is stored in wax – lined glass or plastic vessels in dark. Give reason (2) 10. (a) Write the molecular formula of (i) plaster of Paris and (ii) Gypsum (1) (b) Lithium shows diagonal relationship to magnesium. (i) Give the anomalous behaviour of Li and Mg. (3) 11. (a) Is boric acid a protic acid? Explain (1) (b) Suggest a reason as to why CO is poisonous (1) (c) Carbon exhibits many allotropic forms. One of them is fullerenes. (i) Write short notes on fullerenes (2) 12. (a) The IUPAC name and structural formula of some organic Compounds are given below. Match them properly Column A Column B (1) CH3 - CH2 – CH=CH-CH2OH (1) 2 , 2 – dimethrl propane CH3 (2) CH3 C (2) pentane – 1, 4- diol CH3 CH3 (3) pent – 2 – en – 1 – 01 (3) CH 2 = C CH = CH2 CH3 (4) CH3 CH CH2 (4) 2 methyl but -1, 3 - die CH OH OH (2) (b)Explain the terms Inductive and electrometric effect. (3) 13. (a) Benzene is extra ordinary stable though it contains three double bonds. Give reason (2) Peroxide (b) CH3 – CH = CH2 + HBr CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – Br I CH3 – CH - CH3 Br II Which is the major product. Justify your answer. (3) 14. Taj mahal is being slowly dis figured and the marble is getting discoloured and lusterless. (a) What is the reason behind it (1) (b) Suggest remedial measures. (2) Prepared by HSST (chemistry) A .S. H. S.S PARIPPALLY