* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1.20 Complementary Angles
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Rotation formalisms in three dimensions wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
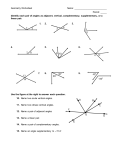
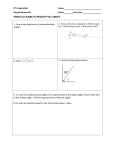
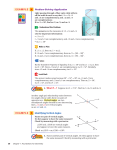
1.20. Complementary Angles www.ck12.org 1.20 Complementary Angles Here you’ll learn what complementary angles are and how to solve complementary angle problems. What if you were given two angles of unknown size and were told they are complementary? How would you determine their angle measures? After completing this Concept, you’ll be able to use the definition of complementary angles to solve problems like this one. Watch This MEDIA Click image to the left for more content. CK-12 Complementary Angles Watch this video beginning at around the 3:20 mark. MEDIA Click image to the left for more content. James Sousa:Angle Basics–ComplementaryAngles Then watch the first part of this video. MEDIA Click image to the left for more content. James Sousa:Complementary Angles Guidance Two angles are complementary if they add up to 90◦ . Complementary angles do not have to be congruent or next to each other. 174 www.ck12.org Chapter 1. Unit 1: Transformations, Congruence and Similarity Example A The two angles below are complementary. m GHI = x. What is x? Because the two angles are complementary, they add up to 90◦ . Make an equation. x + 34◦ = 90◦ x = 56◦ Example B The two angles below are complementary. Find the measure of each angle. The two angles add up to 90◦ . Make an equation. (8r + 9) + (7r + 6) = 90 (15r + 15) = 90 15r = 75 r=5 However, you need to find each angle. Plug r back into each expression. m GHI = 8(5◦ ) + 9◦ = 49◦ m JKL = 7(5◦ ) + 6◦ = 41◦ Example C Find the measure of an angle that is complementary to MRS if m MRS is 70◦ . Because complementary angles have to add up to 90◦ , the other angle must be 90◦ − 70◦ = 20◦ . 175 1.20. Complementary Angles www.ck12.org MEDIA Click image to the left for more content. CK-12 Complementary Angles Guided Practice Find the measure of an angle that is complementary to ABC if m ABC is: 1. 2. 3. 4. 45◦ 82◦ 19◦ 12◦ Answers: 1. Because complementary angles have to add up to 90◦ , the other angle must be 90◦ − 45◦ = 45◦ . 2. Because complementary angles have to add up to 90◦ , the other angle must be 90◦ − 82◦ = 8◦ . 3. Because complementary angles have to add up to 90◦ , the other angle must be 90◦ − 19◦ = 71◦ . 4. Because complementary angles have to add up to 90◦ , the other angle must be 90◦ − 12◦ = 78◦ . Practice Find the measure of an angle that is complementary to ABC if m ABC is: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 4◦ 89◦ 54◦ 32◦ 27◦ (x + y)◦ z◦ ← → Use the diagram below for exercises 8-9. Note that NK ⊥ IL . 8. Name two complementary angles. 9. If m INJ = 63◦ , find m KNJ. 176 www.ck12.org Chapter 1. Unit 1: Transformations, Congruence and Similarity For 10-11, determine if the statement is true or false. 10. Complementary angles add up to 180◦ . 11. Complementary angles are always 45◦ . 177