* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cornea and External Disease
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
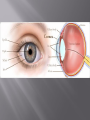
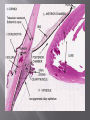
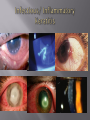
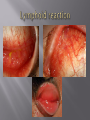
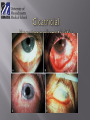
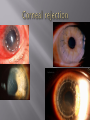
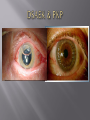
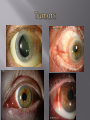
Sara A Mahony, MD, PharmD Assistant Professor Department of Ophthalmology & Visual Sciences Traumatic Shield ulcer (VKC) Herpetic ulcer Neurotrophic Keratopathy • • • • • Pseudophakic Bullous Keratopathy Fuch’s Corneal Dystrophy Endothelial Failure from uveitis Hydrops Angle Closure Degenerations Visual acuity with and without pinhole Quantification – 20/30+ 2, 20/40 -2, CF at how many feet? HM with or without direction at how many feet. Always pinhole even if patient is CF. History of trauma – dropped intraocular lens, dehiscence of natural lens with high plus prescription (pinhole will clue you) Workup Autorefract, Topography, Refraction Pachymetry – corneal edema, fuchs, pseudophakic or aphakic bullous keratopathy Large K ulcer – be prepared for md to request b scan to rule out endophthalmitis if patient is dry, place artificial tears during topography, refraction, and autorefraction, ask patient to blink blink blink Slit lamp photo (when requested) Red or painful and watery eye or blurry vision with acute presentation ?HSV ?HZV Chemical burns, thermal injuries History of HSV or HZV or brain tumor or facial trauma (?trigeminal nerve involvment – schwannoma, acoustic neuroma, memingioma, aneurysms, radiation therapy to route of CN5)) History of neurotrophic keratopathy in chart, multiple sclerosis Zebras: Congenital -Ridley-Day syndrome, anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia, Moebius syndrome, Goldenhar syndrome, and congenital corneal anaesthesia Medications causing K anesthesia: timolol, betaxolol, trifluridine, s Sulfacetamide, diclofenac, antipsychotics, antihistamines Always check for apd as cn5 anesthesia + apd may suggest intraconal nerve injury ? Tumor Cornea ulcers, Epithelial Defects As previously mentioned with regards to proparacaine use Post op day 1 DSAEK, no pressure should be placed on globe, do not touch the eye or eyelid, only visual acuity check (not an issue with PKP) Corneal edema Goldmann is not as accurate as tonopen Corneal hysteresis altered, distorted meyers Tonopen contacts one spot Underestimate iop Corneal calcification (band keratopathy) Falsely elevated iop In general goldmann is more accurate than tonopen, except in above case Swab and cultures brought to room prior to physician arrival. Technician available to assist with eyelid holding, labeling, and transport of samples Rooms stocked with fluoroscein and rose bengal strips for vital staining Rooms stocked with jewelers, bandage contact lens, punctal plugs, 30 gauge needle Appropriate Culture media