* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Summer II
Comparative advantage wikipedia , lookup
Middle-class squeeze wikipedia , lookup
Marginal utility wikipedia , lookup
Economic equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Fei–Ranis model of economic growth wikipedia , lookup
Marginalism wikipedia , lookup
Supply and demand wikipedia , lookup
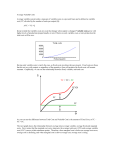
1 Exercise questions 3 Summer III, 2008 Answer all questions Multiple Choice Questions. Choose the best answer. 1. The above table shows the short-run total product schedule for the campus book store. What is the marginal product (MP) of the 6th employee at the book store? A) 83 books sold. B) 13.83 books sold. C) 10 books sold. D) between 11 and 14 books sold. 2. The above table shows the short-run total product schedule for the campus book store. What is the average product (AP) of the 4th employee? A) 58 books sold. B) 14.5 books sold. C) 18 books sold. D) 13.3 books sold. 3. The range of output over which a firm’s average variable cost is decreasing is the same as the range over which its A) marginal cost is increasing. 1 2 B) average fixed cost is decreasing. C) average product is increasing. D) average product is decreasing. 4. Pat’s Catering finds that when it caters 20 meals a week, its total cost is $6,000. If Pat has total variable cost of $5,000, what is Pat’s total fixed cost? A) $50. B) $250. C) $1,000. D) $6,000. 5. Diminishing marginal returns occurs when A) all inputs are increased and output decreases. B) all inputs are increased and output increases by a smaller proportion. C) a variable input is increased and output decreases. D) a variable unit is increased and its marginal product falls. 6. The average product of labor exceeds the marginal product of labor A) when the average product of labor is falling. B) when the average product of labor is rising. C) when the marginal product of labor is at its maximum. D) when the average product of labor is at its maximum. 7. In the above figure, the long-run average cost curve exhibits economies of scale (or increasing returns to scale) 2 3 A) between 5 and 10 units per hour. B) between 10 and 20 units per hour. C) between 20 and 25 units per hour. D) along the entire curve. 8. A firm has fixed costs A) in the short run and in the long run. B) in the short run but not in the long run. C) in the long run but not in the short run. D) neither in the long run nor in the short run. 9. Which of the following is FALSE? A) Long-run average variable costs equal long-run average total costs. B) Fixed costs increase in the long run. C) As a firm produces more output, eventually it experiences diseconomies of scale. D) In the long run, both the amount of capital and labor used by the firm can be changed. 10. If total fixed cost increases, then the average total cost curve ____ and the marginal cost curve ____. A) does not shift; shifts upward B) shifts upward; shifts upward C) does not shift; does not shift D) shifts upward; does not shift 11. In the above table, the total fixed cost is A) $0. B) $20. 3 4 C) $30. D) $50. 12. In the above table, when output increases from 8 to 12 units, the marginal cost of one of those 4 units is A) $1.20. B) $2.00. C) $5.00. D) $15.00. 13. If marginal cost exceeds average variable cost, then ____cost is ____. A) average total; at a maximum B) average total; falling C) average variable; rising D) average fixed; at a maximum 14. When marginal product of labor is a maximum, average product of labor is ____. A) a maximum B) increasing C) decreasing D) equal to marginal product 15. Sticky Cakes is a bakery. A decrease in the wage rate that Sticky Cakes pays its workers A) does not shift its MC curve or its ATC curve. B) shifts its MC curve downward but not its ATC curve. C) shifts both its MC curve and its ATC curve downward. D) does not shift its MC curve but shifts its ATC curve downward. 16. Increasing marginal returns to labor might occur at low levels of labor input because of A) increasing average costs. B) differing factor proportions. C) increasing specialization of tasks. D) decreasing use of machinery and increasing use of technology. 17. The law of diminishing returns implies that, with the use of capital fixed, as the use of labor rises, A) total product will fall eventually. B) the marginal product of labor will fall eventually. C) the total product of labor will fall below the marginal product of labor. 4 5 D) the production process will become technologically inefficient eventually. 18. Decreasing returns to scale occurs a. in the SR. b. in the LR. c. in both the short run and long run. d. because the productivity of labor varies across individuals. 19. Which of the following condition holds? a. AC = w/MPL. b. MC = w/APL. c. AVC = w/APL d. AFC = w/MPL. 20. An upward shift in MC curve, that is an increase in MC for a given level of output, can be due to a. rising prices of fixed inputs. b. falling prices of fixed inputs. c. rising prices of variable inputs d. increasing marginal product. Complete the following Table. Then use the information to answer questions 21 to 23. Q 0 1 2 TFC ___ 10 ___ TVC ___ ___ ___ TC 10 16 22 MC 6 ___ 21. The total fixed costs in the above Table are equal to___. a. b. c. d. $26 $0 $16 $10 22. The total variable costs at Q =1 is ___ a. $10. b. $6. c. $16. d. $20. 5 6 23. The marginal cost is ___ when the second unit of output is produced. a. $10 b. $16 c. $8 d. $6 e. none of the above 24. In perfect competition, the marginal revenue of an individual firm A) is zero. B) is positive but less than the price of the product. C) equals the price of the product. D) exceeds the price of the product. 25. If a firm can change market prices by altering it’s output, then a. it has some market power. b. it is a price taker. c. it faces a horizontal demand curve. d. it is a competitive firm. 26. A firm that can sell all of its output at the prevailing market price a. is a competitive firm. b. receives less than its marginal cost. c. faces a downward-sloping demand curve. d. has a substantial market power. 6 7 27. In the above figure, the firm will produce A) 0 units. B) 5 units. C) 15 units D) 20 units. 28. In the above figure, the firm’s total economic profit is equal to A) $60. B) $200. C) $150. D) MR – MC. 29. Jack owns a chicken farm. Answer questions 29 and 30. Suppose that the price of chicken feed rises. Which of his cost curve(s) will be affected. a. MC, ATC and AVC. b. MC and AVC. c. AFC and ATC. d. MC only. e. ATC only. 30. Suppose that the U.S. government requires that all chicken farms to pay an annual license fee $5,000. Which of his cost curve(s) will be affected. a. MC, ATC and AVC. b. MC and AVC. c. AFC and ATC. d. MC only. e. ATC only.. 31. Which of the following conditions is true for a perfect competitive market? a. P=MR=AR. b. P= AFC. c. P<MR. d. P<AR. 32. When the market demand increases, the competitive firm’s a. MR shifts up. b. MR remains constant. c. both MC and AC shift up. d. MC shifts up. e. AC shifts up. 33. If the firm is a profit maximizer, it must produce at a. the lowest point of its ATC. 7 8 b. the intersection of the MC and MR. c. the lowest point of its AVC. d. the maximum level of output as possible. 34. John has recently remodeled his hamburger store, which operates in a perfectly competitive market. a. John will bear the costs without adjusting his hamburger price. b. John will raise the price of his hamburger to cover his costs. c. John will make money. d. John will have higher variable costs. 35. In a perfectly competitive market, we assume that a. the buyers (or consumers) know more about the product’s quality. b. the producers (or sellers) know more about the product’s quality. c. the buyers know as much as the producers in regard to the product’s quality. d. the government knows more about the product’s quality. 36. Which of the following curves declines (all the time) when the firm’s output increases. a. ATC. b. AVC. c. AFC. d. MC. 37. Which of the following statements is true? a. MC affects ATC and AVC. b. ATC affectss MC and AVC. c. AVC affects MC and TC. d. ATC affects AVC. e. AVC affects MC. 38. To break even, firms must have a. P = AVC b. P = MC c. MR=MC d. P = ATC 39. Whenever the industry demand changes (shift either up or down), which of the following statements must be true. (Assume that the market is perfectly competitive). a. the firm must produce at different level of output. 8 9 b. c. d. e. the firm’s ATC and AVC must change as well. the firm’s MC must change as well. the firm must make economic loss. the firm’s TC must change as well. Costs per unit (dollars per unit) 40. If Gateway Computer Company could produce exactly three times as many computers with three identical plants as it could with one plant, that would be an example of a. diminishing marginal returns. b. decreasing returns to scale. c. increasing returns to scale. d. constant returns to scale. A 20 B 16 C 12 8 4 D 0 20 40 60 80 Quantity (units per day) 9 10 41. In the above figure, the vertical distance between B and C is A) MC. B) AVC. C) AFC. D) ATC. 42. In the above figure, the MC curve is A) A. B) B. C) C. D) D. 43. Which of the following is true (see the above figure)? A) curve A crosses curve B at its minimum (lowest) point. B) curve A crosses curve C at its minimum (lowest) point. C) curve D represents AFC. D) all of the above are true. E) none of the above is true. 44. A perfectly competitive firm’s marginal revenue exceeds its marginal cost at its current output. To increase its profit, the firm will A) lower its price. B) raise its price. C) decrease its output. D) increase its output. 10 11 45. The average total cost curves for plants A, B, C and D are shown in the above figure. Which plant is best to use to produce 20 units per day? A) Plant A. B) Plant B. C) Plant C. D) Plant D. Answer key: 1-5 cbccd 6-10 aabbd 11-15 cccbc 16-20 cbbcc 21-25 dbdca 26-30 adaae 31-35 aabac 36-40 cadad 41-45 cadda 11 12 Some Formulas for your reference: TR = P*Q TC = TFC + TVC ATC = AFC + AVC; ATC = TC/Q, AFC= TFC/Q and AVC = TVC/Q MC= dTC/dQ; where d: changes MP= dQ/dL AP = Q/L Π = TR – TC MR= dTR/dQ MC = W/MP AVC = W/AP (note you can use MP or MPL; AP or APL ) 12